南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 591–600.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.04.017
• • 上一篇
结合区域检测和注意力机制的胸片自动定位与识别
朱伟1,张帅1,辛晓燕2,李文飞1,王骏1,3,张建1( ),王炜1(
),王炜1( )
)
- 1.南京大学物理学院,南京,210023
2.南京大学附属鼓楼医院放射科 ;南京 210008
3.南京大学计算机软件新技术国家重点实验室,南京,210023
Automatic thoracic disease localization and recognition by combining region proposal network and attention mechanism
Wei Zhu1,Shuai Zhang1,Xiaoyan Xin2,Wenfei Li1,Jun Wang1,3,Jian Zhang1( ),Wei Wang1(
),Wei Wang1( )
)
- 1.School of Physics,Nanjing University,Nanjing,210023,China
2.Department of Radiology,Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, 210008,China
3.State Key Laboratory for Novel Software Technology of Nanjing University,Nanjing University,Nanjing,210023,China
摘要:
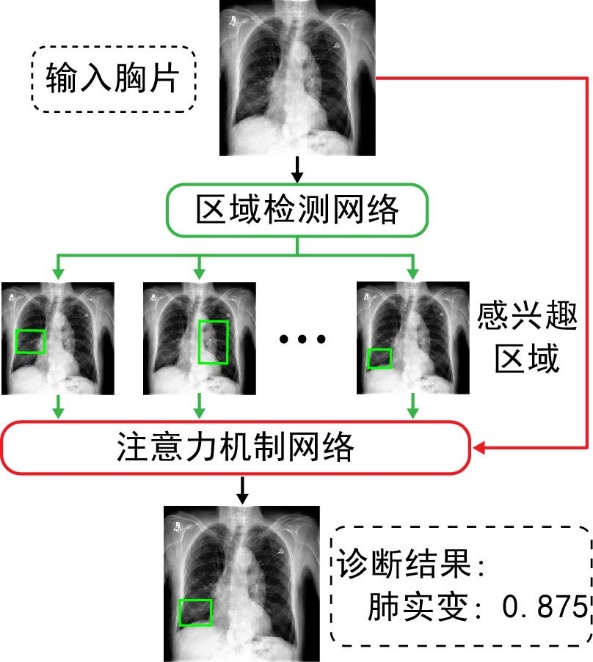
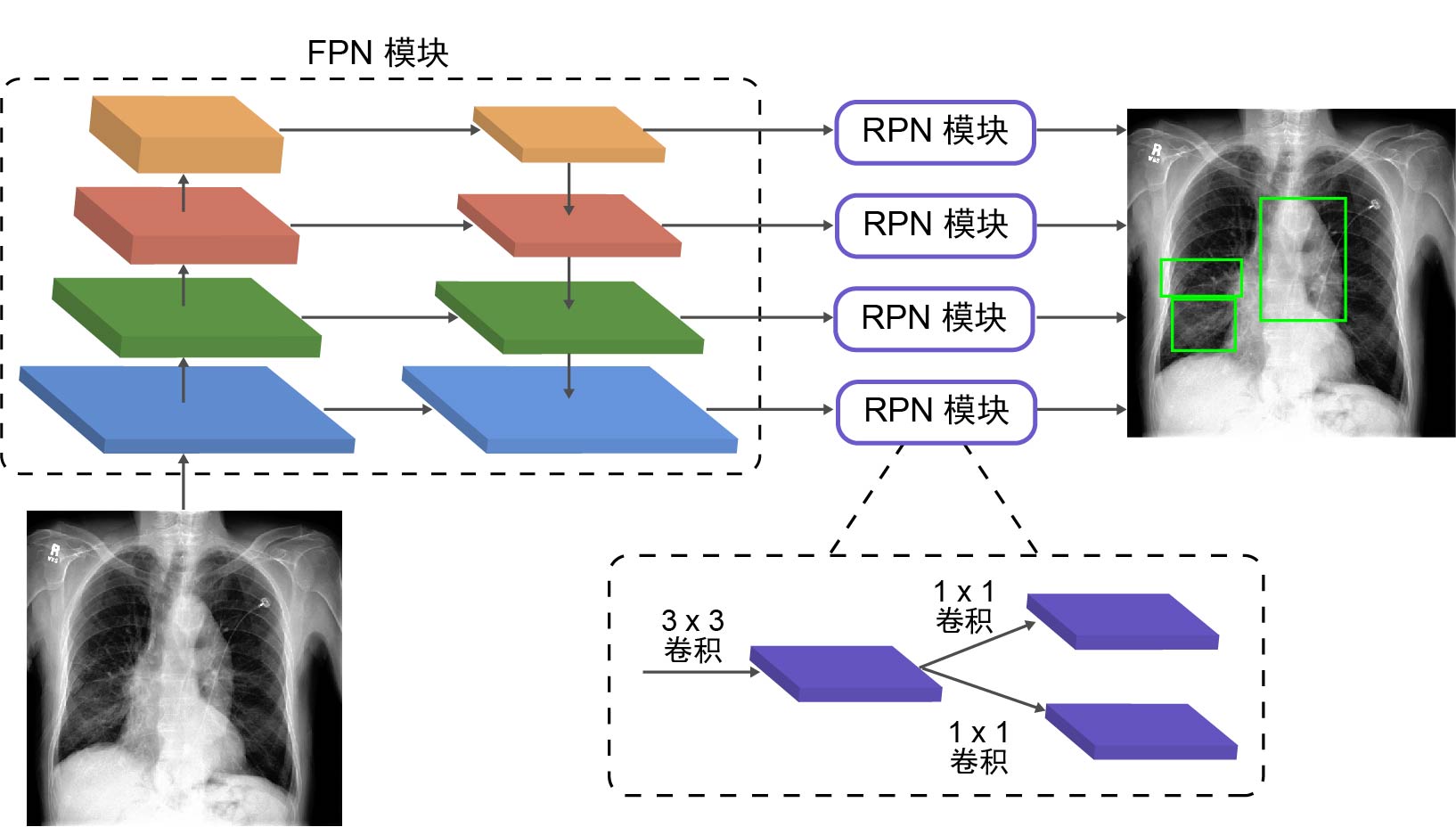
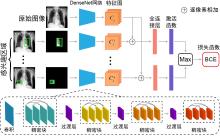
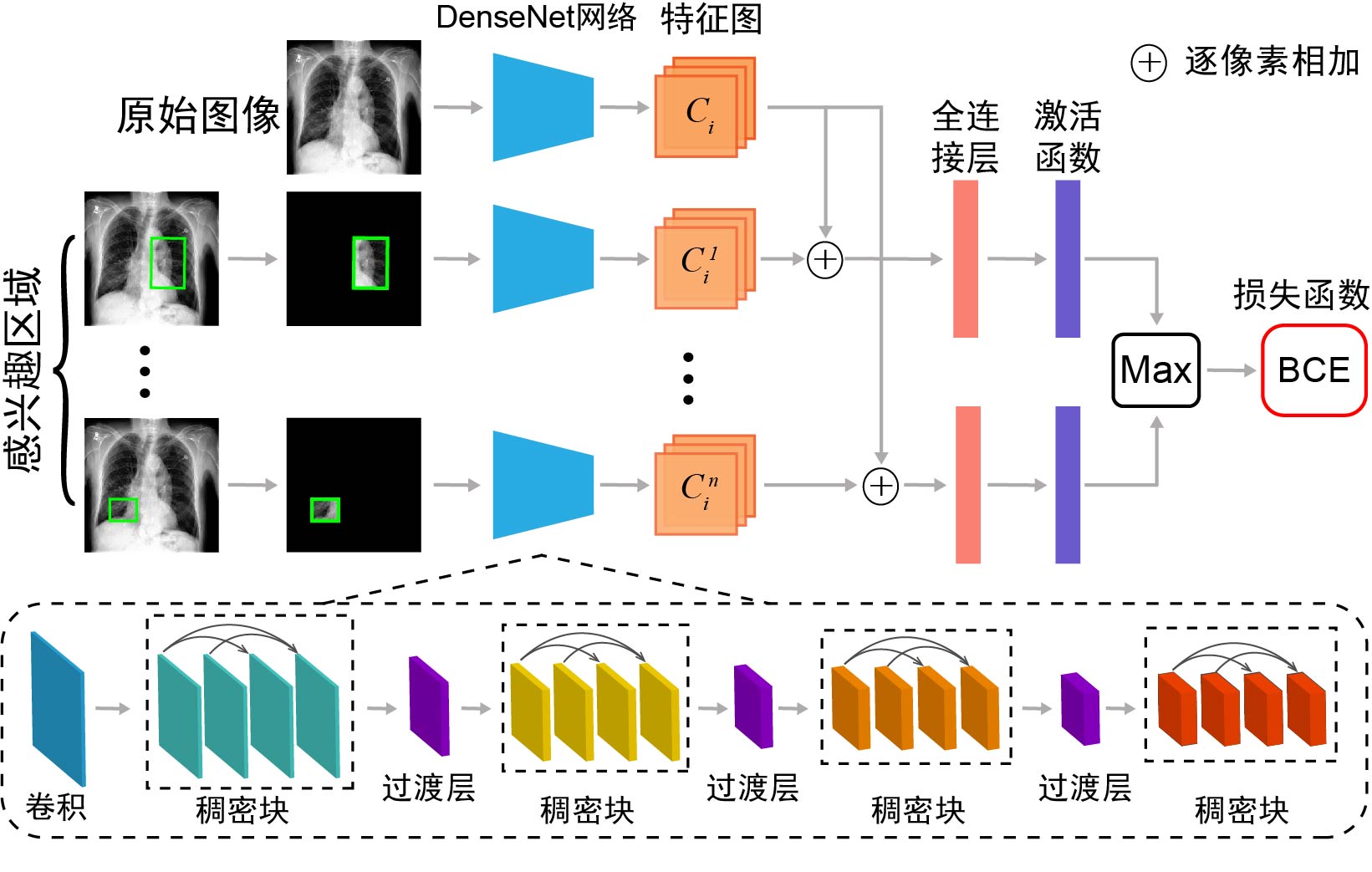
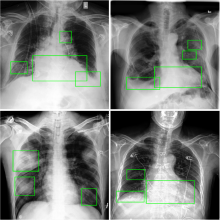
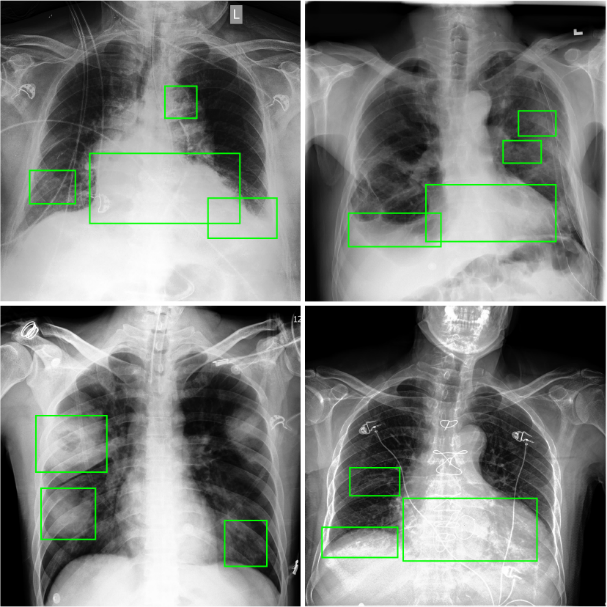
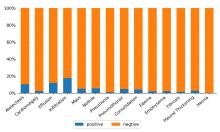
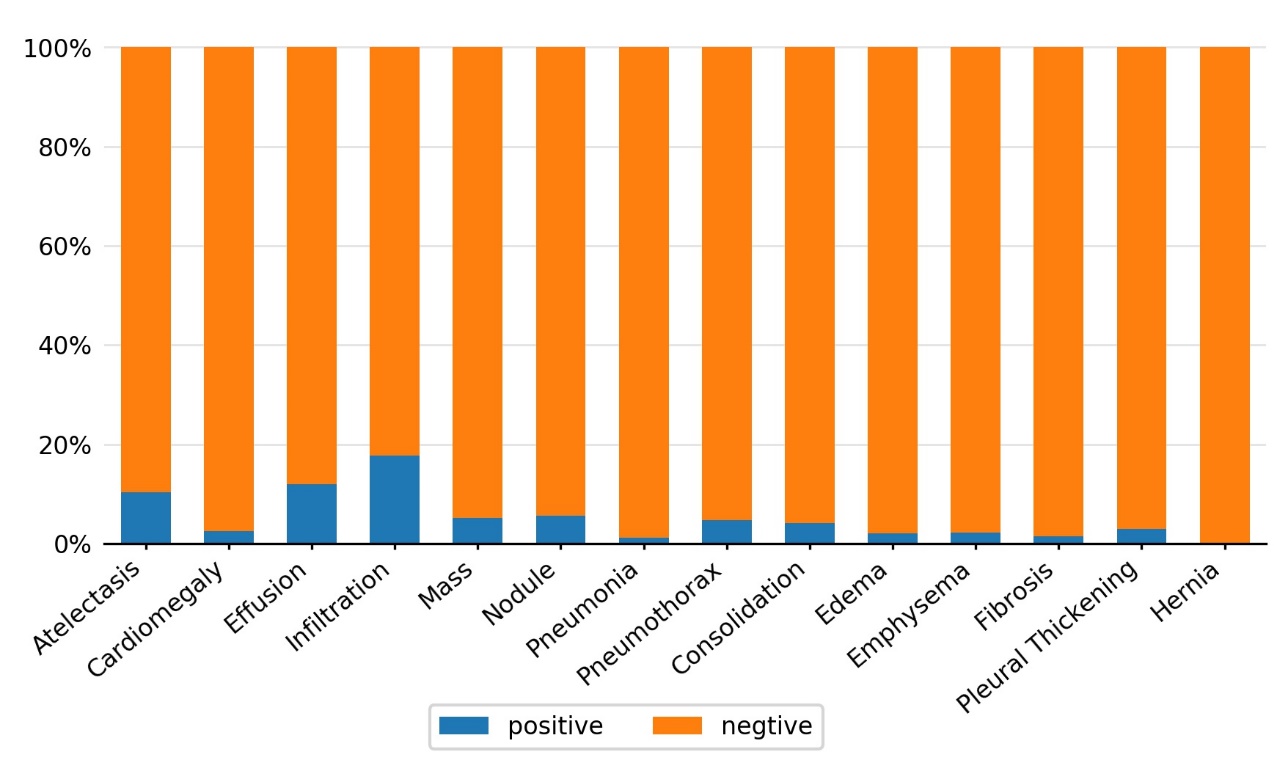
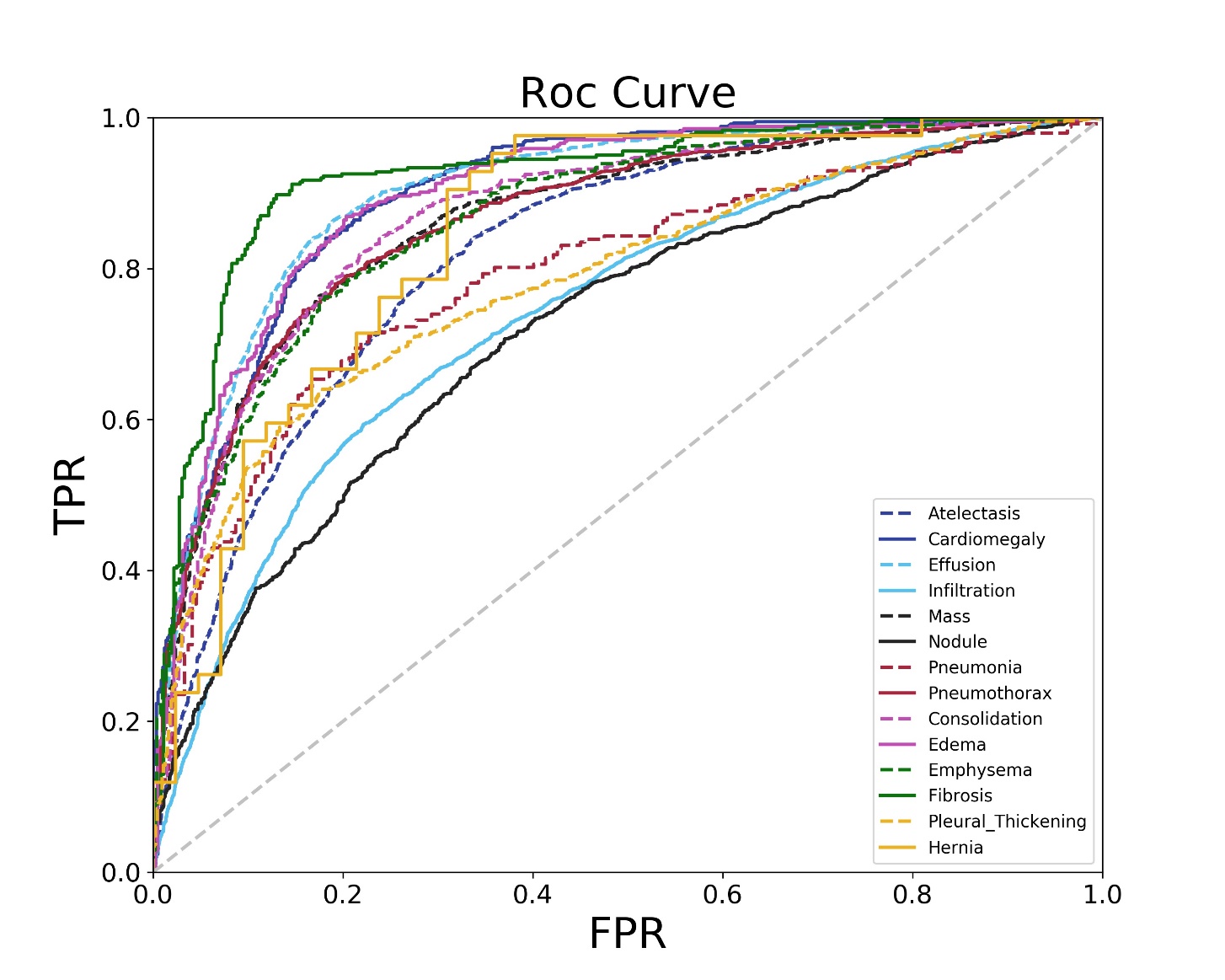
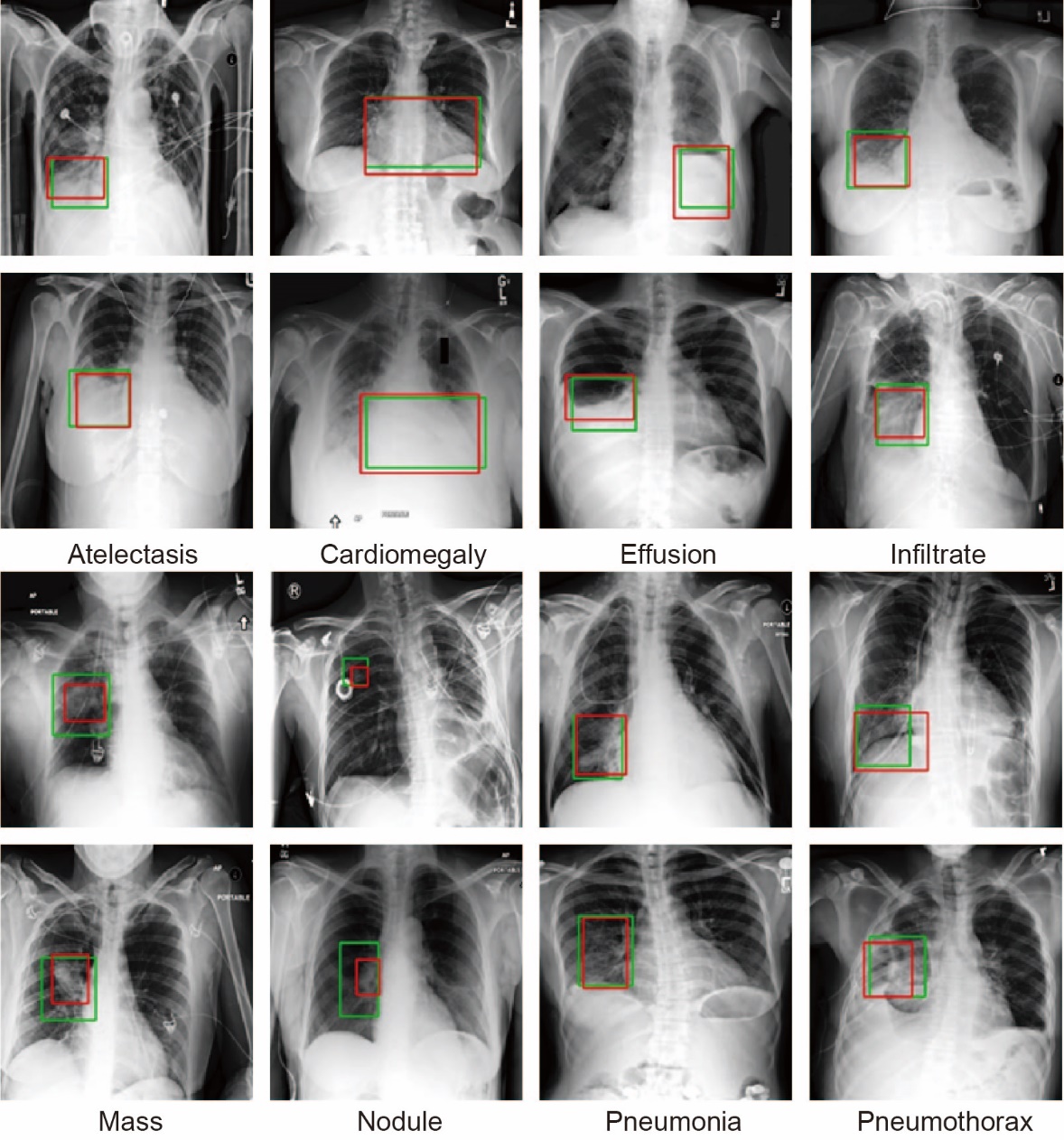
胸部X光片(以下简称胸片)是胸部相关疾病的常用诊断手段,具有辐射量低、速度快、价格低廉等优点,但样本数量巨大,所以开发基于人工智能的、对胸片进行自动识别、分类以及定位的系统具有重大的应用价值.由于胸片拍摄设备不同、胸片质量参差不齐、涉及疾病众多,尤其是缺乏标注框数据集等问题,将深度学习用于胸片的疾病检测和定位仍是一项具有挑战性的任务.为此构建了胸片标注框数据集Chest?box,该数据集中包含3952张阳性胸片和9960个标注框.基于此数据集,提出并训练了一个区域检测网络模型,用于提取胸片中所有可能的病变区域,即图像处理领域中的感兴趣区域.以区域检测网络提取的感兴趣区域为注意力信息,进一步发展了DenseNet卷积网络和注意力机制相结合的方法,通过融合原始胸片和感兴趣区域的特征,使模型更专注于感兴趣区域,再对疾病进行识别和定位.在ChestX?ray14数据集上的测试表明,该网络模型相比之前的工作,具有极佳的分类性能,并能提供更好的疾病定位信息.
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | Raoof S,Feigin D,Sung A,et al. Interpretation of plain chest roentgenogram. Chest,2012,141(2):545-558. |
| 2 | Tudor G R,Finlay D,Taub N. An assessment of inter?observer agreement and accuracy when reporting plain radiographs. Clinical Radiology,1997,52(3):235-238. |
| 3 | Quekel L G B A,Kessels A G H,Goei R,et al. Miss rate of lung cancer on the chest radiograph in clinical practice. Chest,1999,115(3):720-724. |
| 4 | Cicero M,Bilbily A,Colak E,et al. Training and validating a deep convolutional neural network for computer?aided detection and classification of abnormalities on frontal chest radiographs. Investigative Radiology,2017,52(5):281-287. |
| 5 | Lee M Z,Cai W D,Song Y,et al. Fully automated scoring of chest radiographs in cystic fibrosis∥2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Osaka,Japan:IEEE,2013:3965-3968. |
| 6 | Zhu B Y,Luo W,Li B P,et al. The development and evaluation of a computerized diagnosis scheme for pneumoconiosis on digital chest radiographs. Biomedical Engineering OnLine,2014,13:141. |
| 7 | Melendez J,Sánchez C I,Philipsen R H H M,et al. An automated tuberculosis screening strategy combining X?ray?based computer?aided detection and clinical information. Scientific Reports,2016,6:25265. |
| 8 | Lakhani P,Sundaram B. Deep learning at chest radiography:automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology,2017,284(2):574-582. |
| 9 | Setio A A A,Ciompi F,Litjens G,et al. Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images:false positive reduction using multi?view convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2016,35(5):1160-1169. |
| 10 | Pesce E,Ypsilantis P P,Withey S,et al. Learning to detect chest radiographs containing lung nodules using visual attention networks. 2017,arXiv:1712. 00996v1. |
| 11 | Wang X S,Peng Y F,Lu L,et al. ChestX?ray8:hospital?scale chest X?ray database and benchmarks on weakly?supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:3462-3471. |
| 12 | Guendel S,Grbic S,Georgescu B,et al. Learning to recognize abnormalities in chest X?rays with location?aware dense networks∥Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2019:757-765. |
| 13 | Kumar P,Grewal M,Srivastava M M. Boosted cascaded convnets for multilabel classification of thoracic diseases in chest radiographs∥International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2018:546-552. |
| 14 | Liu J Y,Zhao G M,Fei Y,et al. Align,attend and locate:chest X?ray diagnosis via contrast induced attention network with limited supervision∥Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul,Korea (South):IEEE,2019:10632-10641. |
| 15 | Rajpurkar P,Irvin J,Zhu K,et al. Chexnet:Radiologist?level pneumonia detection on chest X?rays with deep learning. 2017,arXiv:1711.05225. |
| 16 | Rajpurkar P,Irvin J,Ball R L,et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis:A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Medicine,2018,15(11):e1002686. |
| 17 | Majkowska A,Mittal S,Steiner D F,et al. Chest radiograph interpretation with deep learning models:assessment with radiologist?adjudicated reference standards and population?adjusted evaluation. Radiology,2020,294(2):421-431. |
| 18 | Ypsilantis P P,Montana G. Learning what to look in chest X?rays with a recurrent visual attention model. 2017,arXiv:1701.06452. |
| 19 | Guan Q J,Huang Y P,Zhong Z,et al. Diagnose like a radiologist:attention guided convolutional neural network for thorax disease classification. arXiv:1801.09927v1,2018. |
| 20 | Li Z,Wang C,Han M,et al. Thoracic disease identification and localization with limited supervision∥Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City,UT,USA:IEEE,2018:8290-8299. |
| 21 | Lin T Y,Dollár P,Girshick R,et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:2117-2125. |
| 22 | Ren S Q,He K M,Girshick R,et al. Faster R?CNN:Towards real?time object detection with region proposal networks∥Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal,Quebec,Canada:MIT Press,2015:91-99. |
| 23 | 李铁一. 更好地发挥胸片在胸部疾病诊断中的作用. 中华放射学杂志,2000,34(3):150. |
| Li T Y. Better use of chest radiograph in the diagnosis of chest diseases. Chinese Journal of Radiology,2000,34(3):150. | |
| 24 | Huang G,Liu Z,Van Der Maaten L,et al. Densely connected convolutional networks∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:4700-4708. |
| 25 | Irvin J,Rajpurkar P,Ko M,et al. Chexpert:a large chest radiograph dataset with uncertainty labels and expert comparison∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Honolulu,HI,USA:AAAI Press,2019:590-597. |
| 26 | Demner?Fushman D,Antani S K,Simpson M,et al. Design and development of a multimodal biomedical information retrieval system. Journal of Computing Science and Engineering,2012,6(2):168-177. |
| 27 | He K M,Zhang X Y,Ren S Q,et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,NV,USA:IEEE,2016:770-778. |
| [1] | 梅志伟,王维东. 基于FPGA的卷积神经网络加速模块设计[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 581-590. |
| [2] | 赵子龙,赵毅强,叶茂. 基于FPGA的多卷积神经网络任务实时切换方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(2): 167-174. |
| [3] | 李康,谢宁,李旭,谭凯. 基于卷积神经网络和几何优化的统计染色体核型分析方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 116-124. |
| [4] | 王吉地,郭军军,黄于欣,高盛祥,余正涛,张亚飞. 融合依存信息和卷积神经网络的越南语新闻事件检测[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 125-131. |
| [5] | 韩普,刘亦卓,李晓艳. 基于深度学习和多特征融合的中文电子病历实体识别研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 942-951. |
| [6] | 张家精,夏巽鹏,陈金兰,倪友聪. 基于张量分解和深度学习的混合推荐算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 952-959. |
| [7] | 钟琪,冯亚琴,王蔚. 跨语言语料库的语音情感识别对比研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(5): 765-773. |
| [8] | 王蔚, 胡婷婷, 冯亚琴. 基于深度学习的自然与表演语音情感识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 660-666. |
| [9] | 狄 岚, 何锐波, 梁久祯. 基于可能性聚类和卷积神经网络的道路交通标识识别算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(2): 238-250. |
| [10] | 胡 太, 杨 明. 结合目标检测的小目标语义分割算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 73-84. |
| [11] | 安 晶, 艾 萍, 徐 森, 刘 聪, 夏建生, 刘大琨. 一种基于一维卷积神经网络的旋转机械智能故障诊断方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 133-142. |
| [12] | 梁蒙蒙1,周 涛1,2*,夏 勇3,张飞飞1,杨 健1. 基于随机化融合和CNN的多模态肺部肿瘤图像识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 775-. |
| [13] | 张鹏,黄毅,阮雅端,陈启美*. 基于稀疏特征的交通流视频检测算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 264-270. |
|