南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 116–124.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.01.013
基于卷积神经网络和几何优化的统计染色体核型分析方法
- 1. 电子科技大学计算机科学与工程学院,成都,611731
2. 电子科技大学格拉斯哥学院,成都,611731
Statistical Karyotype analysis using CNN and geometric optimization
Kang Li1,Ning Xie1( ),Xu Li2,Kai Tan1
),Xu Li2,Kai Tan1
- 1. School of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu,611731, China
2. Glasgow College, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 611731, China
摘要:
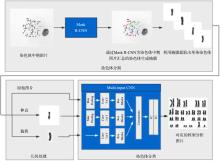
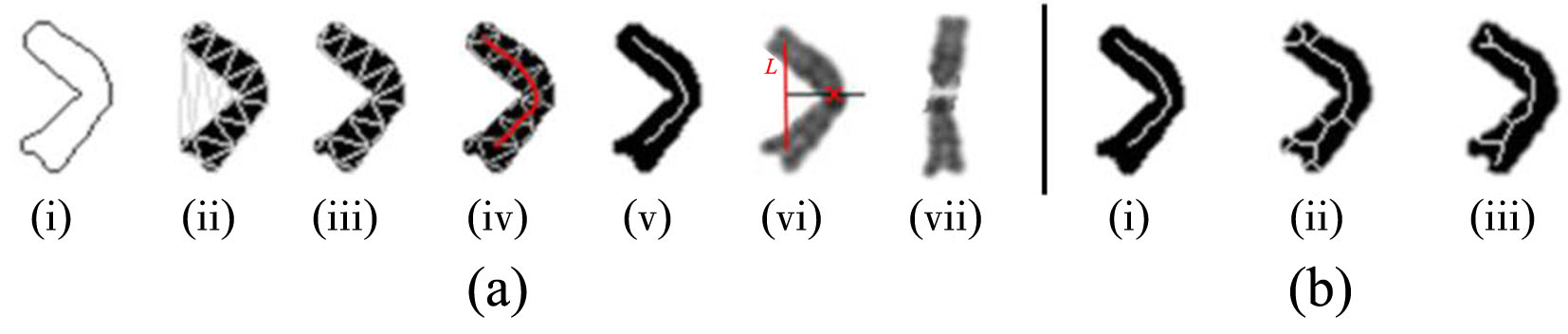
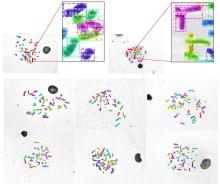
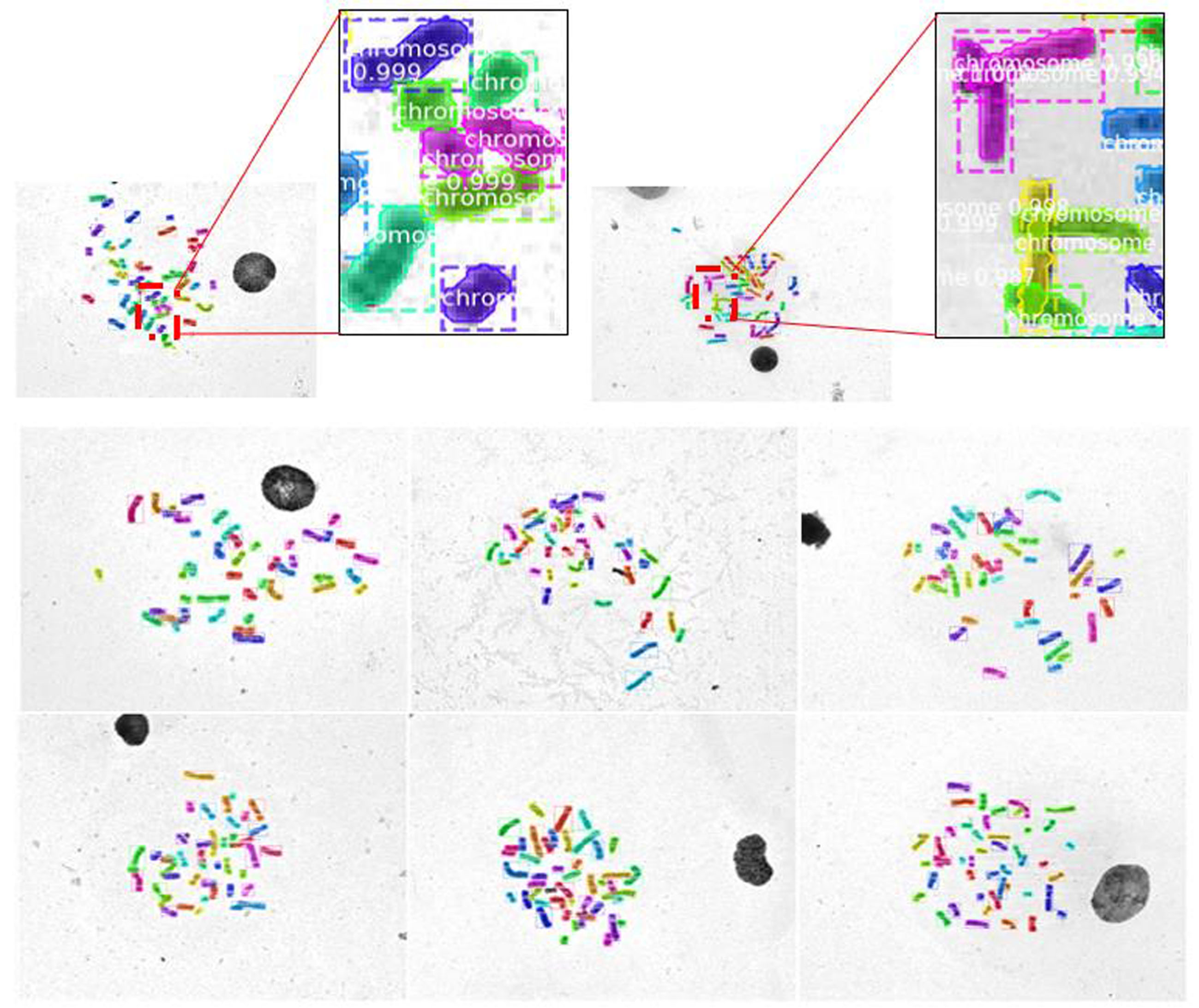
染色体核型分析是细胞遗传学研究的主要技术之一,在现代医学治疗和诊断中有重要的作用.通常在染色体核型分析的过程中,首先需要在染色体中期图像中分割出单条染色体,然后再对染色体逐一进行分析、比较、排序和分类.由于传统的基于几何及基于统计的分割和分类的辅助工具精度低,辅助作用有限,因此在实际工作中仍然需要医生花费大量的时间和精力进行人工核型分析.为此提出一种基于卷积神经网络和几何优化的染色体核型分析新方法,利用Mask R?CNN(Region?Convolutional Neural Networks)从染色体中期图像中分割出染色体,并训练一个新型多输入的卷积神经网络对分割后的单条染色体进行分类;还提出一种全新的基于局部特征的染色体分割数据合成方法对分割数据集进行扩充.此外,为了保证分类训练数据的一致性,提出一种基于中线的染色体伸直几何优化算法.实验结果表明提出的方法在自动核型分析中表现优秀.
中图分类号:
- TP31
| 1 | Sharma M , Saha O , Sriraman A ,et al . Crowdsourcing for chromosome segmentation and deep classification∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:34-41. |
| 2 | He K M , Gkioxari G , Dollár P ,et al . Mask R?CNN∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International |
| Conference on Computer Vision. Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:2961-2969. | |
| 3 | Pham D L , Xu C Y , Prince J L . Current methods in medical image segmentation. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering,2000,2:315-337. |
| 4 | Charters G C , Graham J . Trainable grey?level models for disentangling overlapping chromosomes. Pattern Recognition,1999,32(8):1335-1349. |
| 5 | Ji L . Fully automatic chromosome segmentation. Cytometry,1994,17(3):196-208. |
| 6 | BenTaieb A , Hamarneh G . Topology aware fully convolutional networks for histology gland segmen?tation∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer?Assisted Intervention. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2016:460-468. |
| 7 | Long J , Shelhamer E , Darrell T . Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation∥Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston,MA,USA:IEEE,2015:3431-3440. |
| 8 | Ronneberger O , Fischer P , Brox T . U?net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmen?tation∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer?assisted Intervention. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2015:234-241. |
| 9 | Li Y , Qi H Z , Dai J F ,et al . Fully convolutional instance?aware semantic segmentation∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:2359-2367. |
| 10 | Pinheiro P O , Lin T Y , Collobert R ,et al . Learning to refine object segments∥European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2016:75-91. |
| 11 | Lahiri A , Ayush K , Biswas P K ,et al . Generative adversarial learning for reducing manual annotation in semantic segmentation on large scale miscroscopy images:automated vessel segmentation in retinal fundus image as test case∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:42-48. |
| 12 | Dwibedi D , Misra I , Cut Hebert M. ,paste and learn:surprisingly easy synthesis for instance detection∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:1301-1310. |
| 13 | Ritter G , Gallegos M T . Outliers in statistical pattern recognition and an application to automatic chromosome classification. Pattern Recognition Letters,1997,18(6):525-539. |
| 14 | Lerner B , Guterman H , Dinstein I ,et al . Medial axis transform?based features and a neural network for human chromosome classification. Pattern Recognition,1995,28(11):1673-1683. |
| 15 | Markou C , Maramis C , Delopoulos A ,et al . Automatic chromosome classification using support vector machines.Technicial Report. Aristotle University of Thessaloniki,2012. |
| 16 | Swati S , Gupta G , Yadav M ,et al . Siamese networks for chromosome classification∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:72-81. |
| 17 | Wu Y R , Yue Y S , Tan X ,et al . End?to?end chromosome karyotyping with data augmentation using gan∥2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Athens,Greece:IEEE,2018:2456-2460. |
| 18 | Van Der Walt S , Sch?nberger J L , Nunez?Iglesias J ,et al . Scikit?image:image processing in python. PeerJ,2014,2(2):e453. |
| 19 | Javan?Roshtkhari M , Setarehdan S K . A new approach to automatic classification of the curved chromosomes∥2007 5th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis. Istanbul,Turkey:IEEE,2007:19-24. |
| 20 | Shen W , Zhou M , Yang F ,et al . Multi?scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification∥International Conference on Informa?tion Processing in Medical Imaging. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2015:588-599. |
| 21 | He K M , Zhang X Y , Ren S Q ,et al . Deep residual learning for image recognition∥Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,NV,USA:IEEE,2016:770-778. |
| 22 | Abdulla W . Mask R?CNN for object detection and instance segmentation on keras and tensorflow. https:∥github.com/matterport/Mask_RCNN. GitHub repository,2017. |
| [1] | 朱伟,张帅,辛晓燕,李文飞,王骏,张建,王炜. 结合区域检测和注意力机制的胸片自动定位与识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 591-600. |
| [2] | 韩普,刘亦卓,李晓艳. 基于深度学习和多特征融合的中文电子病历实体识别研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 942-951. |
| [3] | 张家精,夏巽鹏,陈金兰,倪友聪. 基于张量分解和深度学习的混合推荐算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 952-959. |
| [4] | 钟琪,冯亚琴,王蔚. 跨语言语料库的语音情感识别对比研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(5): 765-773. |
| [5] | 王蔚, 胡婷婷, 冯亚琴. 基于深度学习的自然与表演语音情感识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 660-666. |
| [6] | 张鹏,黄毅,阮雅端,陈启美*. 基于稀疏特征的交通流视频检测算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 264-270. |
|