南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 338–353.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.03.004
致密砂岩储层孔⁃喉连通性研究
- 1.南京大学地球科学与工程学院,南京,210023
2.中国石油勘探开发研究院廊坊分院,廊坊,065007
An investigation into pore⁃throat connectivity in tight sandstone reservoir: A case of the Chang 7 Reservoir in Ordos Basin
Yang Qin1,Suping Yao1( ),Hanmin Xiao2
),Hanmin Xiao2
- 1.School of Earth Sciences and Engineering,Nanjing University,Nanjing,210023,China
2.Langfang Branch of PetroChina Exploration and Development Research Institute, Langfang, 065007,China
摘要:
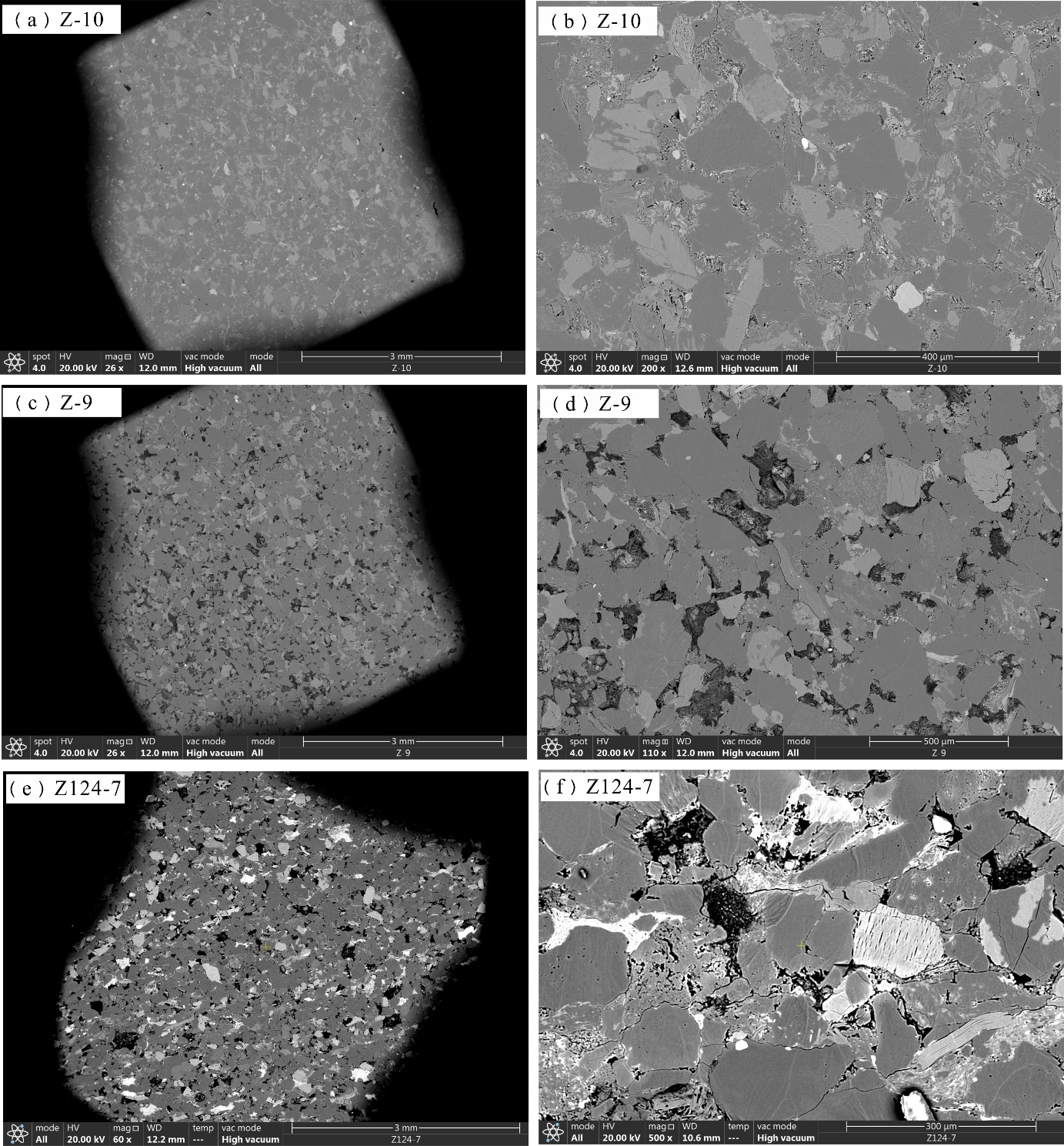
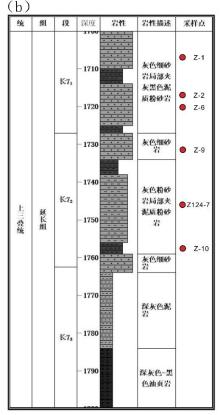
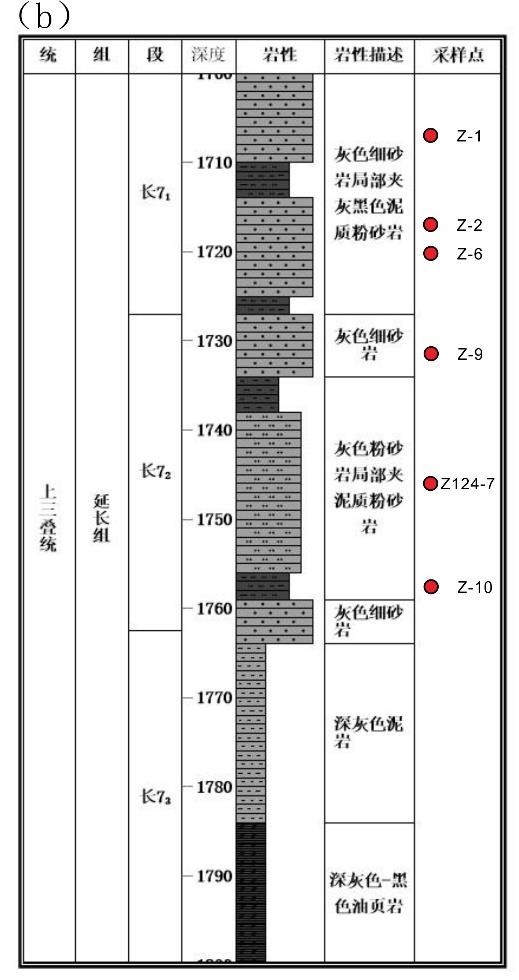
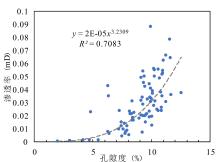
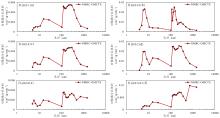
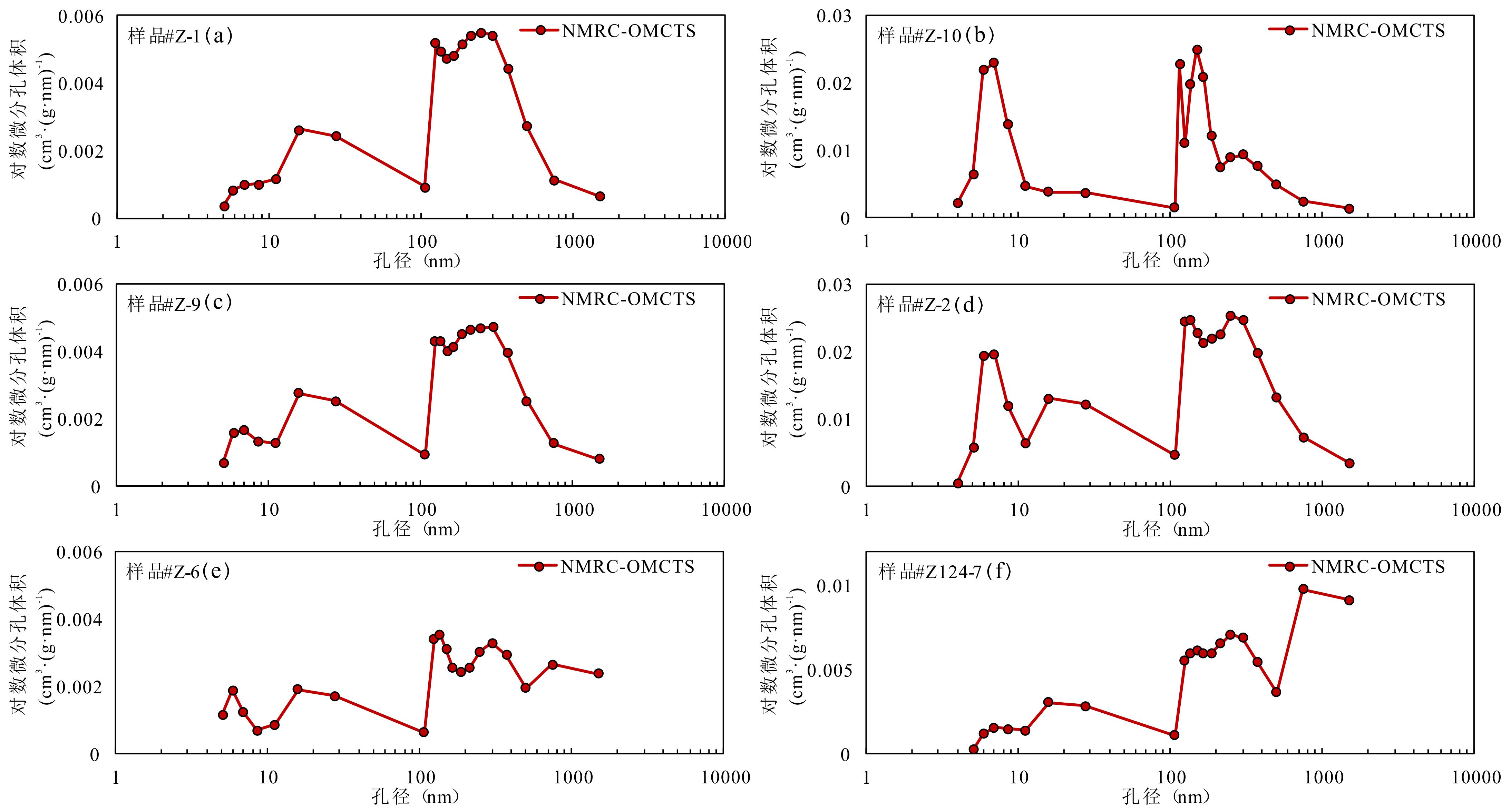
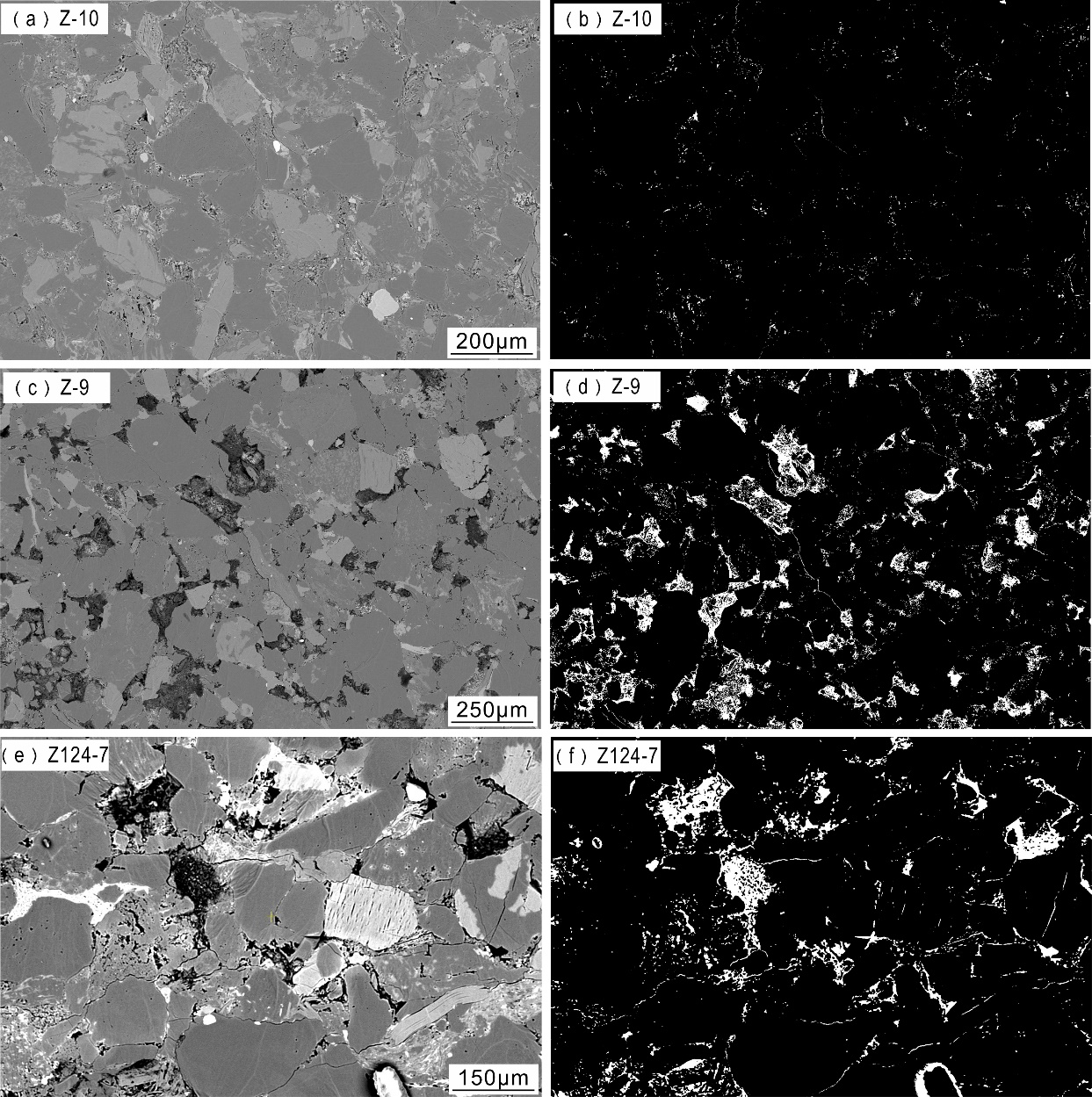
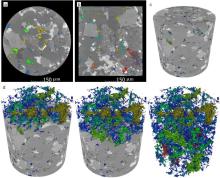
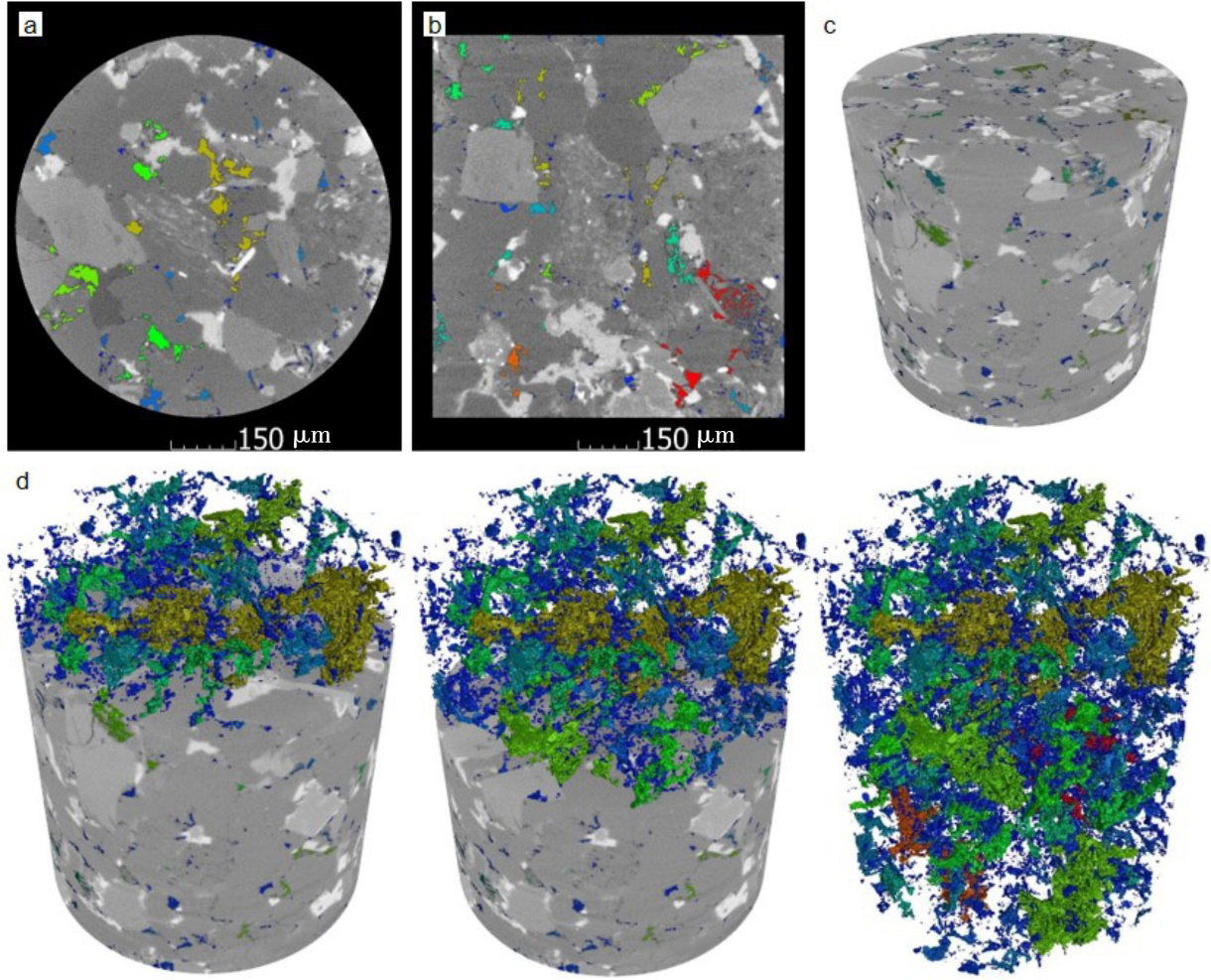
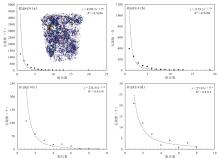
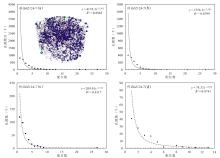
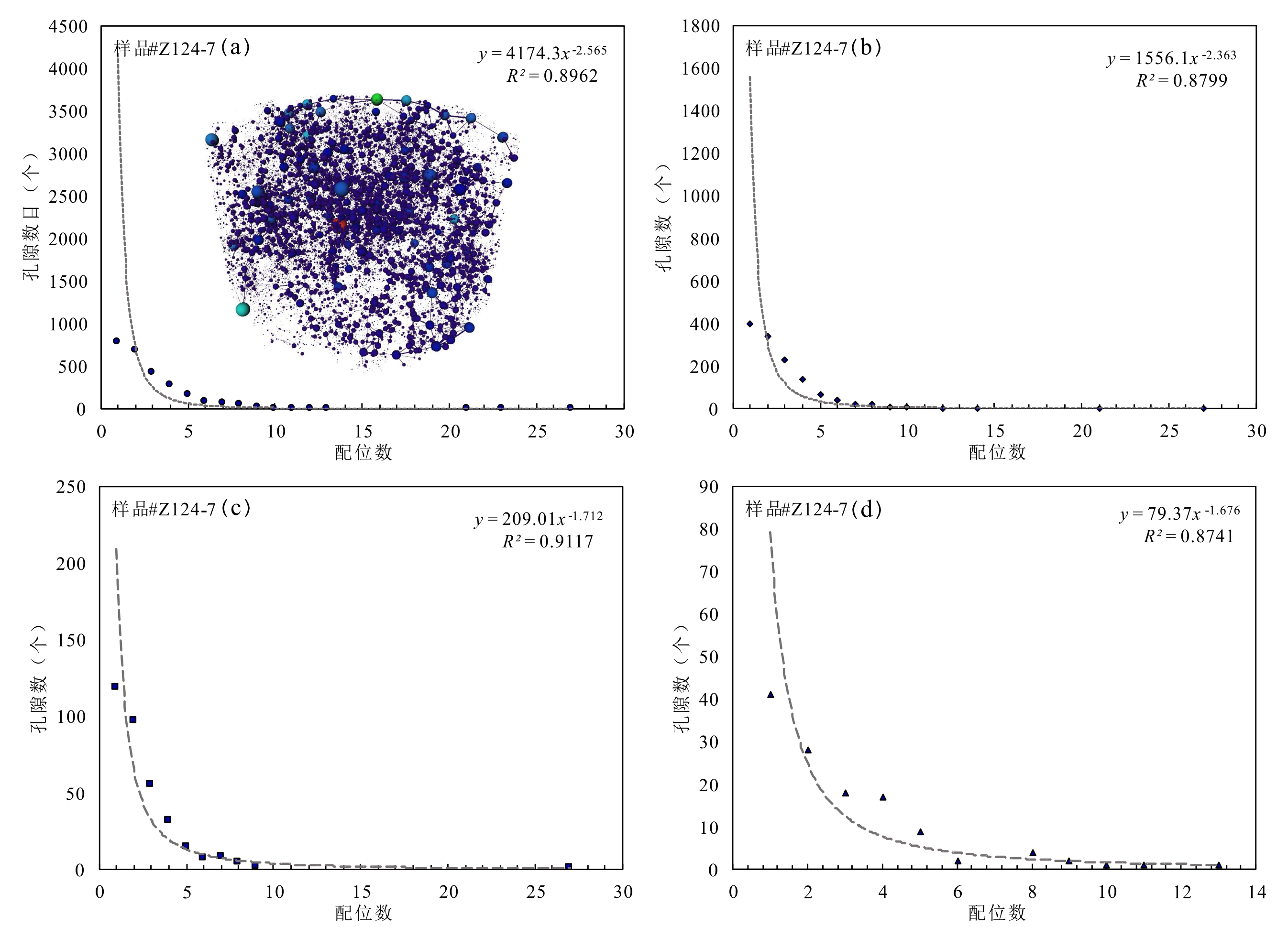
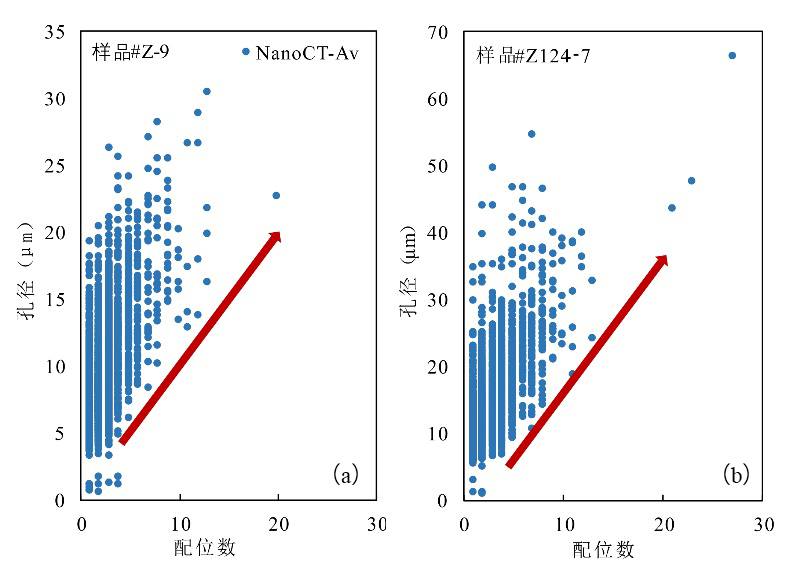
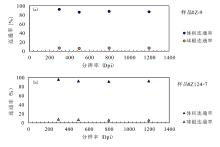
储层的孔?喉连通性是致密砂岩储层评价过程中所用到的一个重要参数,而孔?喉连通性的研究受到致密砂岩储层复杂的纳米喉道影响,其量化手段单一、表征参数不明,是当下该研究领域中的难点.为进一步完善储层连通性的表征手段,利用纳米CT技术、核磁共振冻融技术以及三离子束刻蚀结合场发射扫描电镜?PCAS(Pores and Cracks Analysis System)技术,从定性和定量两个角度对于鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段典型(粉砂、细砂、泥质粉砂)致密砂岩样品的连通性进行不同尺度的表征分析.实验结果表明,致密砂岩孔隙的孔径大小与其所沟通的喉道数目呈正相关;致密砂岩中连通孔隙的体积对于连通性的贡献远高于连通孔隙的数目;油浸的细砂岩样品其连通性高于油斑的粉砂岩样品.实验分析认为,多方法联用的表征方法是致密砂岩储层连通性刻画的重要手段.
中图分类号:
- P59
| 1 | 邹才能,张国生,杨智等. 非常规油气概念、特征、潜力及技术——兼论非常规油气地质学. 石油勘探与开发,2013,40(4):385-399,454. |
| Zou C N,Zhang G S,Yang Z,et al. Geological concepts,characteristics,resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon:on unconventional petroleum geology. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2013,40(4):385-399,454. | |
| 2 | 胡文瑞,翟光明,李景明. 中国非常规油气的潜力和发展. 中国工程科学,2010,12(5):25-29,63. |
| Hu W R,Zhai G M,Li J M. Potential and development of unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China. Engineering Science,2010,12(5):25-29,63. | |
| 3 | 贾承造,郑民,张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景. 石油勘探与开发,2012,39(2):129-136. |
| Jia C Z,Zheng M,Zhang Y F. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2012,39(2):129-136. | |
| 4 | 朱筱敏,潘荣,朱世发等. 致密储层研究进展和热点问题分析. 地学前缘,2018,25(2):141-146. |
| Zhu X M,Pan R,Zhu S F,et al. Research progress and core issues in tight reservoir exploration. Earth Science Frontiers,2018,25(2):141-146. | |
| 5 | 邹才能,朱如凯,白斌等. 致密油与页岩油内涵、特征、潜力及挑战. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2015,34(1):3-17. |
| Zou C N,Zhu R K,Bai B,et al. Significance,geologic characteristics,resource potential and future challenges of tight oil and shale oil. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2015,34(1):3-17. | |
| 6 | 邹才能,朱如凯,吴松涛等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望——以中国致密油和致密气为例. 石油学报,2012,33(2):173-187. |
| Zou C N,Zhu R K,Wu S T,et al. Types,characteristics,genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations:taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,33(2):173-187. | |
| 7 | 邹才能,陶士振,白斌等. 论非常规油气与常规油气的区别和联系. 中国石油勘探,2015,20(1):1-16. |
| Zou C N,Tao S Z,Bai B,et al. Differences and relations between unconventional and conventional oil and gas. China Petroleum Exploration,2015,20(1):1-16. | |
| 8 | 邹才能,朱如凯,白斌等. 中国油气储层中纳米孔首次发现及其科学价值. 岩石学报,2011,27(6):1857-1864. |
| Zou C N,Zhu R K,Bai B,et al. First discovery of nano?pore throat in oil and gas reservoir in China and its scientific value. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011,27(6):1857-1864. | |
| 9 | 胡钦红,刘惠民,黎茂稳等. 东营凹陷沙河街组页岩油储集层润湿性、孔隙连通性和流体?示踪剂运移. 石油学报,2018,39(3):278-289. |
| Hu Q H,Liu H M,Li M W,et al. Wettability,pore connectivity and fluid?tracer migration in shale oil reservoirs of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongying sag of Bohai Bay Basin,East China. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2018,39(3):278-289. | |
| 10 | Sun M D,Yu B S,Hu Q H,et al. Pore connectivity and tracer migration of typical shales in south China. Fuel,2017(203):32-46. |
| 11 | 白斌,朱如凯,吴松涛等. 利用多尺度CT成像表征致密砂岩微观孔喉结构. 石油勘探与开发,2013,40(3):329-333. |
| Bai B,Zhu R K,Wu S T,et al. Multi?scale method of nano (micro)?CT study on microscopic pore structure of tight sandstone of Yanchang Formation,Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2013,40(3):329-333. | |
| 12 | 尤源,牛小兵,李廷艳等. CT技术在致密砂岩微观孔隙结构研究中的应用——以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7段为例. 新疆石油地质,2016,37(2):227-230. |
| You Y,Niu X B,Li T Y,et al. Application of CT scanning system to study of micro?pore structure of tight sandstone:a case study of chang?7 member of Yanchang formation in Ordos BASIN. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2016,37(2):227-230. | |
| 13 | Wirth R. Focused Ion Beam (FIB):a novel technology for advanced application of micro?and nanoanalysis in geosciences and applied mineralogy. European Journal of Mineralogy,2004,16(6):863-876. |
| 14 | Zhou S W,Yan G,Xue H Q,et al. 2D and 3D nanopore characterization of gas shale in Longmaxi formation based on FIB?SEM. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2016,73:174-180. |
| 15 | 王晓琦,金旭,李建明等. 聚焦离子束扫描电镜在石油地质研究中的综合应用. 电子显微学报,2019,38(3):303-319. |
| Wang X Q,Jin X,Li J M,et al. FIB?SEM applications in petroleum geology research. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society,2019,38(3):303-319. | |
| 16 | Hildenbrand A,Urai J L. Investigation of the morphology of pore space in mudstones?first results. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2003,20(10):1185-1200. |
| 17 | Klaver J,Hemes S,Houben M,et al. The connectivity of pore space in mudstones:insights from high?pressure Wood's metal injection,BIB?SEM imaging,and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Geofluids,2015,15(4):577-591. |
| 18 | Kaufmann J. Pore space analysis of cement?based materials by combined Nitrogen sorption:Wood's metal impregnation and multi?cycle mercury intrusion. Cement and Concrete Composites,2010,32(7):514-522. |
| 19 | Wirth R. Focused Ion Beam (FIB) combined with SEM and TEM:advanced analytical tools for studies of chemical composition,microstructure and crystal structure in geomaterials on a nanometre scale. Chemical Geology,2009,261(3-4):217-229. |
| 20 | Hu Q H,Ewing R P,Dultz S. Low pore connectivity in natural rock. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2012,133:76-83. |
| 21 | 赖锦,王贵文,孟辰卿等. 致密砂岩气储层孔隙结构特征及其成因机理分析. 地球物理学进展,2015,30(1):217-227. |
| Lai J,Wang G W,Meng C Q,et al. Pore structure characteristics and formation mechanisms analysis of tight gas sandstones. Progress in Geophysics,2015,30(1):217-227. | |
| 22 | 杨华,李士祥,刘显阳. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油、页岩油特征及资源潜力. 石油学报,2012,34(1):1-11. |
| Yang H,Li S X,Liu X Y. Characteristics and resource prospects of tight oil and shale oil in Ordos Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,34(1):1-11. | |
| 23 | 屈红军,蒲仁海,曹金舟等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部地区长7致密油储层特征. 非常规油气,2015,2(1):1-9. |
| Qu H J,Pu R H,Cao J Z,et al. Characteristics of Chang 7 tight oil reservoir in the southern Ordos Basin. Unconventional Oil & Gas,2015,2(1):1-9. | |
| 24 | 姚泾利,邓秀芹,赵彦德等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组致密油特征. 石油勘探与开发,2013,40(2):150-158. |
| Yao J L,Deng X Q,Zhao Y D,et al. Characteristics of tight oil in Triassic Yanchang Formation,Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2013,40(2):150-158. | |
| 25 | 邓秀芹,付金华,姚泾利等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中及上三叠统延长组沉积相与油气勘探的突破. 古地理学报,2011,13(4):443-455. |
| Deng X Q,Fu J H,Yao J L,et al. Sedimentary facies of the Middle?Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin and breakthrough in petroleum exploration. Journal of Palaeogeography,2011,13(4):443-455. | |
| 26 | 何自新. 鄂尔多斯盆地演化与油气. 北京:石油工业出版社,2003,119-138. |
| 27 | 刘标,姚素平,胡文瑄等. 核磁共振冻融法表征非常规油气储层孔隙的适用性. 石油学报,2017,38(12):1401-1410. |
| Liu B,Yao S P,Hu W X,et al. Application of nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry in unconventional reservoir rocks. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2017,38(12):1401-1410. | |
| 28 | 苏绍明,邹珍. 页岩气藏纳米孔隙的冻融核磁共振测量表征方法. 资源环境与工程,2016,30(1):66-71. |
| Su S M,Zou Z. Characterization methods of freeze?thaw nuclear magnetic resonance measurement of shale gas reservoir nano?pore. Resources Environment & Engineering,2016,30(1):66-71. | |
| 29 | Zhang Q,Dong Y H,Tong S Q,et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry as a tool to measure pore size distribution of shale rock. Chinese Science Bulletin,2016,61(21):2387-2394. |
| 30 | Zhu F,Hu W X,Cao J,et al. Probe material choice for nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry (NMRC) measurements of the nano?scale pore size distribution of unconventional reservoirs. Energy Exploration & Exploitation,2019,37(1):412-428. |
| 31 | Liu B,Yao S P,Hu W X,et al. Applying octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane as a probe liquid for characterizing the pore size distribution of oil?bearing tight sandstones by nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2017,88:814-825. |
| 32 | Liu C,Tang C S,Shi B,et al. Automatic quantification of crack patterns by image processing. Computers & Geosciences,2013,57:77-80. |
| 33 | Loucks R G,Reed R M,Ruppel S C,et al. Morphology,genesis,and distribution of nanometer?scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the mississippian barnett shale. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2009,79(12):848-861. |
| 34 | Liu C,Shi B,Zhou J,et al. Quantification and characterization of microporosity by image processing,geometric measurement and statistical methods:application on SEM images of clay materials. Applied Clay Science,54(1):97-106. |
| 35 | Sezer G I,Ramyar K,Karasu B,et al. Image analysis of sulfate attack on hardened cement paste. Mater Des,2008,29(1):224-231. |
| 36 | Soroushian P,Elzafraney M. Morphological operations,planar mathematical formulations,and stereological interpretations for automated image analysis of concrete microstructure. Cement and Concrete Composites,2005,27(7-8):823-833. |
| 37 | Wang Y,Pu J,Wang L H,et al. Characterization of typical 3D pore networks of Jiulaodong formation shale using nano?transmission X?ray microscopy. Fuel,2015,170:84-91. |
| 38 | 何更生.油层物理.北京:石油工业出版社,1994,5-16. |
| 39 | 赵斌,尚彦军. 基于复杂网络理论的页岩纳米孔隙连通性表征. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):504-509. |
| Zhao B,Shang Y J. Characterizing connectivity of nano?sized pores of shale based on complex network theory. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):504-509. | |
| 40 | Zipf G K. Human behavior and the principle of least effort:An introduction to human ecology. Cambridge,MA,USA:Addison?Wesley Press,1949. |
| 41 | Deng W B,Li W,Cai X,et al. The exponential degree distribution in complex networks:non?equilibrium network theory,numerical simulation and empirical data. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications,2011,390(8):1481-1485. |
| 42 | Wu L S,Tan Q M,Zhang Y H. Network connectivity entropy and its application on network connectivity reliability. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,2013,392(21):5536-5541. |
| 43 | 赵华伟,宁正福,段太忠等. 基于微米CT扫描成像实验及格子Boltzmann模拟方法的致密砂岩孔隙结构表征. 东北石油大学学报,2019 (5):1-10. (Zhao H W,Ning Z F,Duan T Z,et al. Pore structure characterization of tight sandstones by X?ray computed tomography experiment combined with Lattice Boltzmann Method. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University,2019 (5):1-10.) |
| 44 | 沈珊,卢双舫,唐明明等. 致密砂岩储层微观孔喉表征及渗流模拟. 河南科学,2016,34(10):1699-1705. |
| Shen S,Lu S F,Tang M M,et al. Micro pore throat characterization and seepage stimulation of tight sandstone reservoir. Henan Science,2016,34(10):1699-1705. |
| [1] | 王俞策,曹剑,陶柯宇,李二庭,向宝力,施春华. 准噶尔盆地芦草沟组致密油系统油源对比与成藏非均质性研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 322-337. |
| [2] | 刘显, 陈强路, 王小林, 丘靥, 杨源显. 方解石晶体定向性对水的拉曼光谱影响的实验评估[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 297-307. |
| [3] | 游杰, 胡广, 张玺华, 沈安江, 彭瀚霖, 田兴旺, 赵东方. 微生物碳酸盐岩同生⁃早成岩阶段有机质降解示踪:以四川盆地灯影组四段为例[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 308-321. |
|