南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 322–337.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.03.003
准噶尔盆地芦草沟组致密油系统油源对比与成藏非均质性研究
王俞策1,曹剑1( ),陶柯宇1,李二庭2,向宝力2,施春华1
),陶柯宇1,李二庭2,向宝力2,施春华1
- 1.南京大学地球科学与工程学院,南京,210023
2.中国石油新疆油田分公司,克拉玛依,834000
Oil⁃source correlation and accumulation heterogeneity of tight oils in the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation, Junggar Basin
Yuce Wang1,Jian Cao1( ),Keyu Tao1,Erting Li2,Baoli Xiang2,Chunhua Shi1
),Keyu Tao1,Erting Li2,Baoli Xiang2,Chunhua Shi1
- 1.School of Earth Sciences and Engineering,Nanjing University,Nanjing,210023,China
2.Research Institute of Experiment and Testing,PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company, Karamay,834000,China
摘要:
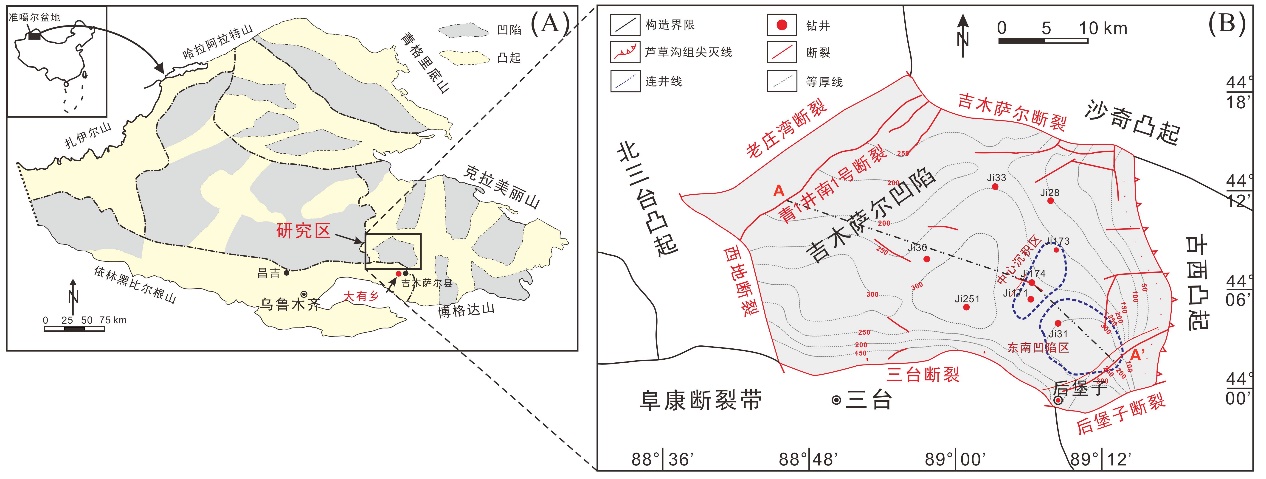
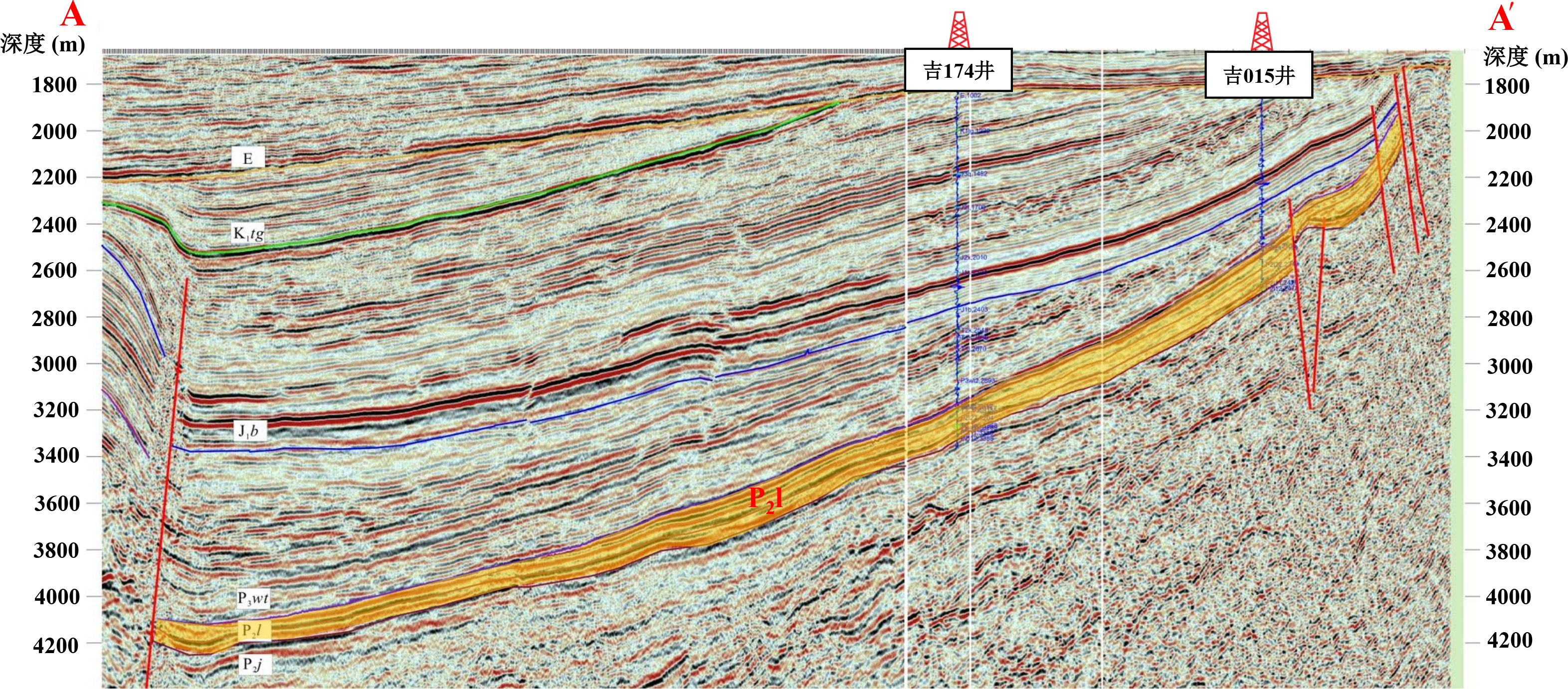
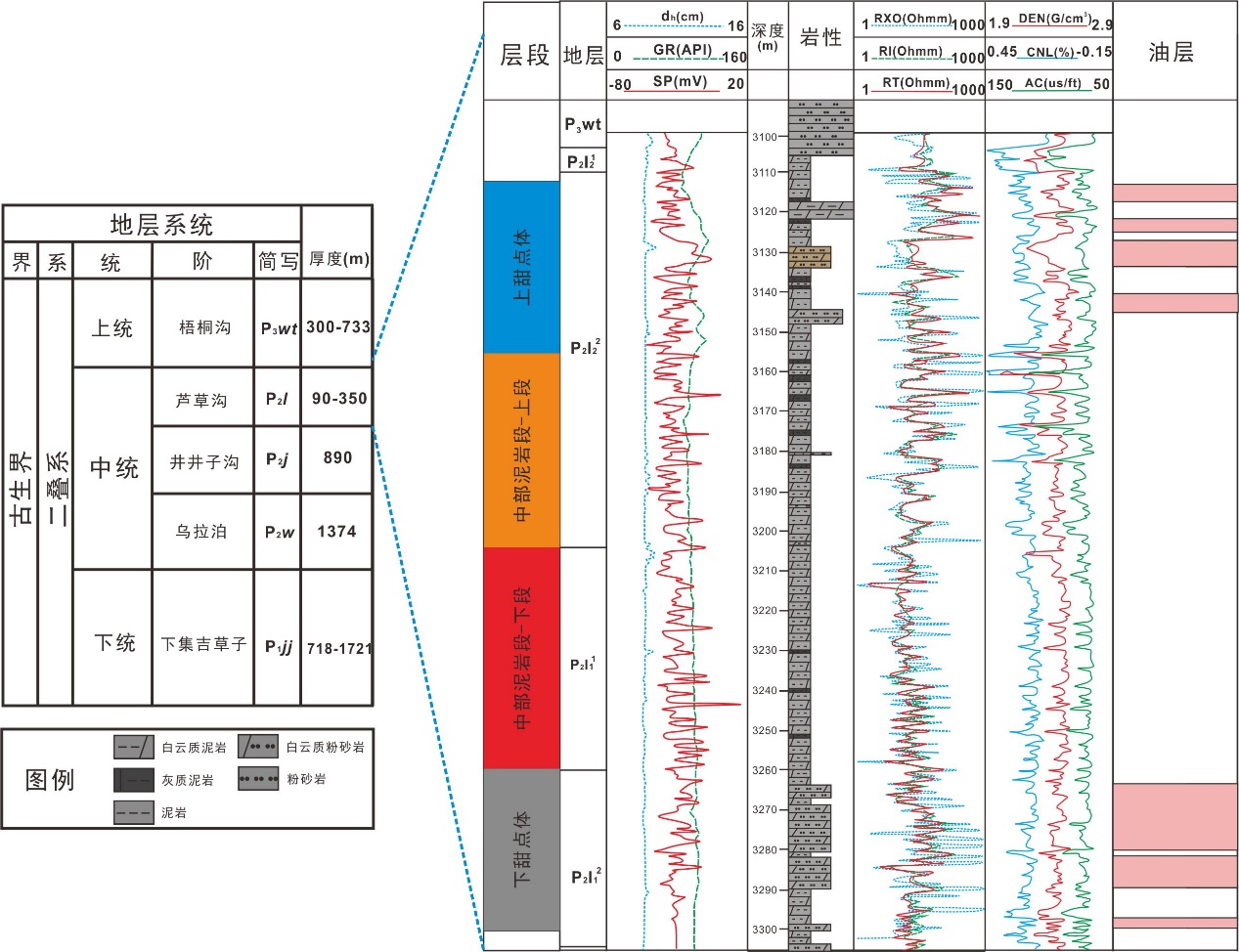
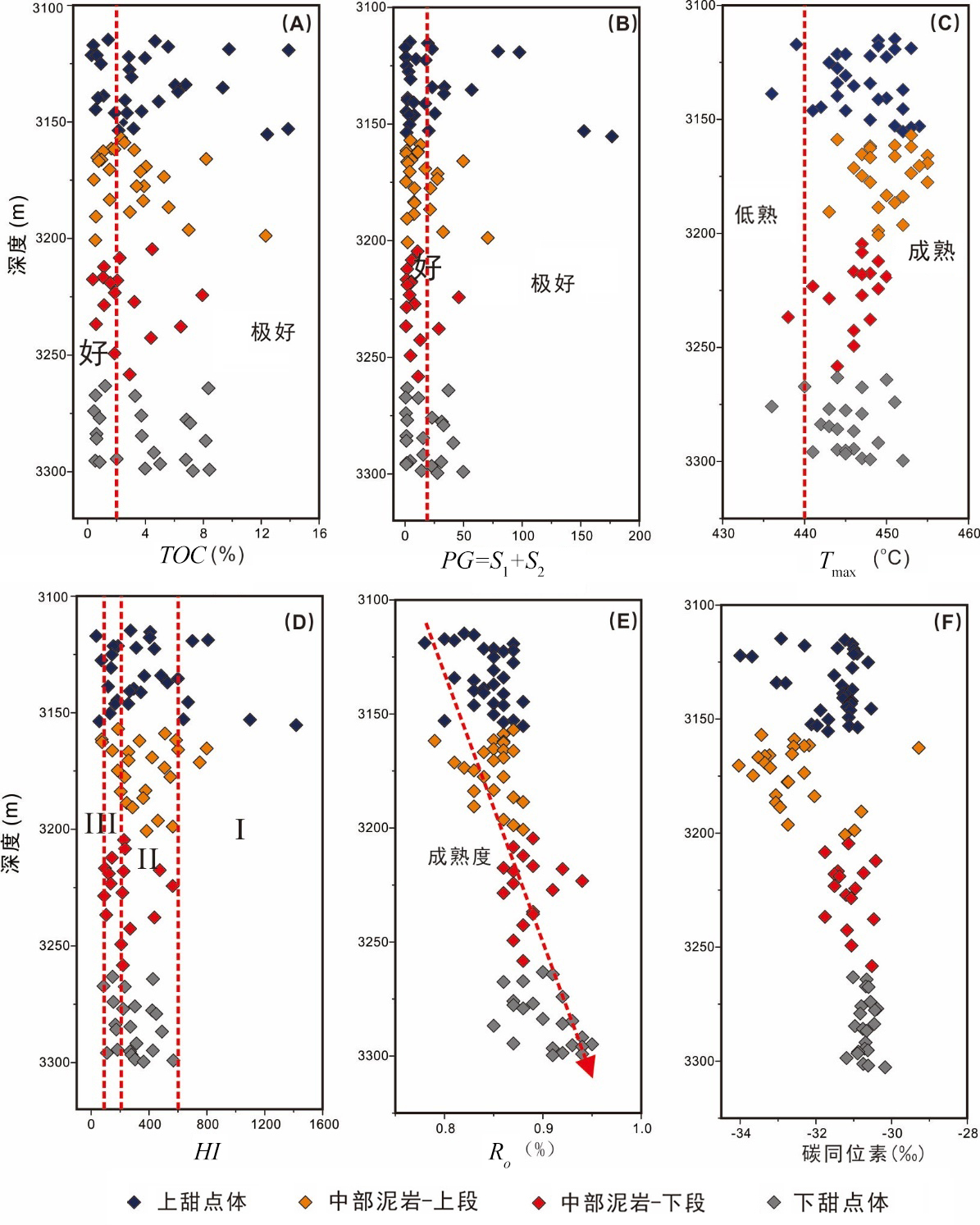
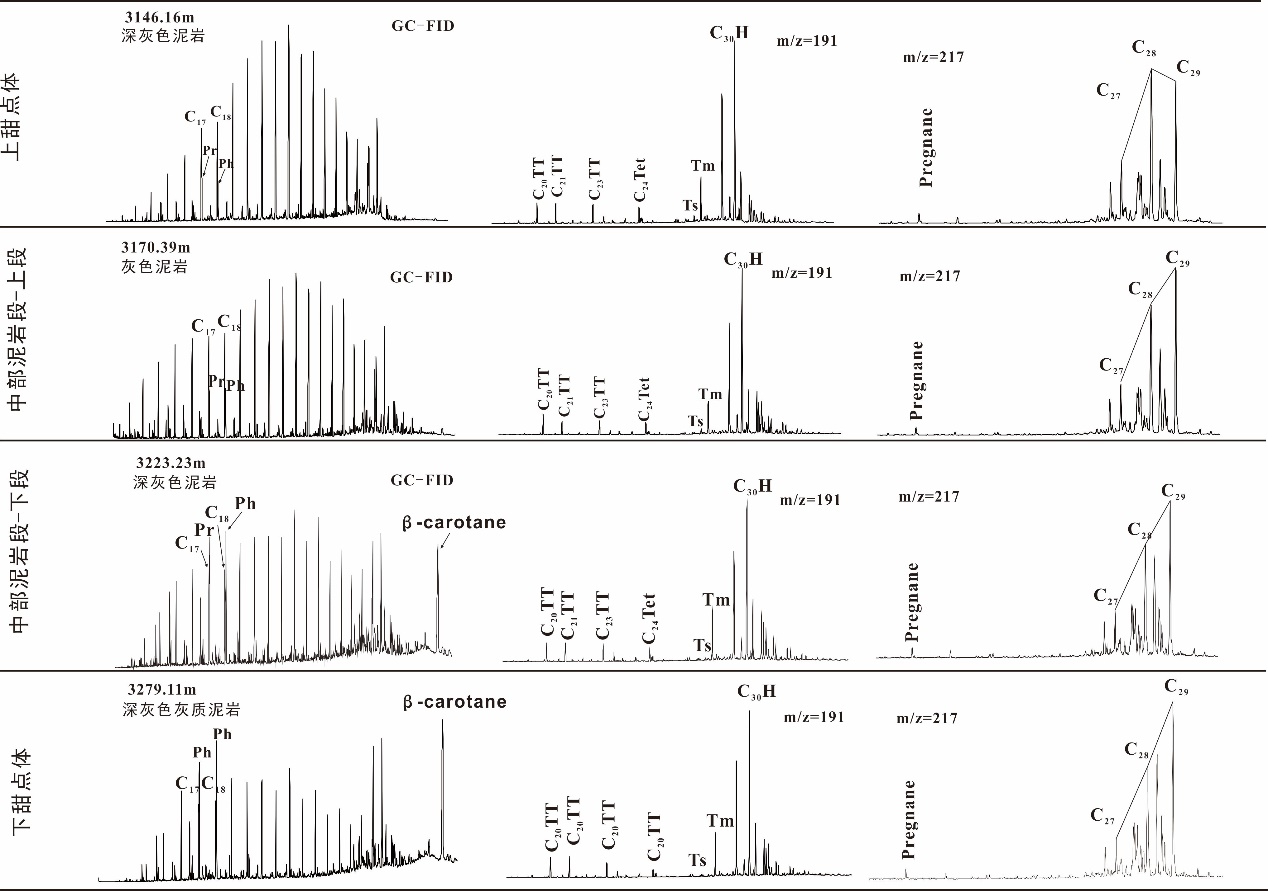
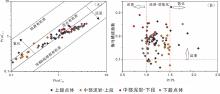
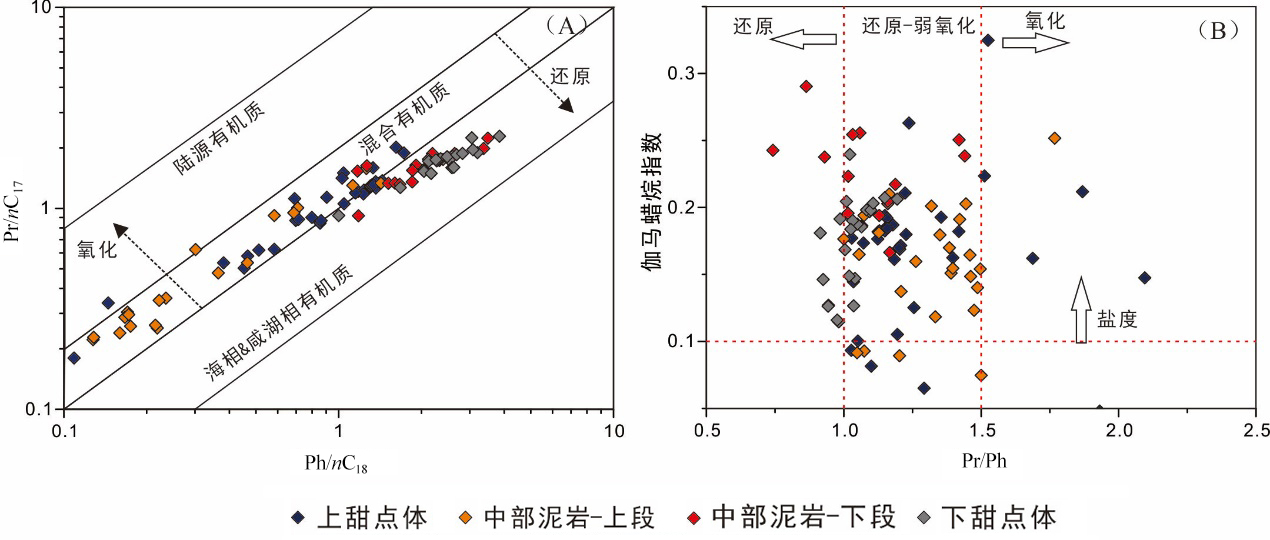
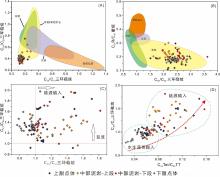
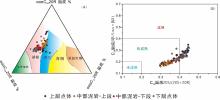
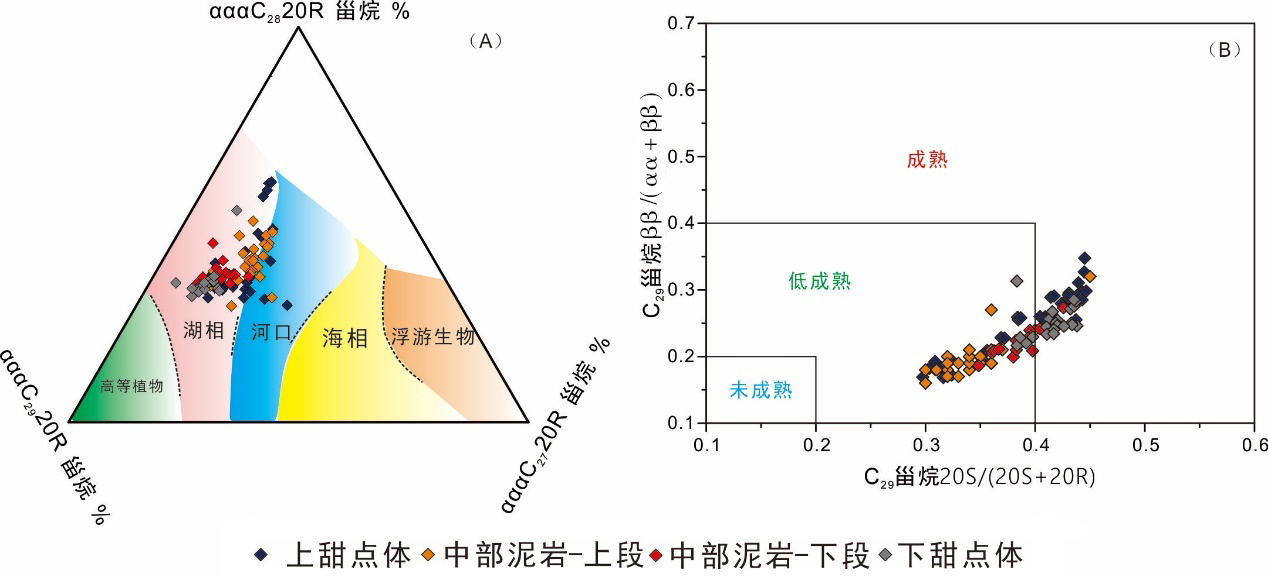
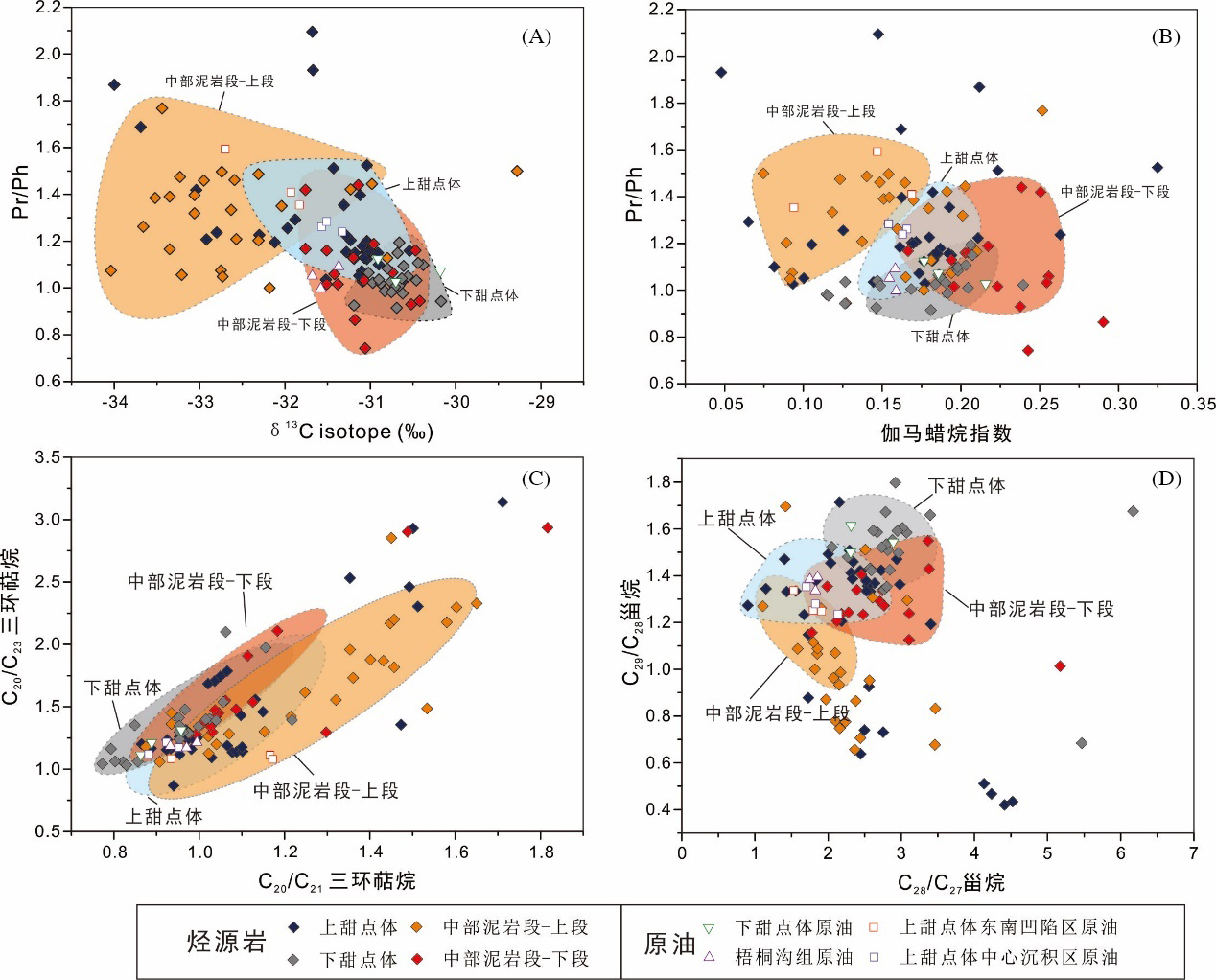
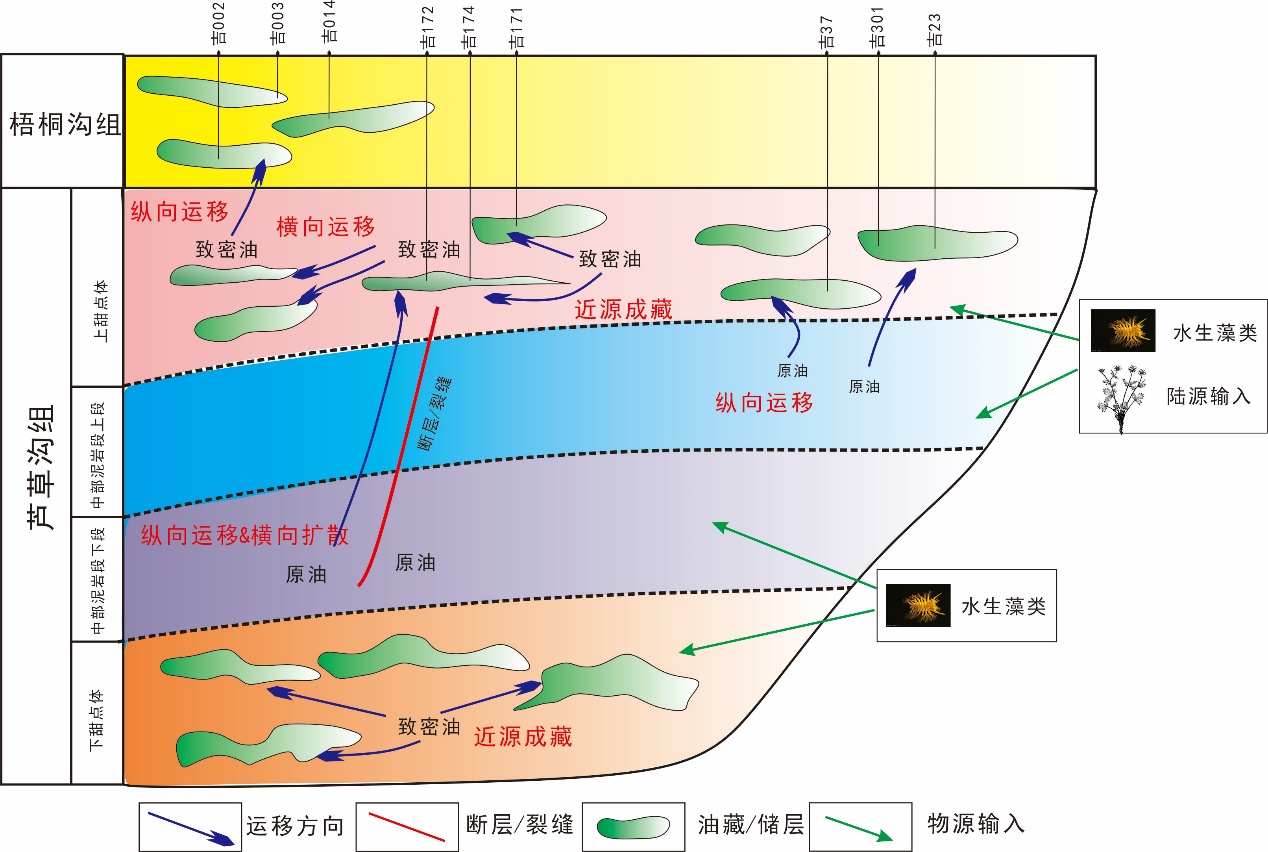
致密油成藏的非均质性是当前致密油研究的热点与难点,为进一步深化对其的理解,以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷中二叠统芦草沟组为例,开展了一个实例研究.结果表明,芦草沟组垂向上总体可分为上、下甜点体及其所夹的中部泥岩段.烃源岩研究发现,芦草沟组整段发育优质烃源岩,并以上下甜点体更好,主要生物母质为水生藻类,干酪根类型主要是II型,成熟演化.油源对比研究发现,芦草沟组“下甜点体”自生自储、近源聚集.相比而言,“上甜点体”除了也有近源聚集特征外,同时跨层为上覆上二叠统梧桐沟组提供油源.而中部泥岩段所生原油主要运移至“上甜点体”成藏.故芦草沟组的成藏从下到上依次为近源聚集、纵向运移、近源聚集以及纵向运移,表现出强烈的非均质性,这可能是陆相致密油聚集的普遍特征,在勘探开发中需加以关注,从页岩油?致密油?常规油全含油气系统的角度考虑.这些认识可应用于区域下一步油气勘探部署中.
中图分类号:
- P59
| 1 | Jarvie D M,Hill R J,Ruble T E,et al. Unconventional shale?gas systems:the Mississippian Barnett Shale of north?central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale?gas assessment. AAPG Bulletin,2007,91(4):475-499. |
| 2 | 邹才能,朱如凯,吴松涛等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望——以中国致密油和致密气为例. 石油学报,2012,33(2):173-187. |
| Zou C N,Zhu R K,Wu S T,et al. Types,characteristics,genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations:taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,33(2):173-187. | |
| 3 | 邹才能. 非常规油气地质. 北京:地质出版社,2014,1-463. |
| 4 | Meissner F F. Petroleum geology of the Bakken Formation Williston Basin,North Dakota and Montana∥Demaison G,Murris R J. Petroleum Geochemistry and Basin Evaluation. Tulsa,OK,USA:American Association of Petroleum Geologists,1991,303:19-42. |
| 5 | Schmoker J W,Hester T C. Organic carbon in Bakken formation,United States portion of Williston basin. AAPG Bulletin,1983,67(12):2165-2174. |
| 6 | Mullen J. Petrophysical characterization of the Eagle Ford Shale in south Texas∥Canadian Unconventional Resources and International Petroleum Conference. Calgary,Canada:Society of Petroleum Engineers,2010. |
| 7 | Zhang L Y,Bao Y S,Li J Y,et al. Movability of lacustrine shale oil:a case study of Dongying Sag,Jiyang Depression,Bohai Bay Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2014,41(6):703-711. |
| 8 | Cao Z,Liu G L,Kong Y H,et al. Lacustrine tight oil accumulation characteristics:permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag,Junggar Basin. International Journal of Coal Geology,2016,153:37-51. |
| 9 | Yao J L,Deng X Q,Zhao Y D,et al. Characteristics of tight oil in Triassic Yanchang formation,Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2013,40(2):161-169. |
| 10 | 匡立春,唐勇,雷德文等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力. 石油勘探与开发,2012,39(6):657-667. |
| Kuang L C,Tang Y,Lei D W,et al. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock,Junggar Basin,NW China. Petroleum Exploration & Development,2012,39(6):657-667. | |
| 11 | Cao Z,Liu G D,Xiang B L,et al. Geochemical characteristics of crude oil from a tight oil reservoir in the Lucaogou Formation,Jimusar sag,Junggar Basin. AAPG Bulletin,2017,101(1):39-72. |
| 12 | Qiu Z,Tao H F,Zou C N,et al. Lithofacies and organic geochemistry of the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusar Sag of the Junggar Basin,NW China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2016,140:97-107. |
| 13 | 斯春松,陈能贵,余朝丰等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层沉积特征. 石油实验地质,2013,35(5):529-533. |
| Si C S,Chen N G,Yu C F,et al. Sedimentary characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou Formation,Jimsar Sag. Petroleum Geology and Experiment,2013,35(5):529-533. | |
| 14 | Hu T,Pang X,Wang X,et al. Tight oil play characterisation:the lower?middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusar Sag,Junggar Basin,Northwest China. Fuel,2016,63(3):349-365. |
| 15 | 向宝力,廖健德,周妮等. 吉木萨尔凹陷吉174井二叠系芦草沟组烃源岩地球化学特征. 科学技术与工程,2013,13(32):9636-9640. |
| Xiang B L,Liao J D,Zhou N,et al. Geochemical characteristic of the source rock of Lucaogou Formation in Ji174 Well,Junggar Basin. Science Technology and Engineering,2013,13(32):9636-9640. | |
| 16 | Luo X R,Wang Z M,Zhang L Q,et al. Overpressure generation and evolution in a compressional tectonic setting,the southern margin of Junggar Basin,northwestern China. AAPG Bulletin,2007,91(8):1123-1139. |
| 17 | 汪新伟,汪新文,马永生. 新疆博格达山的构造演化及其与油气的关系. 现代地质,2007,21(1):116-124. |
| Wang X W,Wang X W,Ma Y S. The Tectonic Evolution of Bogda Mountain,Xinjiang,Northwest China and its relationship to oil and gas accumulation. Geoscience,2007,21(1):116-124. | |
| 18 | Graham S A,Hendrix M S,Wang L B,et al. Collisional successor basins of western China:impact of tectonic inheritance on sand composition. GSA Bulletin,1993,105(3):323-344. |
| 19 | 吴晓智,何登发,杨迪生等. 准噶尔盆地陆梁隆起构造特征与油气成藏. 地质科学,2012,47(1):73-91. |
| Wu X Z,He D F,Yang D S,et al. Structural character and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Luliang uplift,Junggar Basin. Chinese Journal of Geology,2012,47(1):73-91. | |
| 20 | 宋永,周路,郭旭光等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组湖相云质致密油储层特征与分布规律. 岩石学报,2017,33(4):1159-1170. |
| Song Y,Zhou L,Guo X G,et al. Characteristics and occurrence of lacustrine dolomitic tight?oil reservoir in the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation,Jimusaer sag,southeastern Junggar Basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2017,33(4):1159-1170. | |
| 21 | Peters K E,Moldowan J M. The biomarker guide:interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments. The 2nd Edition. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,2005,1-985. |
| 22 | Tissot B P,Welte D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1984,1-521. |
| 23 | Peters K E,Moldowan J M,Schoell M,et al. Petroleum isotopic and biomarker composition related to source rock organic matter and depositional environment. Organic Geochemistry,1986,10(1-3):17-27. |
| 24 | Peters K E,Moldowan,J M,Sundararaman P. Effects of hydrous pyrolysis on biomarker thermal maturity parameters:monterey Phosphatic and Siliceous members. Organic Geochemistry,1990,15(3):249-265. |
| 25 | Noble R A,Alexander R,Kagi R I,et al. Tetracyclic diterpenoid hydrocarbons in some Australian coals,sediments and crude oils. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1985,49(10):2141-2147. |
| 26 | Azevedo D A,Neto F R A,Simoneit B R T,et al. Novel series of tricyclic aromatic terpanes characterized in Tasmanian tasmanite. Organic Geochemistry,1992,18(1):9-16. |
| 27 | Lerch B,Karlsen D A,Matapour Z,et al. Organic geochemistry of Barents Sea Petroleum:thermal maturity and alteration and mixing processes in oils and condensates. Journal of Petroleum Geology,2016,39(2):125-148. |
| 28 | Huang W Y,Meinschein W G. Sterols as ecological indicators. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1979,43(5):739-745. |
| 29 | Grantham P J,Wakefield L L. Variations in the sterane carbon number distributions of marine source rock derived crude oils through geological time. Organic Geochemistry,1988,12(1):61-73. |
| 30 | Rubinstein I,Sieskind O,Albrecht P. Rearranged sterenes in a shale:occurrence and simulated formation. Journal of Chemical Society,Perkin Transaction,1975(19):1833-1836. doi.org/10. 1039/P19750001833. |
| 31 | Seifert W K,Moldowan J M. The effect of thermal stress on source?rock quality as measured by hopane stereochemistry. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,1980,12:229-237. |
| 32 | Murray A P,Summons R E,Boreham C J,et al. Biomarker and n?alkane isotope profiles for Tertiary oils:relationship to source rock depositional setting. Organic Geochemistry,1994,22(3-5):521-542. |
| 33 | Riboulleau A,Schnyder J,Riquier L,et al. Environmental change during the Early Cretaceous in the Purbeck?type Durlston Bay section (Dorset,Southern England):a biomarker approach. Organic Geochemistry,2007,38(11):1804-1823. |
| 34 | Didyk B M,Simoneit B R T,Brassell S C,et al. Organic geochemical indicators of palaeoen?vironmental conditions of sedimentation. Nature,1978,272(5650):216-222. |
| 35 | Moldowan J M,Sundararaman P,Schoell M. Sensitivity of biomarker properties to depositional environment and/or source input in the Lower Toarcian of SW?Germany. Organic Geochemistry,1986,10(4-6):915-926. |
| 36 | Abarghani A,Ostadhassan M,Gentzis T,et al. Organofacies study of the Bakken source rock in North Dakota,USA,based on organic petrology and geochemistry. International Journal of Coal Geology,2018,188:79-93. |
| 37 | French K L,Birdwell J E,Whidden K J. Geochemistry of a thermally immature Eagle Ford Group drill core in central Texas. Organic Geochemistry,2019,131:19-33. |
| 38 | Denne R A,Hinote R E,Breyer J A,et al. The Cenomanian?Turonian Eagle Ford Group of South Texas:insights on timing and paleoceanographic conditions from geochemistry and micropaleontologic analyses. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2014,413:2-28. |
| 39 | Li Q,Wu S H,Xia D L,et al. Major and trace element geochemistry of the lacustrine organic?rich shales from the Upper Triassic Chang 7 Member in the southwestern Ordos Basin,China:implications for paleoenvironment and organic matter accumulation. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,111:852-867. |
| [1] | 秦洋,姚素平,萧汉敏. 致密砂岩储层孔⁃喉连通性研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 338-353. |
| [2] | 刘显, 陈强路, 王小林, 丘靥, 杨源显. 方解石晶体定向性对水的拉曼光谱影响的实验评估[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 297-307. |
| [3] | 游杰, 胡广, 张玺华, 沈安江, 彭瀚霖, 田兴旺, 赵东方. 微生物碳酸盐岩同生⁃早成岩阶段有机质降解示踪:以四川盆地灯影组四段为例[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 308-321. |
|