南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 142–150.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.01.016
基于社区划分的空气质量指数(AQI)预测算法
- 淮阴工学院计算机与软件工程学院,淮安,223003
Prediction of Air Quality Index (AQI) based on community division
Yan Yuan,Bolun Chen( ),Guochang Zhu,Yong Hua,Yongtao Yu
),Guochang Zhu,Yong Hua,Yongtao Yu
- College of Computer and Software Enginnering,Huaiyin Institute of Technology,Huaian,223003,China
摘要:
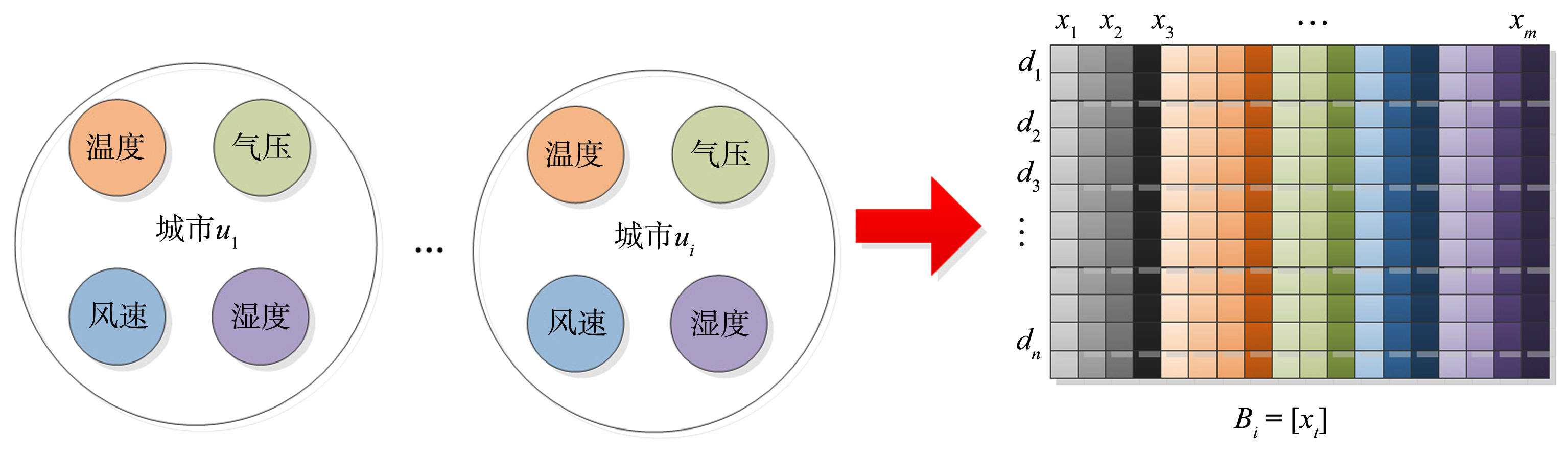
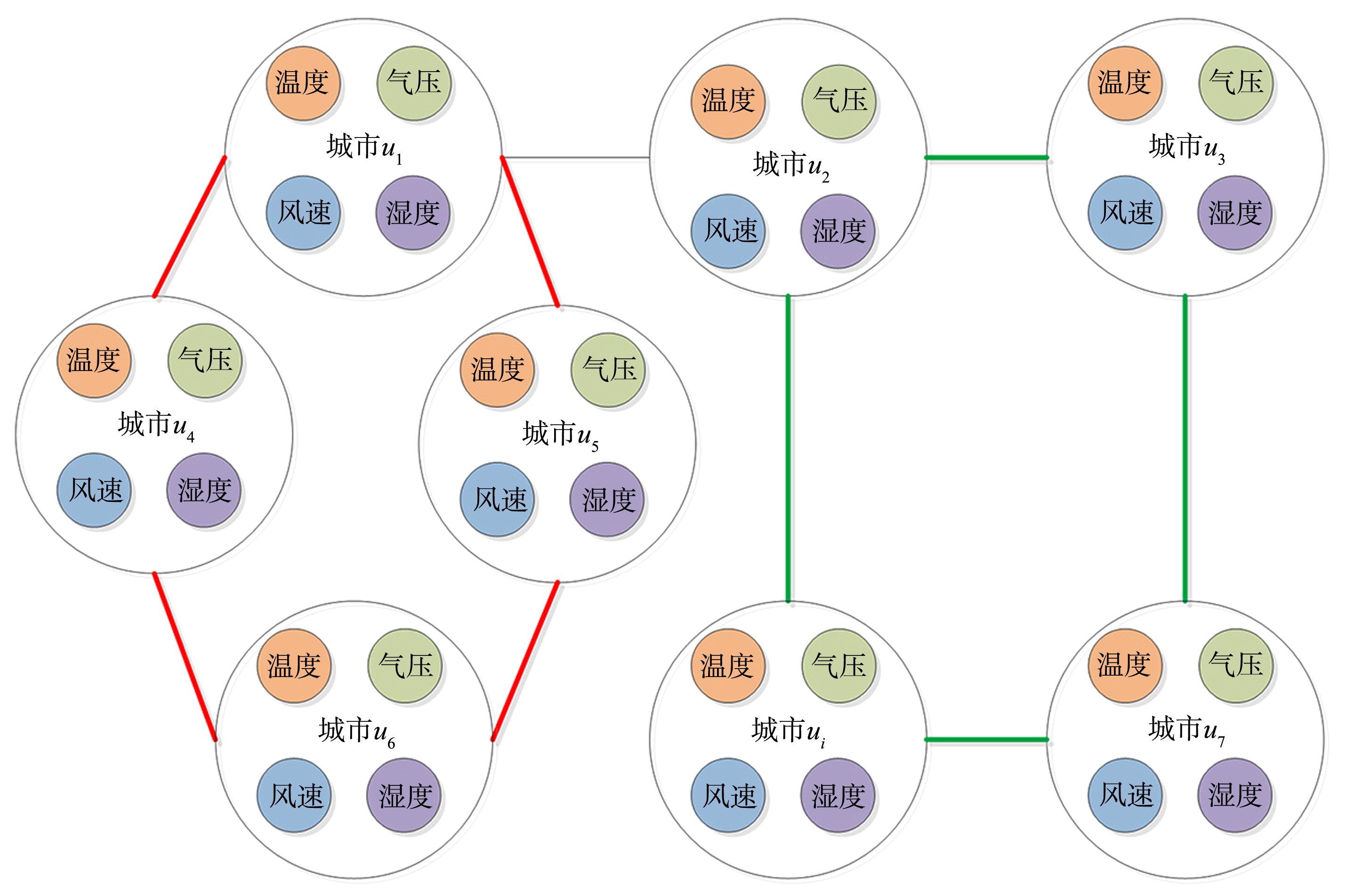
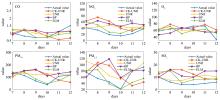
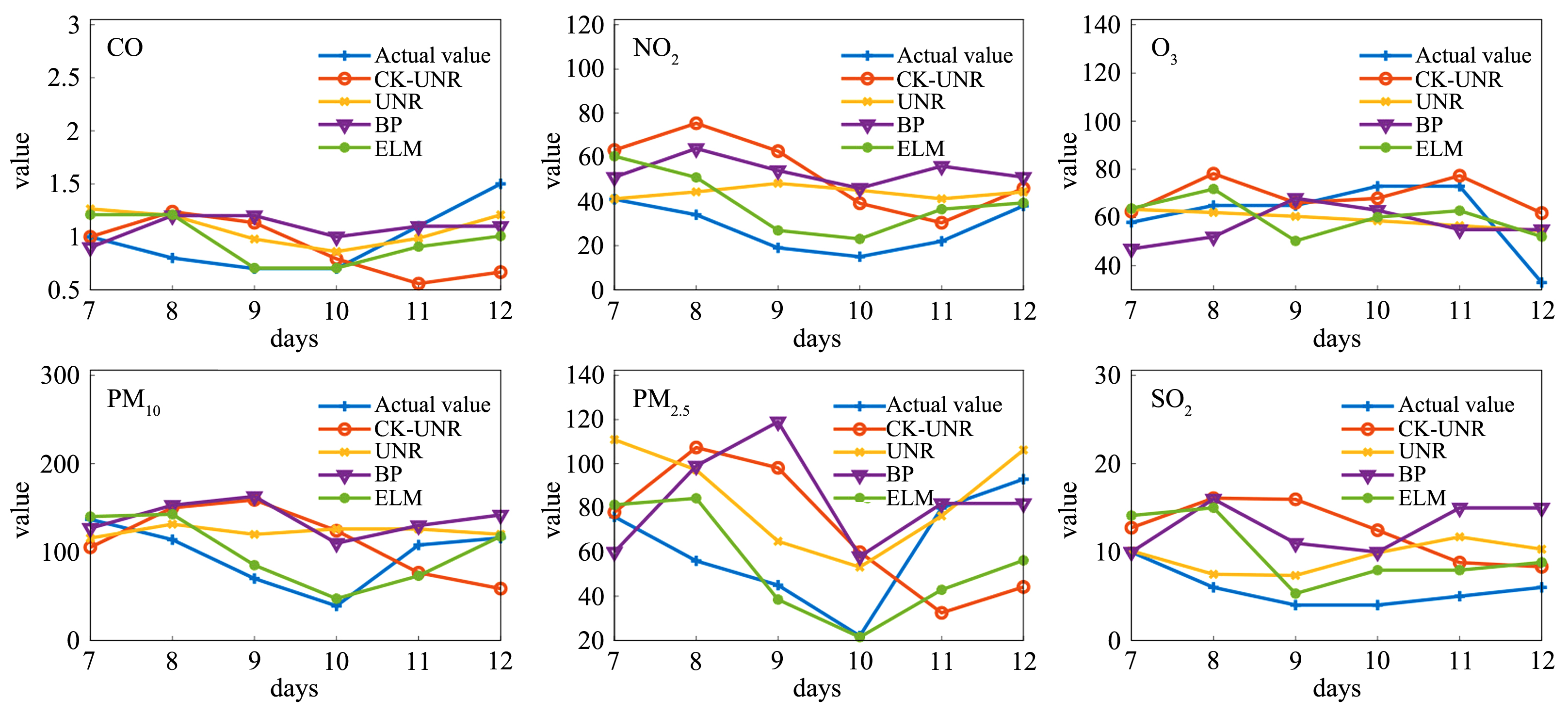
AQI (Air Quality Index)是判定空气质量好坏的重要指标,做好AQI的预测,对大气污染的治理有积极的推进作用,但目前预测AQI的算法通常没有综合考虑气象因素和周边城市对预测性能的影响.将气象因素和周边城市的污染物因素作为算法设计的基础,提出一种基于社区划分的空气质量指数预测的算法.首先根据气象特征计算城市之间的相似度,接着对各城市间的相似度矩阵进行社区划分;然后将属于同一社区的城市污染物时序信息作为预测目标城市空气质量指数的依据,并考虑目标城市的周边城市对其的影响;最后使用非线性回归的方法进行预测建模.通过对江苏省内20座城市的大气污染数据和气象数据的采集与分析,证明该算法不但预测精度有所提高,而且与传统的时间序列预测模型相比,降低了时间复杂度.
中图分类号:
- TP301.6
| 1 | Thach T Q,Tsang H,Cao P H,et al. A novel method to construct an air quality index based on air pollution profiles. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health,2017,221(1):17-26. |
| 2 | Brunekreef B,Holgate S T. Air pollution and health. The Lancet,2002,360(9341):1233-1242. |
| 3 | 张欣,许建明,王体健等. 上海市一次重霾污染过程的特征及成因分析. 南京大学学报(自然科学),2015(3):463-472. |
| Zhang X,Xu J M,Wang T J,et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of a serious haze episode in December 2013 in Shanghai. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science),2015(3):463-472. | |
| 4 | Fu B,Xiao H G,Wu L F. Grey relational analysis for the AQI of Beijing,Tianjin,and Shijiazhuang and related countermeasures. Grey Systems:Theory and Application,2018,8(2):156-166. |
| 5 | Yao W X,Zhang C X,Xiao W,et al. The research of new daily diffuse solar radiation models modified by air quality index (AQI) in the region with heavy fog and haze. Energy Conversion and Management,2017,139:140-150. |
| 6 | Liu C M. Effect of PM2.5 on AQI in Taiwan. Environmental Modelling & Software,2002,17(1):29-37. |
| 7 | Carbajal?Hernández J J,Sánchez?Fernández L P,Carrasco?Ochoa J A,et al. Assessment and prediction of air quality using fuzzy logic and autoregressive models. Atmospheric Environment,2012,60:37-50. |
| 8 | Corani G,Scanagatta M. Air pollution prediction via multi?label classification. Environmental Modelling & Software,2016,80:259-264. |
| 9 | Singh K P,Gupta S,Kumar A,et al. Linear and nonlinear modeling approaches for urban air quality prediction. Science of the Total Environment,2012,426:244-255. |
| 10 | 李博群,贾政权,刘利平. 基于模糊时间序列的空气质量指数预测. 华北理工大学学报(自然科学版),2018,40(3):78-86. |
| Li B Q,Jia Z Q,Liu L PAir quality index forecast based on fuzzy time series models. Journal of North China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018,40(3):78-86. | |
| 11 | 高帅,胡红萍,李洋等. 基于改进的思维进化算法与BP神经网络的AQI预测. 数学的实践与认识,2018,48(19):151-157. |
| Gao S,Hu H P,Li Y,et al. AQI prediction based on mind evolutionary algorithm and BP neural network. Mathematics in Practice and Theory,2018,48(19):151-157. | |
| 12 | 刘洪通,冯百明,温向慧等. 基于Storm的AQI实时预测模型. 计算机工程与设计,2019,40(1):296-301. |
| Liu H T,Feng B M,Wen X H,et al. Real?time AQI prediction model based on Storm. Computer Engineering and Design,2019,40(1):296-301. | |
| 13 | 张春露,白艳萍. 基于TensorFlow的LSTM模型在太原空气质量AQI指数预测中的应用. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2018,32(8):137-141. |
| Zhang C L,Bai Y P.Application of LSTM prediction model based on tensor flow in taiyuan air quality AQI index. Journal of Chongqing Institute of Technology,2018,32(8):137-141. | |
| 14 | 白鹤鸣,沈润平,师华定等. 基于BP神经网络的空气污染指数预测模型研究. 环境科学与技术,2013,36(3):186-189. |
| Bai H M,Shen R P,Shi H D,et al. Forecasting model of air pollution index based on BP neural network. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,36(3):186-189. | |
| 15 | Li X,Peng L,Hu Y,et al. Deep learning architecture for air quality predictions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(22):22408-22417. |
| 16 | Xi X,Wei Z,Rui X G,et al. A comprehensive evaluation of air pollution prediction improvement by a machine learning method∥2015 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations,Logistics and Informatics (SOLI). Hammamet,Tunisia:IEEE,2015:176-181. |
| 17 | Han L J,Zhou W Q,Li W F,et al. Meteorological and urban landscape factors on severe air pollution in Beijing. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association,2015,65(7):782-787. |
| 18 | Sharma M,Aggarwal S,Bose P,et al. Meteorology?based forecasting of air quality index using neural network∥IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics. Banff, Canada:IEEE,2003:374-378. |
| 19 | Cui H,Ma R,Gao F. Relationship between meteorological factors and diffusion of atmospheric pollutants. Chemical Engineering Transactions,2018,71:1417-1422. |
| 20 | Li Y,Chiu Y H,Lu L C. Energy and AQI performance of 31 cities in China. Energy Policy,2018,122:194-202. |
| 21 | Liu M,Gu J L,Liu L J,et al. Air quality analysis of Dalian in summer based on AQI data. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics,2016,11(2):111-117. |
| 22 | Newman M E J. Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Physical Review E,2004,69(6):066133. |
| 23 | Newman M E J. Community detection in networks:. modularity optimization and maximum likelihood are equivalent2016,arXiv:1606.02319. |
| [1] | 李亚重,杨有龙,仇海全. 一种基于嵌入式的弱标记分类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 549-560. |
| [2] | 刘亮,何庆. 基于改进蝗虫优化算法的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 41-50. |
| [3] | 洪思思,曹辰捷,王 喆*,李冬冬. 基于矩阵的AdaBoost多视角学习[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1152-1160. |
| [4] | 周星星,张海平,吉根林. 具有时空特性的区域移动模式挖掘算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1171-1182. |
|