南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1083–1091.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.06.017
• • 上一篇
一种有效更新多源数据约简的增量算法
- 1.南昌师范学院数学与信息科学学院,南昌,330032
2.运城学院数学与信息技术学院,运城,044000
An efficient updating reduction for the multi⁃source data
- 1.School of Mathematics and Information Science,Nanchang Normal University,Nanchang,330032, China
2.Maths &Information Technology School,Yuncheng University,Yuncheng,044000,China
摘要:
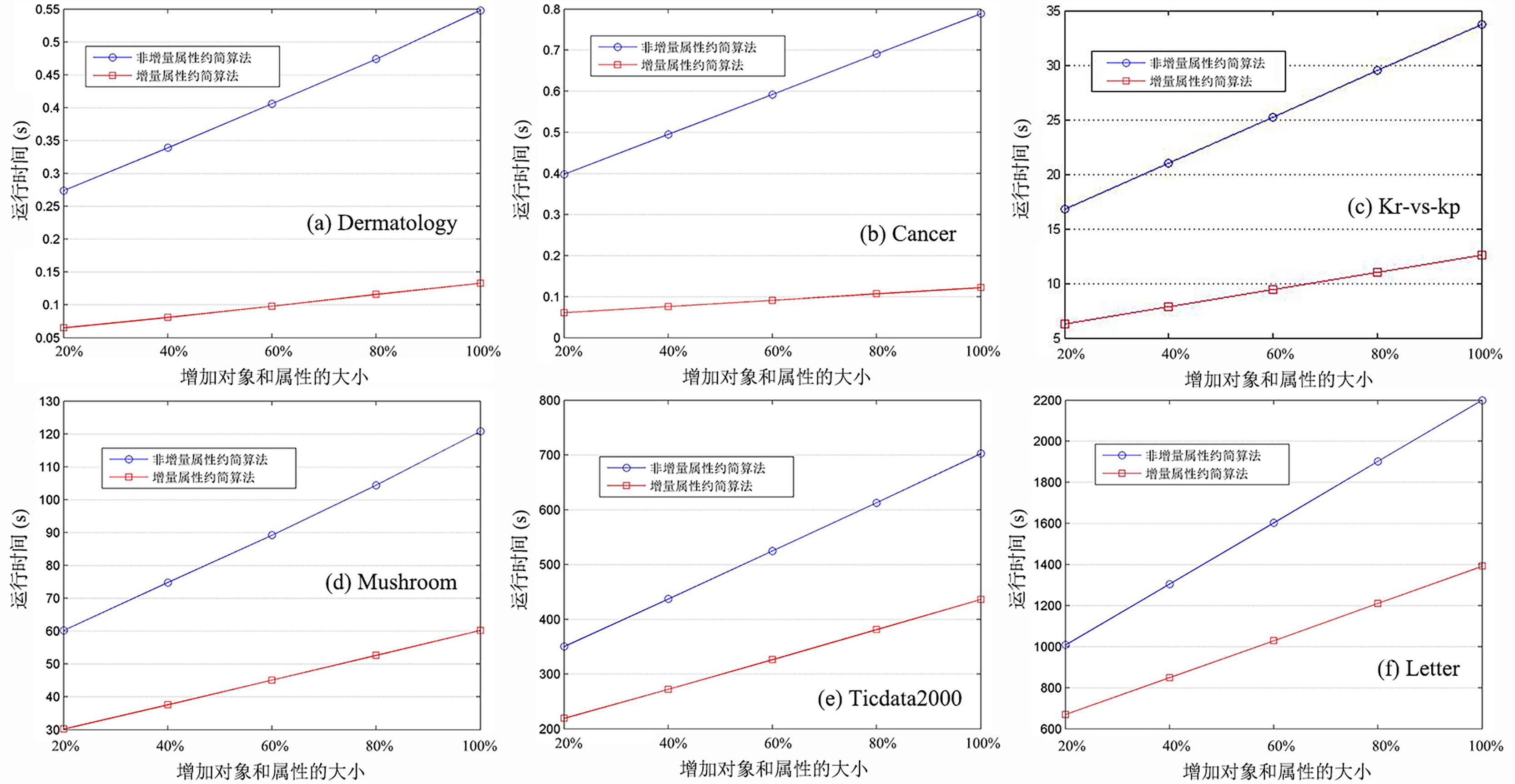
随着网络技术和存储技术的迅速发展,各行业形成了大量多源数据,为企业提供了良好的发展机遇.由于这些数据随着时间的变化而变化,如何快速更新这些数据的属性约简是目前计算机科学研究领域中备受关注的热点之一.首先介绍多源数据相关矩阵的基础知识,根据多源数据的相关理论知识设计多源数据非增量矩阵约简算法.另外,当多源数据的属性和对象同时变化时,给出了多源数据等价关系矩阵融合方法,分析了属性和对象同时变化时基于矩阵方法计算知识粒度的增量更新机制,设计了有效更新多源数据属性约简的增量算法.最后,在六个UCI数据集上对增量和非增量属性约简算法做了大量对比仿真实验.实验结果表明:与非增量属性约简算法相比,增量属性约简算法计算约简所需运行时间远小于非增量属性约简算法,同时,两算法所得的分类精确度基本一致.
中图分类号:
- TP301.6
| 1 | Eurek K,Sullivan P,Gleason M,et al. An improved global wind resource estimate for integrated assessment models. Energy Economics,2017,64:552-567. |
| 2 | Rafiei M H,Adeli H. A novel unsupervised deep learning model for global and local health condition assessment of structures. Engineering Structures,2018,156:598-607. |
| 3 | Fink J D S,De Mello E D,Beghetto M G,et al. Nutritional assessment score:A new tool derived from subjective global assessment for hospitalized adults. Clinical Nutrition,2018,37(2):706-711. |
| 4 | Khaleghi B,Khamis A,Karray F O,et al. Multisensor data fusion:A review of the state?of?the?art. Information Fusion,2013,14(1):28-44. |
| 5 | Zadeh L A. Some reflections on soft computing,granular computing and their roles in the conception,design and utilization of information/intelligent systems. Soft Computing,1998,2(1):23-25. |
| 6 | Mahajan P,Kandwal R,Vijay R. Rough set approach in machine learning:A review. International Journal of Computer Applications,2012,56(10):1-13. |
| 7 | Zhang Q H,Xie Q,Wang G Y. A survey on rough set theory and its applications. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology,2016,1(4):323-333. |
| 8 | Sun L,Xu J C,Tian Y. Feature selection using rough entropy?based uncertainty measures in incomplete decision systems. Knowledge?Based Systems,2012,36:206-216. |
| 9 | Cornelis C,Jensen R,Hurtado G,et al. Attribute selection with fuzzy decision reducts. Information Sciences,2010,180(2):209-224. |
| 10 | Huang Y Y,Li T R,Luo C,et al. Dynamic fusion of multi?source interval?valued data by fuzzy granulation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,2018,26(6):3403-3417. |
| 11 | Li S Y,Hong Z Y,Li T R. Efficient composing rough approximations for distributed data. Know?ledge?Based Systems,2019,182:104793. |
| 12 | Wang S,Li T R,Luo C,et al. Efficient updating rough approximations with multi?dimensional variation of ordered data. Information Sciences,2016,372:690-708. |
| 13 | Hu J,Li T R,Luo C,et al. Incremental fuzzy probabilistic rough sets over two universes. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2017,81:28-48. |
| 14 | Liang J Y,Wang F,Dang C Y,et al. A group incremental approach to feature selection applying rough set technique. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2014,26(2):294-308. |
| 15 | Jing Y G,Li T R,Luo C,et al. An incremental approach for attribute reduction based on knowledge granularity. Knowledge?Based Systems,2016,104:24-38. |
| 16 | Zeng A P,Li T R,Liu D,et al. A fuzzy rough set approach for incremental feature selection on hybrid information systems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,2015,258:39-60. |
| 17 | Shu W H,Shen H. Updating attribute reduction in incomplete decision systems with the variation of attribute set. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2014,55(3):867-884. |
| 18 | 桑彬彬,杨留中,陈红梅等. 优势关系粗糙集增量属性约简算法. 计算机科学,2020,47(8):137-143. |
| Sang B B,Yang L Z,Chen H M,et al. Incremental attribute reduction algorithm in dominance?based rough set. Computer Science,2020,47(8):137-143. | |
| 19 | 刘清. Rough集及Rough推理. 北京:科学出版社,2001. |
| 20 | Jing Y G,Li T R,Fujita H,et al. An incremental attribute reduction method for dynamic data mining. Information Sciences,2018,465:202-218. |
| [1] | 孙颖, 蔡天使, 张毅, 鞠恒荣, 丁卫平. 基于合理粒度的局部邻域决策粗糙计算方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(2): 262-271. |
| [2] | 刘琼, 代建华, 陈姣龙. 区间值数据的代价敏感特征选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 121-129. |
| [3] | 郑嘉文, 吴伟志, 包菡, 谭安辉. 基于熵的多尺度决策系统的最优尺度选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 130-140. |
| [4] | 郑文彬, 李进金, 张燕兰, 廖淑娇. 基于矩阵的多粒度粗糙集粒度约简方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 141-149. |
| [5] | 毛振宇, 窦慧莉, 宋晶晶, 姜泽华, 王平心. 共现邻域关系下的属性约简研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 150-159. |
| [6] | 李同军,于洋,吴伟志,顾沈明. 经典粗糙近似的一个公理化刻画[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 445-451. |
| [7] | 任睿,张超,庞继芳. 有限理性下多粒度q⁃RO模糊粗糙集的最优粒度选择及其在并购对象选择中的应用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 452-460. |
| [8] | 王宝丽,姚一豫. 信息表中约简补集对及其一般定义[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 461-468. |
| [9] | 刘鑫,胡军,张清华. 属性组序下基于代价敏感的约简方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 469-479. |
| [10] | 崔紫薇,王成,陈德蕾,雷蕾. 基于历史出行记录扩充的公交乘客下车站点推算方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(2): 227-235. |
| [11] | 姚宁, 苗夺谦, 张远健, 康向平. 属性的变化对于流图的影响[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 519-528. |
| [12] | 程永林, 李德玉, 王素格. 基于极大相容块的邻域粗糙集模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 529-536. |
| [13] | 张龙波, 李智远, 杨习贝, 王怡博. 决策代价约简求解中的交叉验证策略[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 601-608. |
| [14] | 李藤, 杨田, 代建华, 陈鸰. 基于模糊区分矩阵的结直肠癌基因选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 633-643. |
| [15] | 张 婷1,2,张红云1,2*,王 真3. 基于三支决策粗糙集的迭代量化的图像检索算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 714-. |
|
||