南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 150–159.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.01.016
• • 上一篇
共现邻域关系下的属性约简研究
毛振宇1, 窦慧莉1( ), 宋晶晶1,3, 姜泽华1, 王平心2
), 宋晶晶1,3, 姜泽华1, 王平心2
- 1.江苏科技大学计算机学院,镇江,212003
2.江苏科技大学理学院,镇江,212003
3.数据科学与智能应用福建省高校重点实验室,漳州,363000
Research on attribute reduction via co⁃occurrence neighborhood relation
Zhenyu Mao1, Huili Dou1( ), Jingjing Song1,3, Zehua Jiang1, Pingxin Wang2
), Jingjing Song1,3, Zehua Jiang1, Pingxin Wang2
- 1.School of Computer,Jiangsu University of Science and Technology,Zhenjiang,212003,China
2.School of Science,Jiangsu University of Science and Technology,Zhenjiang,212003,China
3.Fujian Province University Key Laboratory of Data Science and Intelligent Application,Zhangzhou,363000,China
摘要:
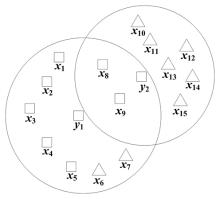
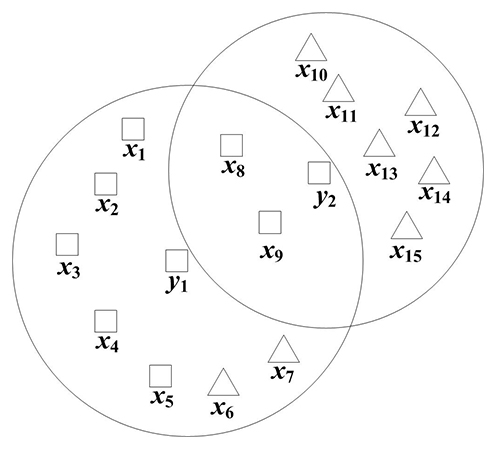
在邻域粗糙集的研究中,往往借助给定的半径来约束样本之间的相似性进而实现邻域信息粒化,需要注意的是,若给定的半径较大,则不同类别的样本将落入同一邻域中,易引起邻域中信息的不精确或不一致.为改善这一问题,已有学者给出了伪标记邻域的策略,然而无论是传统邻域还是伪标记邻域,都仅仅使用样本间的距离来度量样本之间的相似性,忽略了邻域信息粒内部不同样本所对应的邻域之间的结构关系.鉴于此,通过引入邻域距离度量,提出一种共现邻域的信息粒化机制,并构造了新型的共现邻域以及伪标记共现邻域粗糙集模型,在此基础上使用前向贪心搜索策略实现了所构造的两种模型下的约简求解.实验结果表明,与传统邻域关系以及伪标记邻域关系所求得的约简相比,利用共现邻域方法求得的约简能够在不降低分类器准确率的前提下产生更高的约简率.
中图分类号:
- TP18
| 1 | 胡清华,于达仁,谢宗霞. 基于邻域粒化和粗糙逼近的数值属性约简. 软件学报,2008,19(3):640-649. |
| Hu Q H,Yu D R,Xie Z X. Numerical attribute reduction based on neighborhood granulation and rough approximation. Journal of Software,2008,19(3):640-649. | |
| 2 | Zhao H,Wang P,Hu Q H. Cost?sensitive feature selection based on adaptive neighborhood granularity with multi?level confidence. Information Sciences,2016,366:134-149. |
| 3 | Ferone A. Feature selection based on composition of rough sets induced by feature granulation. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2018,101:276-292. |
| 4 | Liu K Y,Yang X B,Fujita H,et al. An efficient selector for multi?granularity attribute reduction. Information Sciences,2019,505:457-472. |
| 5 | Yang X B,Liang S C,Yu H L,et al. Pseudo?label neighborhood rough set:measures and attribute reductions. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2019,105:112-129. |
| 6 | Jiang H B,Chen Y M. Neighborhood granule classifiers. Applied Sciences,2018,8(12):2646. |
| 7 | Yao Y Y,Zhang X Y. Class?specific attribute reducts in rough set theory. Information Sciences,2017,418-419:601-618. |
| 8 | Yang X B,Yao Y Y. Ensemble selector for attribute reduction. Applied Soft Computing,2018,70:1-11. |
| 9 | 高媛,陈向坚,王平心等. 面向一致性样本的属性约简. 智能系统学报,2019,14(6):1170-1178. |
| Gao Y,Chen X J,Wang P X,et al. Attribute reduction over consistent samples. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2019,14(6):1170-1178. | |
| 10 | Li J Z,Yang X B,Song X N,et al. Neighborhood attribute reduction:a multi?criterion approach. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics,2017,10(4):731-742. |
| 11 | 姜泽华,王怡博,徐刚等. 面向多尺度的属性约简加速器. 计算机科学,2019,46(12):250-256. |
| Jiang Z H,Wang Y B,Xu G,et al. Multi?scale based accelerator for attribute reduction. Computer Science,2019,46(12):250-256. | |
| 12 | Hu Q H,Yu D R,Liu J F,et al. Neighborhood rough set based heterogeneous feature subset selection. Information Sciences,2008,178(18):3577-3594. |
| 13 | Liu K Y,Yang X B,Yu H L,et al. Rough set based semi-supervised feature selection via ensemble selector. Knowledge?Based Systems,2019,165:282-296. |
| 14 | Xu S P,Yang X B,Yu H L,et al. Multi?label learning with label?specific feature reduction. Knowledge?Based Systems,2016,104:52-61. |
| 15 | 张文冬,亓慧,刘克宇等. 基于粗糙集特征选择的过拟合现象及应对策略. 南京航空航天大学学报,2019,51(5):687-692. |
| Zhang W D,Qi H,Liu K Y,et al. Over?fitting and its countermeasure in feature selection based on rough set. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics,2019,51(5):687-692. | |
| 16 | Song J J,Tsang E C C,Chen D G,et al. Minimal decision cost reduct in fuzzy decision?theoretic rough set model. Knowledge?Based Systems,2017,126:104-112. |
| 17 | 李京政,杨习贝,王平心等. 模糊粗糙集的稳定约简方法. 南京理工大学学报,2018,42(1):68-75. |
| Li J Z,Yang X B,Wang P X,et al. Stable attribute reduction approach for fuzzy rough set. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology,2018,42(1):68-75. | |
| 18 | Hu Q H,Pedrycz W,Yu D R,et al. Selecting discrete and continuous features based on neighborhood decision error minimization. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics,Part B (Cybernetics),2010,40(1):137-150. |
| 19 | Chen Y,Liu K Y,Song J J,et al. Attribute group for attribute reduction. Information Sciences,2020,535:64-80. |
| 20 | lzak D. Approximate entropy reducts. Fundamenta Informaticae,2002,53:365-390. |
| 21 | Zhang X,Mei C L,Chen D G,et al. Feature selection in mixed data:a method using a novel fuzzy rough set?based information entropy. Pattern Recognition,2016,56:1-15. |
| [1] | 刘琼, 代建华, 陈姣龙. 区间值数据的代价敏感特征选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 121-129. |
| [2] | 郑嘉文, 吴伟志, 包菡, 谭安辉. 基于熵的多尺度决策系统的最优尺度选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 130-140. |
| [3] | 郑文彬, 李进金, 张燕兰, 廖淑娇. 基于矩阵的多粒度粗糙集粒度约简方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 141-149. |
| [4] | 李同军,于洋,吴伟志,顾沈明. 经典粗糙近似的一个公理化刻画[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 445-451. |
| [5] | 任睿,张超,庞继芳. 有限理性下多粒度q⁃RO模糊粗糙集的最优粒度选择及其在并购对象选择中的应用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 452-460. |
| [6] | 王宝丽,姚一豫. 信息表中约简补集对及其一般定义[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 461-468. |
| [7] | 姚宁, 苗夺谦, 张远健, 康向平. 属性的变化对于流图的影响[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 519-528. |
| [8] | 程永林, 李德玉, 王素格. 基于极大相容块的邻域粗糙集模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 529-536. |
| [9] | 张龙波, 李智远, 杨习贝, 王怡博. 决策代价约简求解中的交叉验证策略[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 601-608. |
| [10] | 李藤, 杨田, 代建华, 陈鸰. 基于模糊区分矩阵的结直肠癌基因选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 633-643. |
| [11] | 张 婷1,2,张红云1,2*,王 真3. 基于三支决策粗糙集的迭代量化的图像检索算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 714-. |
| [12] | 温 欣1,李德玉1,2*,王素格1,2. 一种基于邻域关系和模糊决策的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 733-. |
| [13] | 敬思惠,秦克云*. 决策系统基于特定决策类的上近似约简[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 804-. |
| [14] | 胡玉文1,2,3*,徐久成1,2,张倩倩1,2. 决策演化集的膜结构抑制剂[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 810-. |
| [15] | 陶玉枝1,2,赵仕梅1,2,谭安辉1,2*. 一种基于决策表约简的集覆盖问题的近似解法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 821-. |
|
||