南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 98–106.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.01.011
求解非凸截断L 1⁃SVM的多阶段非精确线搜割平面方法
- 中国人民解放军陆军炮兵防空兵学院,合肥,230031
A multi⁃stage cutting plane method with inexact line search forsolving non⁃convex truncated L 1⁃SVMs
Youhong Yuan,Xin Liu,Lei Bao( )
)
- Army Academy of Artillery and Air Defense of PLA,Hefei,230031,China
摘要:
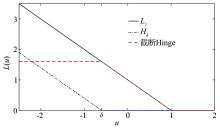
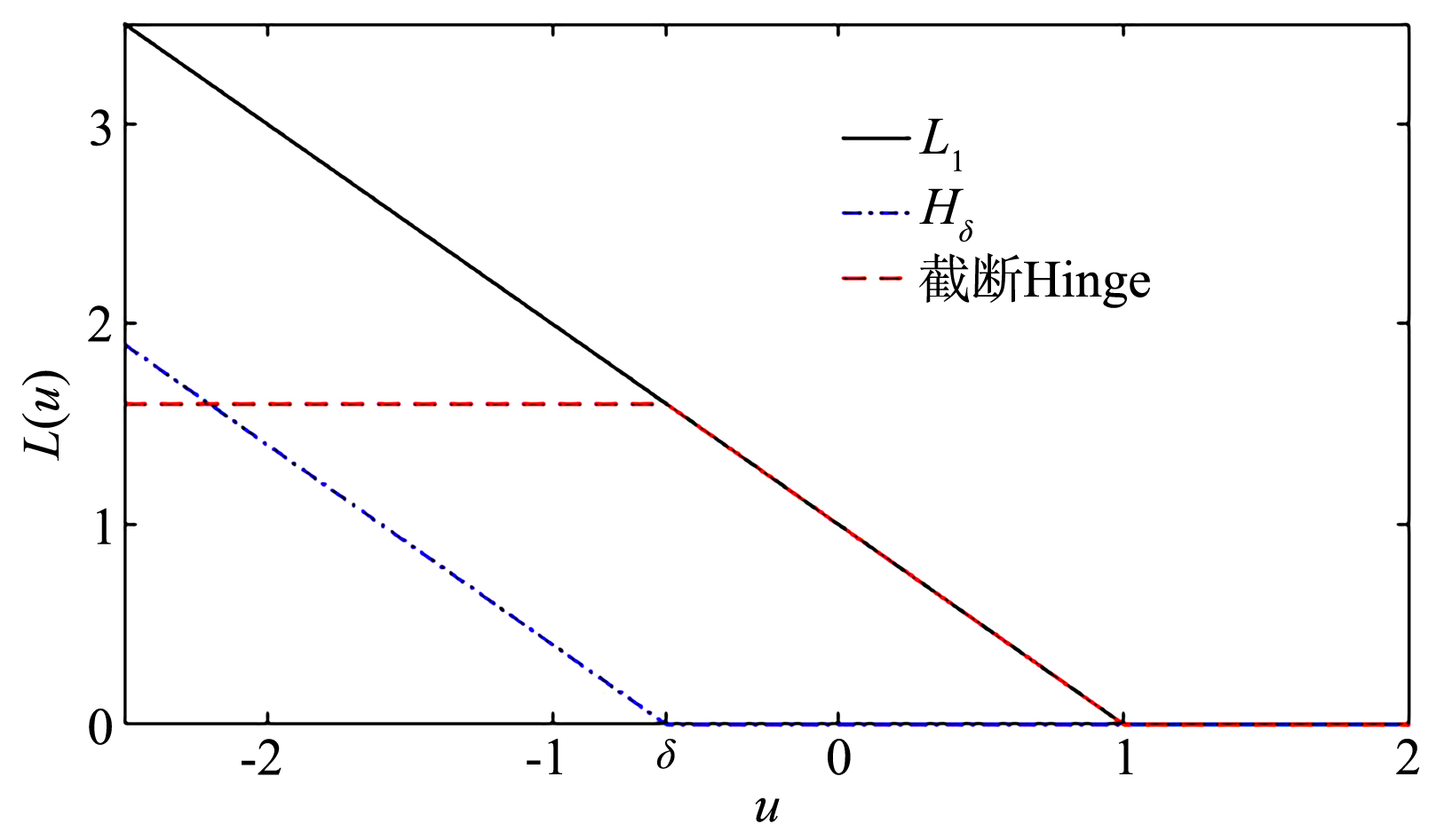
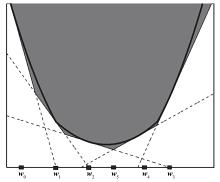
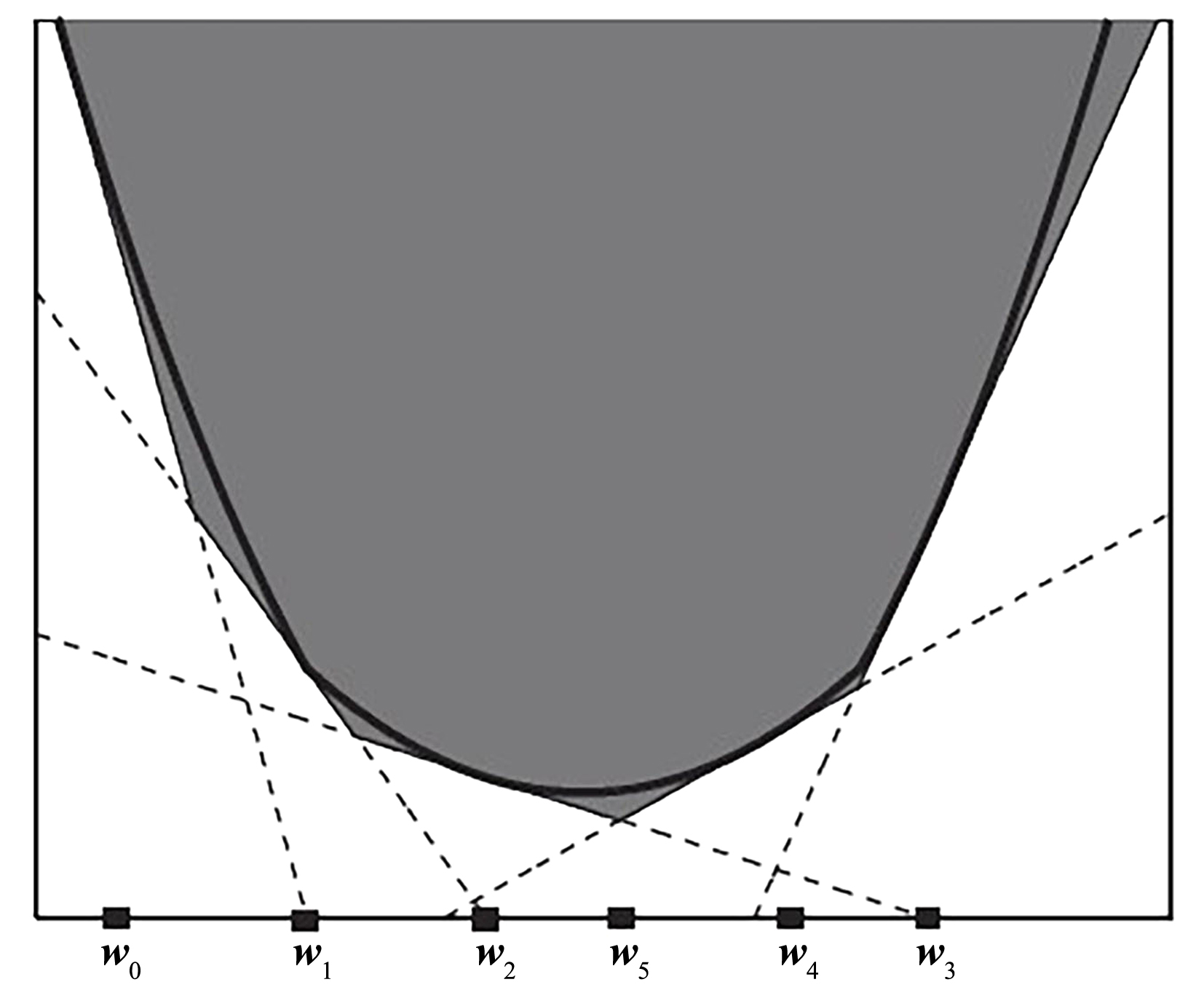
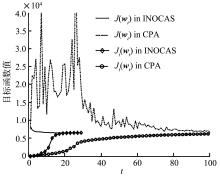
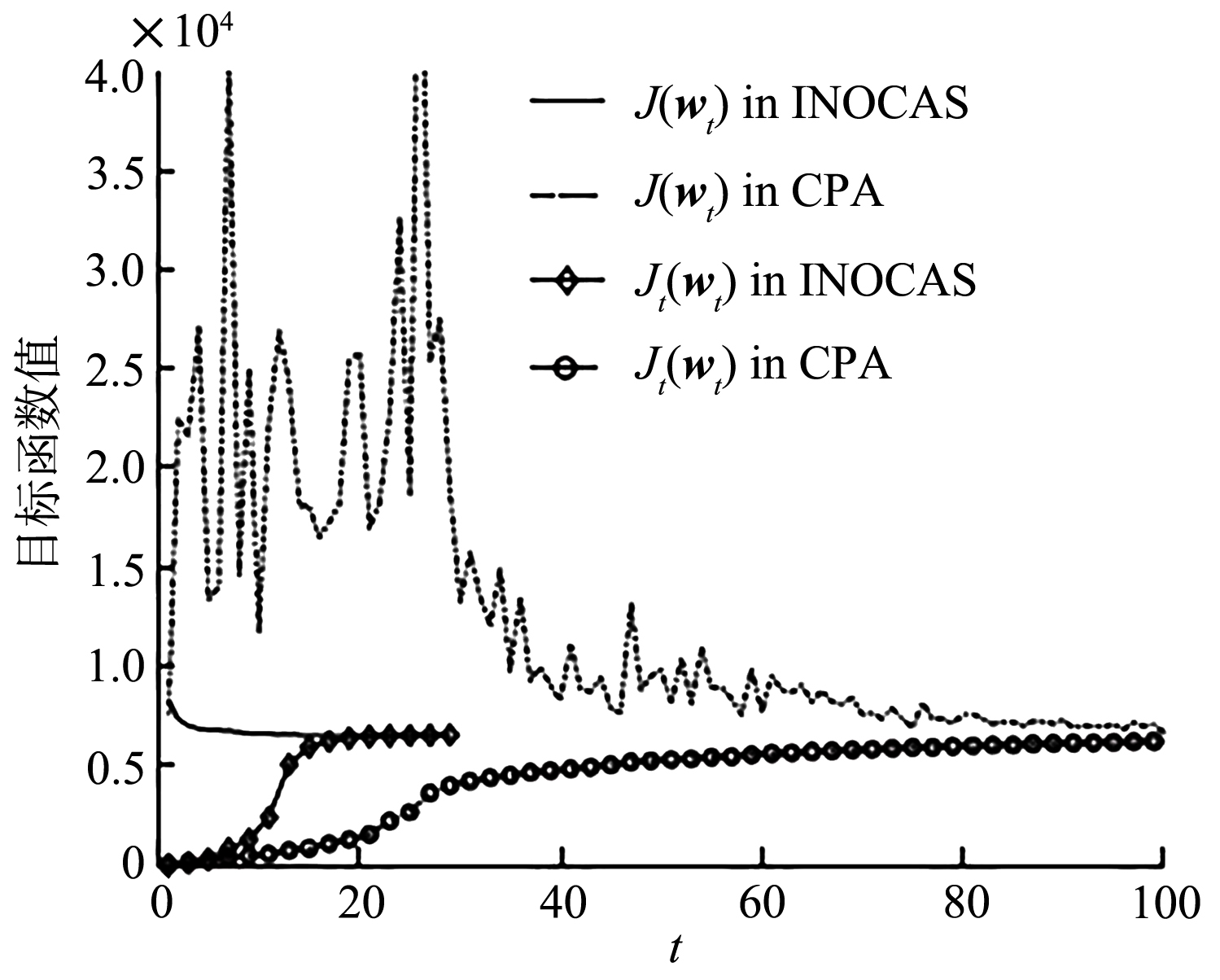
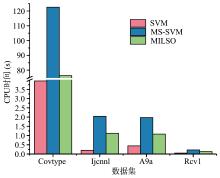
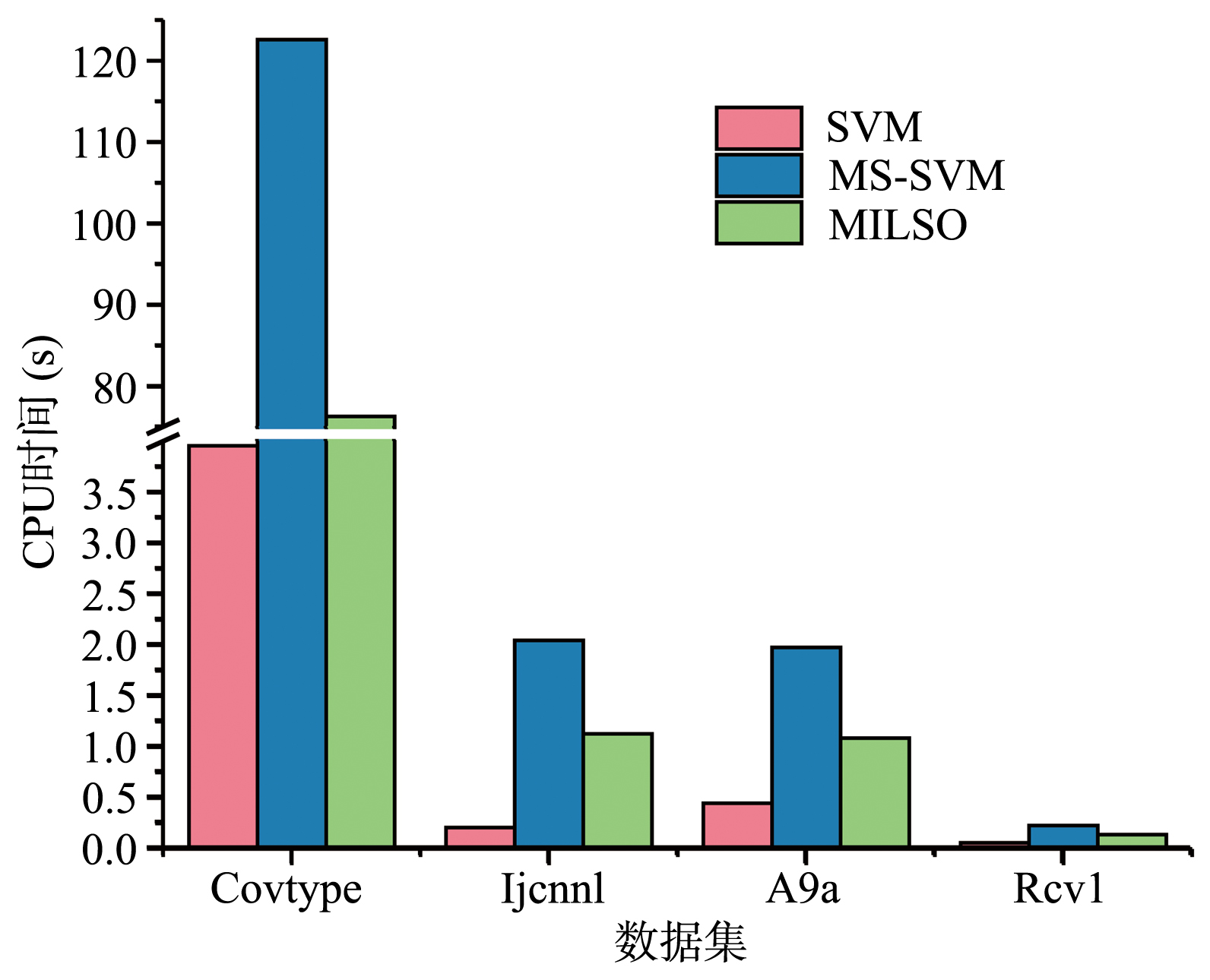
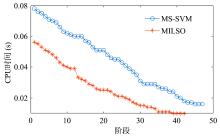
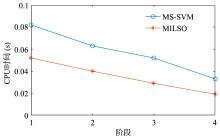
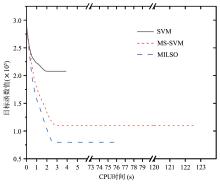
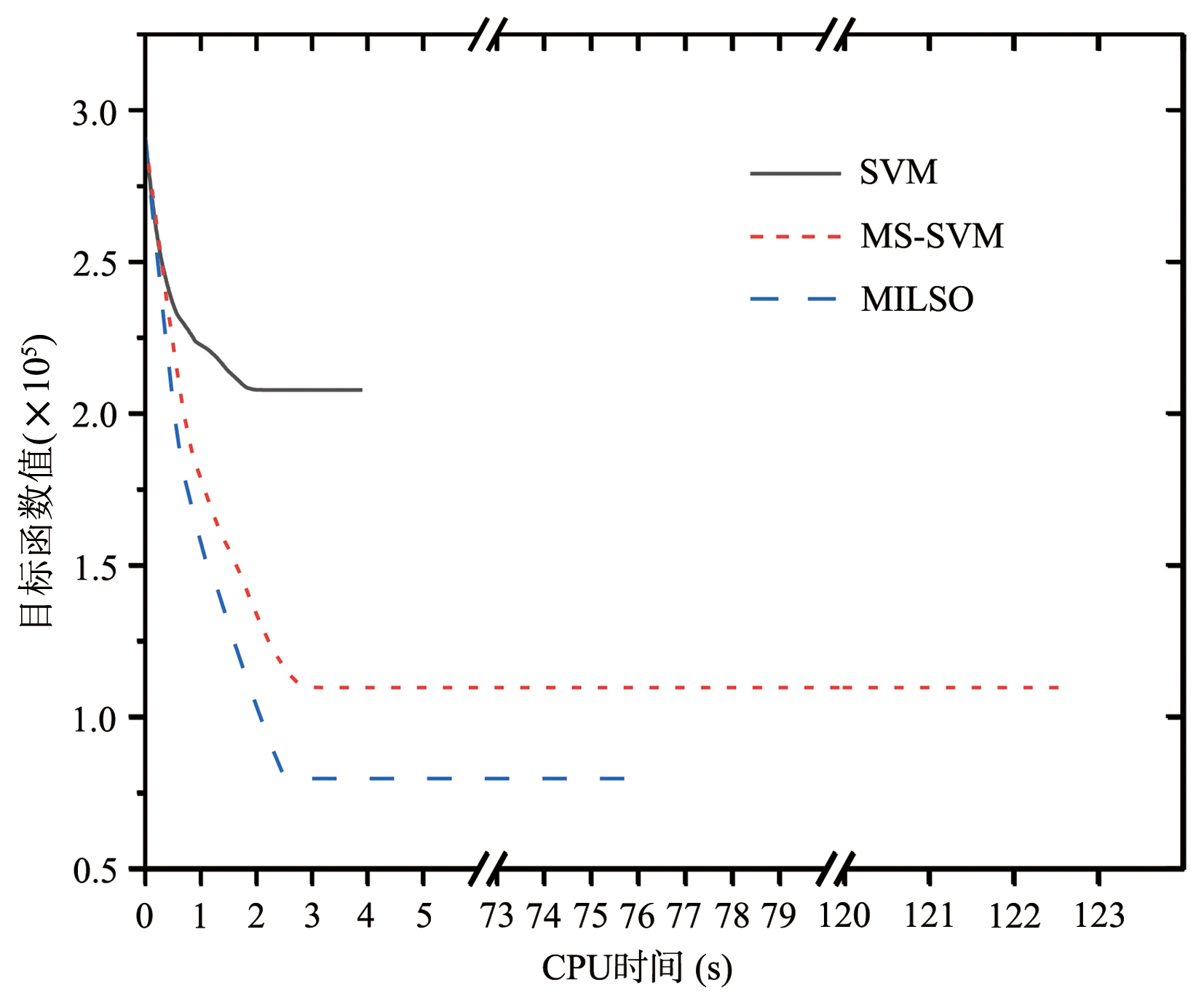
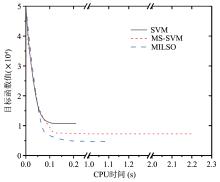
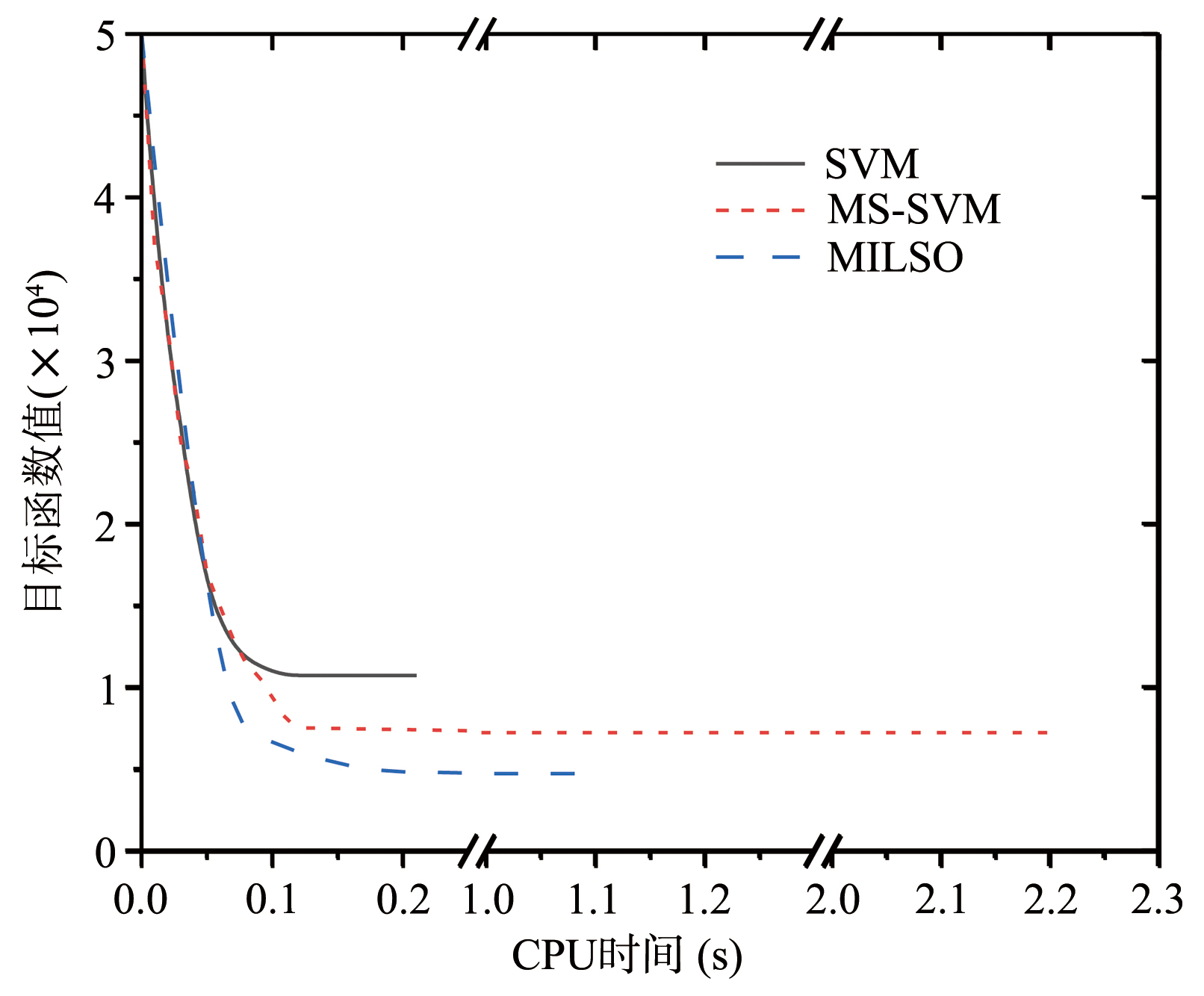
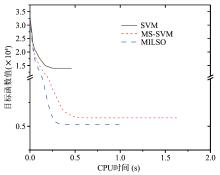
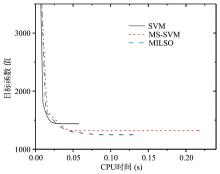
截断Hinge损失能够获得更为稀疏的支持向量,因此在鲁棒性上有显著的优点,但却由此导致了难以求解的非凸问题.MM(Majorization?Minimization)是一种求解非凸问题的一般框架,多阶段MM策略已经在稀疏性上取得了很好的效果,但是计算复杂度较高.另一方面,非精确线搜割平面方法可以高效求解线性支持向量机问题.针对截断L 1?SVM(L 1 Support Vector Machine)这一非凸非光滑问题,提出一种基于非精确线性搜索的多阶段割平面方法,避免每个阶段都进行批处理求解,克服了计算复杂度高的缺点,具有每个阶段求解速度快的优点.该算法适用于大规模问题的求解,也从理论上保证了其收敛性.最后,与其他多阶段算法进行了实验对比,验证了该方法的有效性.
中图分类号:
- TP301
| 1 | Vapnik V . The nature of statistical learning theory. New York:Springer,1995,314. |
| 2 | Kelley J E . The cutting plane method for solving convex problems. Journal of the Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics,1960,8(4):703-712. |
| 3 | Chang K W , Hsieh C J , Lin C J . Coordinate descent method for large?scale L2?loss linear support vector machines. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2008,9(3):1369-1398. |
| 4 | Hastie T , Zhu J . Comment on "Support vector machines with applications". Statistical Science,2006,21(3):352-357. |
| 5 | Zhang T . Statistical behavior and consistency of classification methods based on convex risk minimization. The Annals of Statistics,2004,32(1):56-85. |
| 6 | Cheung Y M , Lou J . Efficient generalized conditional gradient with gradient sliding for composite optimization∥Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Buenos Aires,Argentina:AAAI Press,2015:3409-3415. |
| 7 | Steinwart I . Sparseness of support vector machines. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2003,4(6):1071-1105. |
| 8 | Collobert R , Sinz F , Weston J ,et al . Trading convexity for scalability∥Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning. Pittsburgh,PA,USA:ACM,2006:201-208. |
| 9 | Liu S J , Shen X T , Wong W H . Computational developments of ψ?learning∥Proceedings of the 5th SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. Newport Beach,CA,USA:Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics,2005:1-11. |
| 10 | Wu Y C , Liu Y F . Robust truncated hinge loss support vector machines. Journal of the American Statistical Association,2007,102(479):974-983. |
| 11 | An L T H , Tao P D . Solving a class of linearly constrained indefinite quadratic problems by D.C. algorithms. Journal of Global Optimization,1997,11(3):253-285. |
| 12 | Yuille A L , Rangarajan A . The concave?convex procedure. Neural computation,2003,15(4):915-936. |
| 13 | Mairal J . Stochastic majorization?minimization algorithms for large?scale optimization∥Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe,NV,USA:Curran Associates Inc.,2013:2283-2291. |
| 14 | Mairal J . Incremental majorization?minimization optimization with application to large?scale machine learning. SIAM Journal on Optimization,2015,25(2):829-855. |
| 15 | Fang C , Li C J , Lin Z C ,et al . Spider:near?optimal non?convex optimization via stochastic path integrated differential estimator. 2018,arXiv:1807. 01695. |
| 16 | Carmon Y , Duchi J C , Hinder O ,et al . Accelerated methods for nonconvex optimization. SIAM Journal on Optimization,2018,28(2):1751-1772. |
| 17 | Lan G H , Yang Y . Accelerated stochastic algorithms for nonconvex finite?sum and multi?block optimi?zation. 2018,arXiv:1805.05411. |
| 18 | Tao Q , Wu G W , Chu D J . Improving sparsity and scalability in regularized nonconvex truncated?loss learning problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2018,29(7):2782-2793. |
| 19 | Shalev?Shwartz S , Singer Y , Srebro N ,et al . Pegasos:primal estimated sub?gradient solver for SVM. Mathematical Programming,2011,127(1):3-30. |
| 20 | Joachims T . Training linear SVMs in linear time∥Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Philadelphia,PA,USA:ACM,2006:217-226. |
| 21 | Teo C H , Smola A , Vishwanathan S V N ,et al . A scalable modular convex solver for regularized risk minimization∥Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Jose,CA,USA:ACM,2007:727-736. |
| 22 | Franc V , Sonnenburg S . Optimized cutting plane algorithm for support vector machines∥Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. Helsinki,Finland:ACM,2008:320-327. |
| 23 | Chu D J , Zhang C S , Tao Q . A faster cutting plane algorithm with accelerated line search for linear SVM. Pattern Recognition,2017,67:127-138. |
| 24 | 储德军,陶安,高乾坤 等 . 求解线性SVM的非精确步长搜索割平面方法. 模式识别与人工智能,2014,27(8):692-700. |
| Chu D J , Tao A , Gao Q K ,et al . Optimized cutting plane method for linear SVM via inexact step?length search. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence,2014,27(8):692-700. | |
| 25 | Langford J , Li L H , Zhang T . Sparse online learning via truncated gradient. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2009,10:777-801. |
| 26 | Duchi J C , Shalev?Shwartz S , Singer Y ,et al . Composite objective mirror descent∥23rd International Conference on Learning Theory. Haifa,Israel:COLT,2010:14-26. |
| 27 | Xiao L . Dual averaging methods for regularized stochastic learning and online optimization. The Journal of Machine Learning Research,2010,11:2543-2596. |
| 28 | Zhang T . Analysis of multi?stage convex relaxation for sparse regularization. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2010,11:1081-1107. |
| [1] | 李亚重,杨有龙,仇海全. 一种基于嵌入式的弱标记分类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 549-560. |
| [2] | 王丽娟,丁世飞,丁玲. 基于迁移学习的软子空间聚类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 515-523. |
| [3] | 李俊余, 李星璇, 王霞, 吴伟志. 基于三元因子分析的三元概念约简[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 480-493. |
| [4] | 李子龙,周勇,鲍蓉. AdaBoost图像到类距离学习的图像分类方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [5] | 刘亮,何庆. 基于改进蝗虫优化算法的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 41-50. |
| [6] | 袁燕,陈伯伦,朱国畅,花勇,于永涛. 基于社区划分的空气质量指数(AQI)预测算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 142-150. |
| [7] | 何昕,徐珺平,赵登吉. 基于社交网络的分布式机制设计[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 107-115. |
| [8] | 王霞, 谭斯文, 李俊余, 吴伟志. 基于条件属性蕴含的概念格构造及简化[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 553-563. |
| [9] | 王博闻, 史江峰, 史逝远, 张伟杰, 马晓琦, 赵业思. 基于遥感数据定位老龄树群[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 699-707. |
| [10] | 陈晓冬, 底晓强, 李锦青. 基于多混沌和分数Fourier的光学图像加密算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(2): 251-263. |
| [11] | 洪思思,曹辰捷,王 喆*,李冬冬. 基于矩阵的AdaBoost多视角学习[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1152-1160. |
| [12] | 周星星,张海平,吉根林. 具有时空特性的区域移动模式挖掘算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1171-1182. |
|