南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 984–999.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2019.06.011
一种基于相对熵的随机游走相似性度量模型
- 1. 山西大学计算机与信息技术学院,太原,030006
2. 计算智能与中文信息处理教育部重点实验室,山西大学,太原,030006
3. 山西大学大数据科学与产业研究院,太原,030006
A random walk similarity measure model based on relative entropy
Wenping Zheng1,2,3( ),Shaoqian Liu1,2,3,Junfang Mu1,2,3
),Shaoqian Liu1,2,3,Junfang Mu1,2,3
- 1. School of Computer and Information Technology,Shanxi University,Taiyuan,030006,China
2. Key Laboratory of Computation Intelligence and Chinese Information Processing,Ministry of Education,Shanxi University,Taiyuan,030006,China
3. Research Institute of Big Data Science and Industry,Shanxi University,Taiyuan,030006,China
摘要:
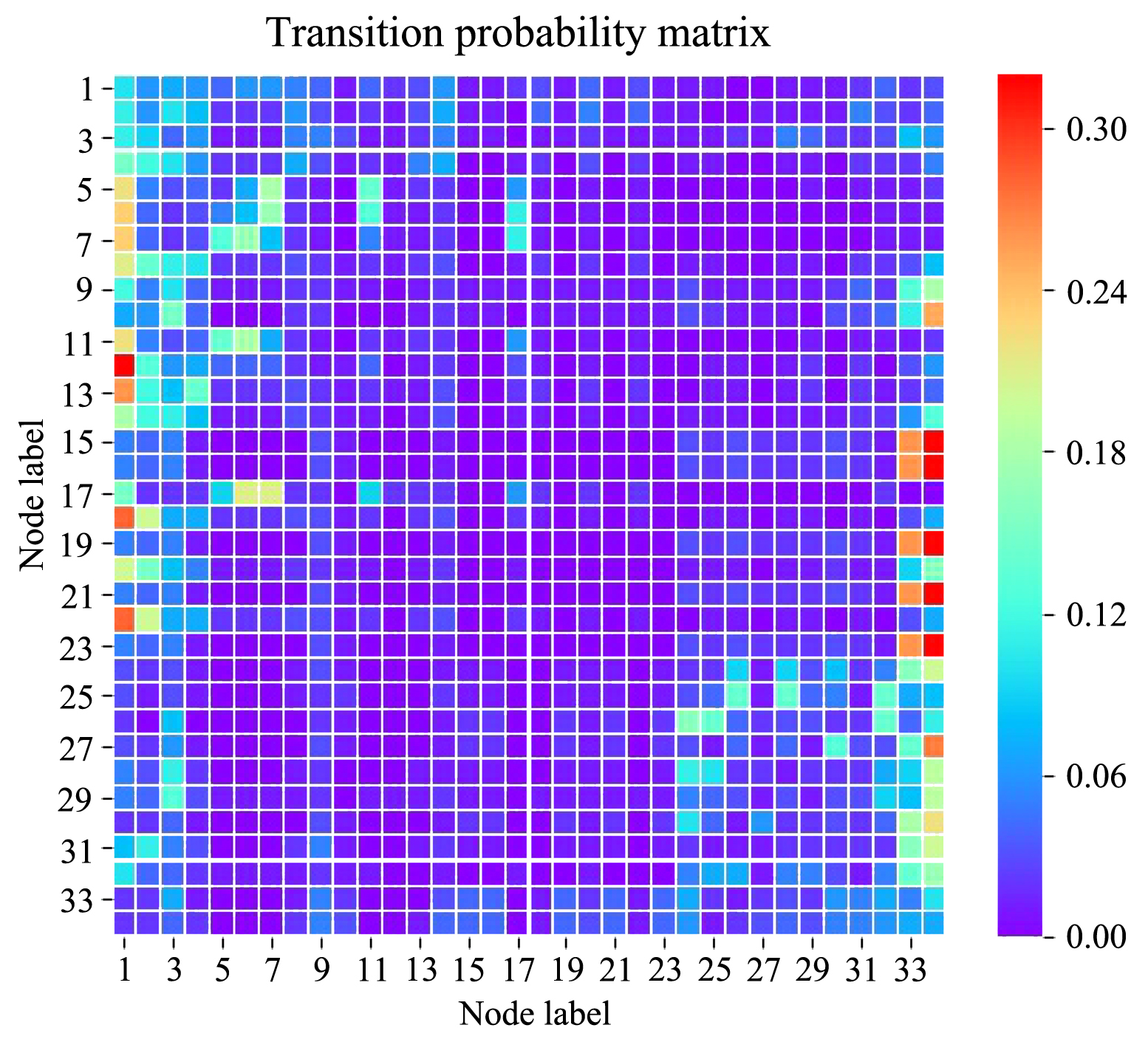
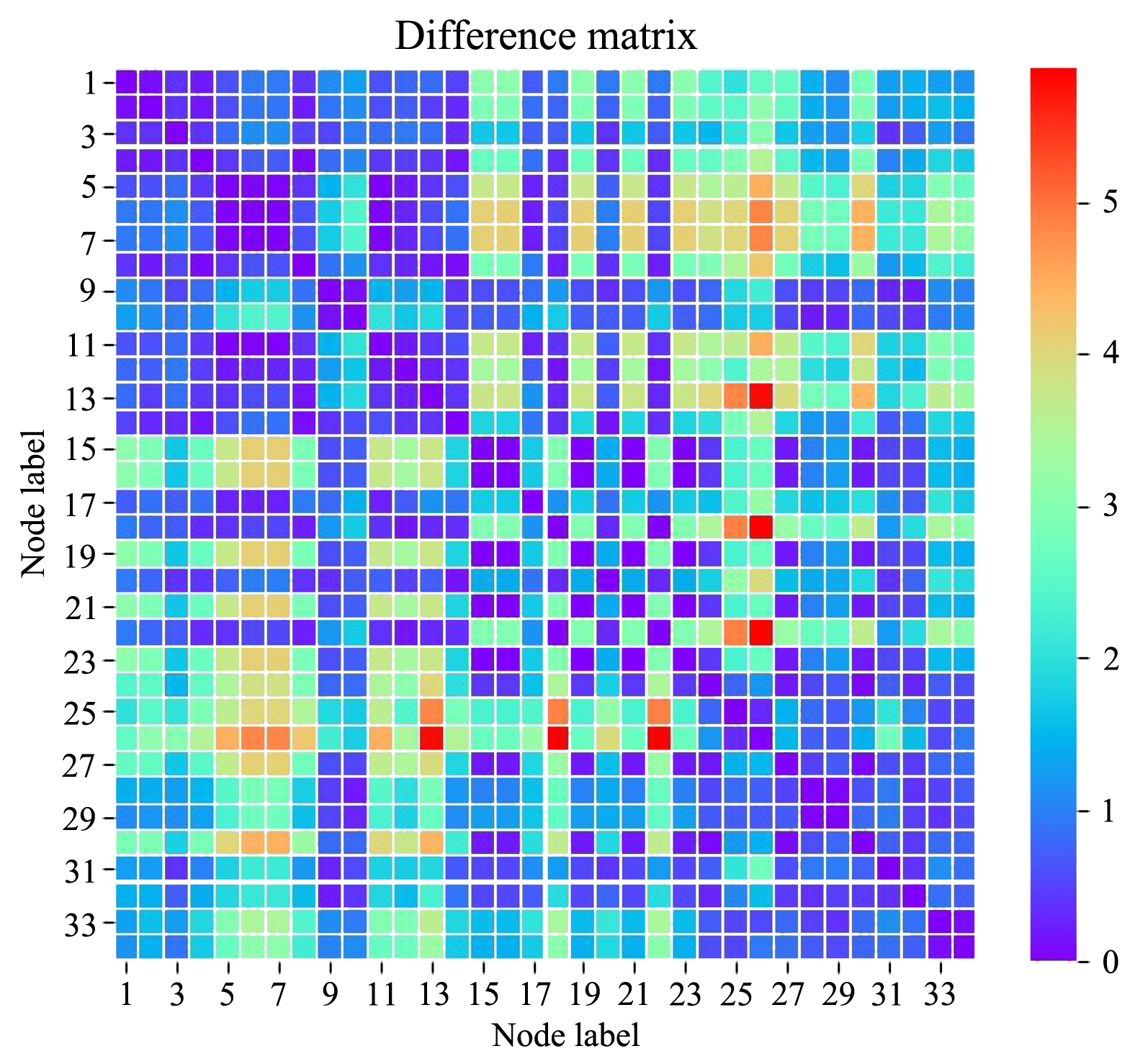
针对基于随机游走的节点相似性度量模型中存在的大度节点依赖问题,从信息论的角度提出了一种改进的随机游走节点相似性度量
基于相对熵的随机游走相似性度量方法RE?model (A random walk similarity measure model based on Relative Entropy).首先根据随机游走模型得到网络中节点的转移概率向量,再计算两个节点转移概率向量的相对熵得到该节点对的相似性.由于转移概率向量给出了从一个特定节点出发经过多步随机游走后到达网络其他所有节点的概率,导致网络中的每个节点在计算相对熵的过程中都被等同看待,并且网络规模的增大会使计算得到的节点间相似性耗时更多且存在较大偏差.根据节点经过多步随机游走后到达网络中影响力较大的节点的转移概率来构造该节点的转移概率分布,计算两个节点的转移概率分布的相对熵以得到网络中节点对之间的差异分数,进而得到网络节点间的相似性矩阵.RE?model度量方法降低了传统随机游走相似性度量对于大度节点的依赖性.通过在真实网络数据集上的实验表明,RE?model算法在对称性、网络传播及社区发现等方面表现良好.
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | Zhu X Y , Yang X M , Ying C Z ,et al . A new classification algorithm recommendation method based on link prediction. Knowledge?Based Systems,2018,159:171-185. |
| 2 | Zhang J P , Ding X Y , Yang J . Revealing the role of node similarity and community merging in community detection. Knowledge?Based Systems,2019,165:407-419 |
| 3 | Ding J Y , Jiao L C , Wu J S ,et al . Prediction of missing links based on community relevance and ruler inference. Knowledge?Based Systems,2016,98:200-215. |
| 4 | Wang Z Q , Liang J Y , Li R . A fusion probability matrix factorization framework for link prediction. Knowledge?Based Systems,2018,159:72-85. |
| 5 | Bastami E , Mahabadi A , Taghizadeh E . A gravitation?based link prediction approach in social networks. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation,2019,44:176-186. |
| 6 | 汪小帆,李翔,陈关荣 . 网络科学导论. 北京:高等教育出版社,2012,397. |
| Wang X F , Li X , Chen G R . Network science:an introduction. Beijing:Higher Education Press,2012,397. | |
| 7 | Newman M E J . 网络科学引论. 郭世泽,陈哲译. 北京:电子工业出版社,2014,496. |
| 8 | Jaccard P . étude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et du Jura. Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles,1901,37(142):547-579. |
| 9 | Salton G , Mcgill M J . Introduction to modern information retrieval. New York:Mcgraw?Hill Book Co.,1983,120-127. |
| 10 | Katz L . A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika,1953,18(1):39-43. |
| 11 | Lü L Y , Zhou T . Link prediction in complex networks:a survey. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,2011,390(6):1150-1170. |
| 12 | Martínez V , Berzal F , Cubero J C . A survey of link prediction in complex networks. ACM Computing Surveys,2016,49(4):69. |
| 13 | Pearson K . The problem of the random walk. Nature,1905,72(1865):294. |
| 14 | Zhou H J , Lipowsky R . Network Brownian motion:a new method to measure vertex?vertex proximity and to identify communities and subcommunities∥The 4th international conference on computational science. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2004:1062-1069. |
| 15 | Javed M A , Younis M S , Latif S ,et al . Community detection in networks:A multidisciplinary review. Journal of Network and Computer Applications,2018,108:87-111. |
| 16 | Tong H H , Faloutsos C , Pan J Y . Fast random walk with restart and its applications∥The 6th international conference on data mining. Hong Kong,China:IEEE,2006:613-622. |
| 17 | Burda Z , Duda J , Luck J M ,et al . Localization of the maximal entropy random walk. Physical Review Letters,2012,102(16):160602. |
| 18 | Liu W P , Lü L Y . Link prediction based on local random walk. Europhysics Letters,2010,89(5):58007. |
| 19 | Tan F , Xia Y X , Zhu B Y . Link prediction in complex networks:a mutual information perspective. PLOS One,2014,9(9):e107056. |
| 20 | Zhang Q , Li M Z , Deng Y . Measure the structure similarity of nodes in complex networks based on relative entropy. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,2018,491:749-763. |
| 21 | George M , Jafarpour S , Bullo F . Markov chains with maximum entropy for robotic surveillance. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2019,64(4):1566-1580. |
| 22 | Kullback S , Leibler R A . On information and sufficiency. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1951,22(1):79-86. |
| 23 | Albert R , Jeong H , Barabási A L . Diameter of the world?wide web. Nature,1999,401(6):130-131. |
| 24 | Newman M E . Spread of epidemic disease on networks. Physical Review E,2002,66(1):016128. |
| 25 | Danon L , Díaz?Guilera A , Duch J ,et al . Comparing community structure identification. Journal of Statistical Mechanics:Theory and Experiment,2005,2005(9):09008. |
| 26 | Rand W M . Objective criteria for the evaluation of clustering methods. Journal of the American Statistical Association,1971,66(336):846-850. |
| 27 | Newman M E J , Girvan M . Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Physical Review E,2004,69(2):026113. |
| 28 | Pons P , Latapy M . Computing communities in large networks using random walks. Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applications,2006,10(2):191-218. |
| [1] | 刘胜久,李天瑞,珠杰,刘佳. 带权图的多重分形研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 85-97. |
| [2] | 马娜, 范敏, 李金海. 复杂网络下的概念认知学习[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 609-623. |
| [3] | 钱付兰, 黄鑫, 赵姝, 张燕平. 基于路径相互关注的网络嵌入算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 573-580. |
| [4] | 钱 峰1,2,张 蕾1,2,赵 姝1*,陈 洁1,张燕平1. 基于加权树的层次社团划分算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 696-. |
| [5] | 朱 尧, 朱启海, 毛晓蛟, 杨育彬. 基于有监督显著性检测的目标跟踪[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 747-. |
| [6] | 张泽华1*,段力畑1,段 富1,张 楠2. 基于局部结构特征的重叠社区挖掘研究进展[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(3): 537-. |
| [7] | 宾 晟*,孙更新. 基于多子网复合复杂网络模型的多关系社交网络重要节点发现算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(2): 378-. |
| [8] | 梁晋1,2,梁吉业1,2*,赵兴旺1,2. 一种面向大规模社会网络的社区发现算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(1): 159-166. |
| [9] | 曹江中1*,陈 佩2,戴青云3,凌永权1. 基于Markov随机游走的谱聚类相似图构造方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(4): 772-780. |
| [10] | 施静静,张鹏,阮雅端,陈启美*. 多媒体信息网络相似度计算方法研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 290-296. |
| [11] | 张燕平1,2,汪 洋1,2,赵 姝1,2, 段 震1,2**. 基于覆盖的社团发现算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(5): 539-545. |
|