南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 60–70.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.01.007
基于多粒度一致性邻域的多标记特征选择
卢舜1,2, 林耀进1,2( ), 吴镒潾1,2, 包丰浩1,2, 王晨曦1,2
), 吴镒潾1,2, 包丰浩1,2, 王晨曦1,2
- 1.闽南师范大学计算机学院, 漳州, 363000
2.福建省数据科学与智能应用高校重点实验室, 闽南师范大学, 漳州, 363000
Multi⁃label feature selection based on multi⁃granularity consistent neighborhood
Shun Lu1,2, Yaojin Lin1,2( ), Yilin Wu1,2, Fenghao Bao1,2, Chenxi Wang1,2
), Yilin Wu1,2, Fenghao Bao1,2, Chenxi Wang1,2
- 1.School of Computer Science,Minnan Normal University,Zhangzhou,363000,China
2.Key Laboratory of Data Science and Intelligence Application,Minnan Normal University,Zhangzhou,363000,China
摘要:
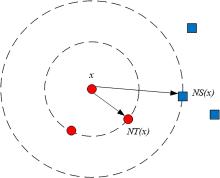
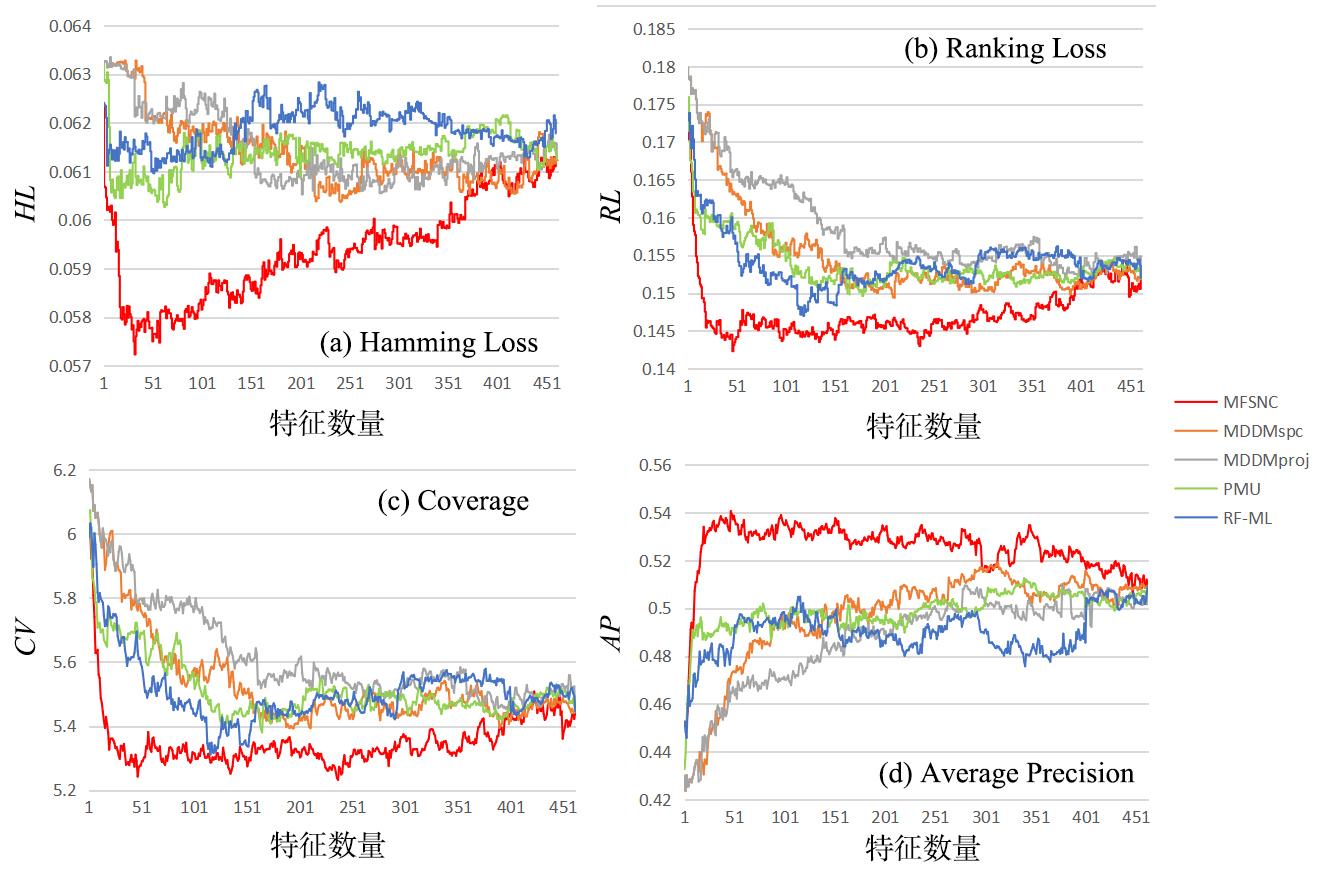
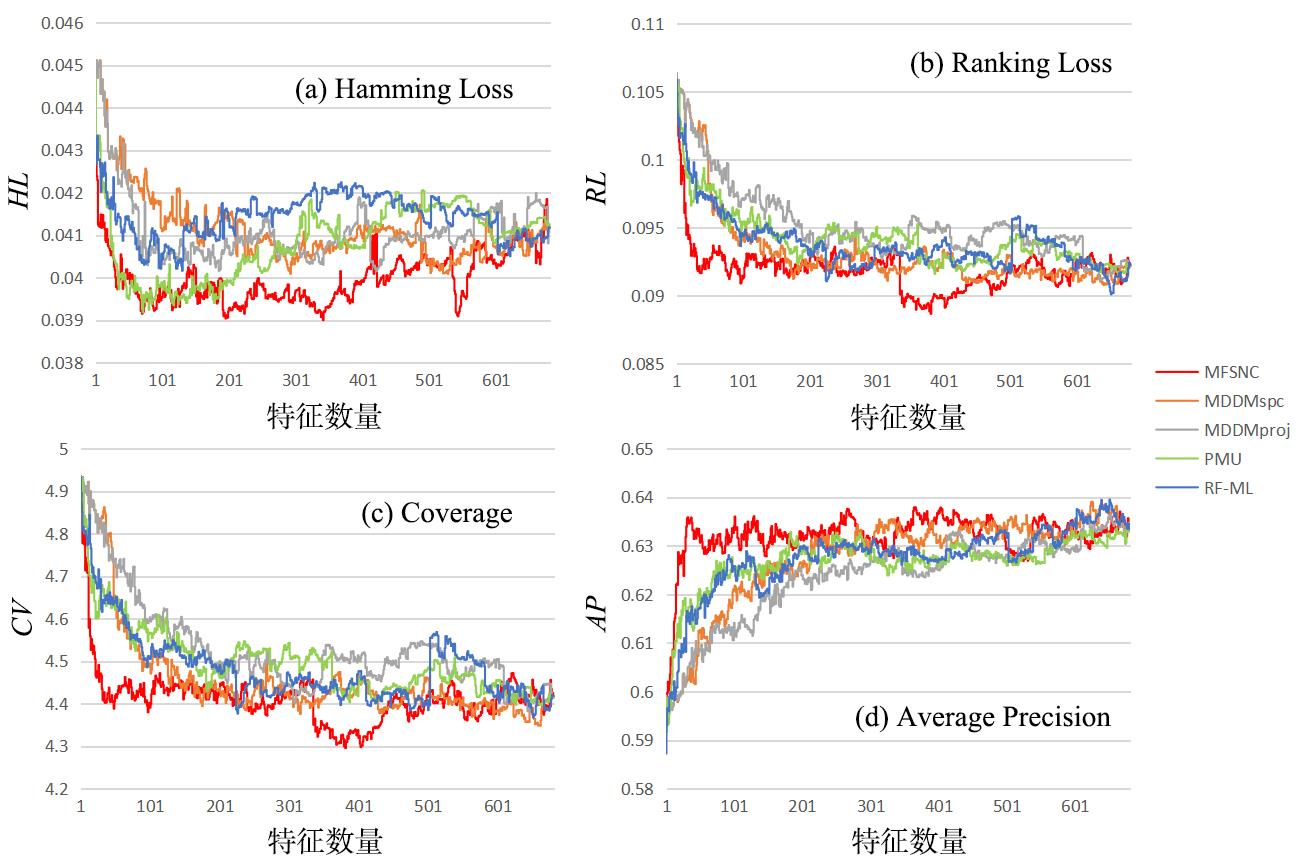
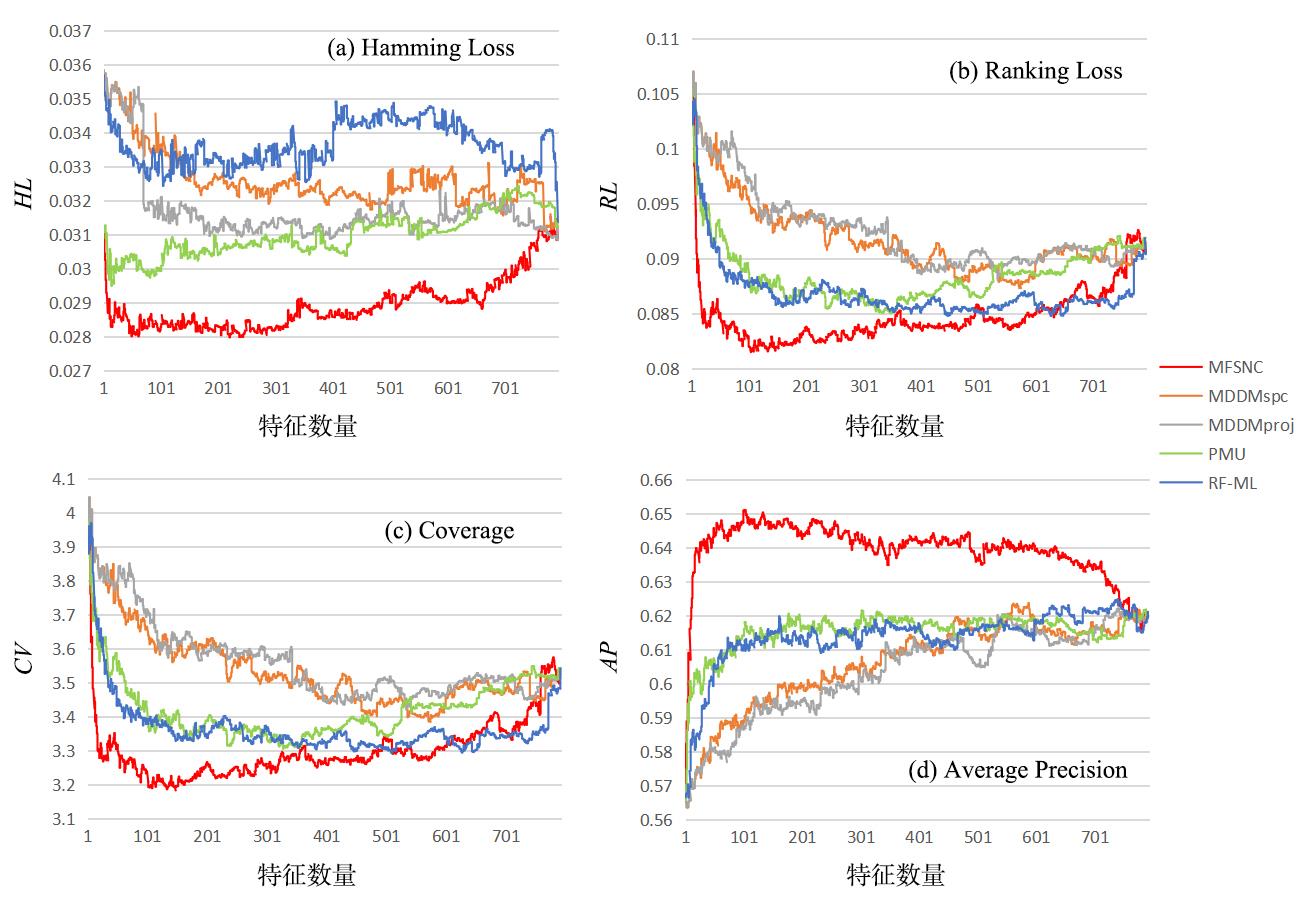
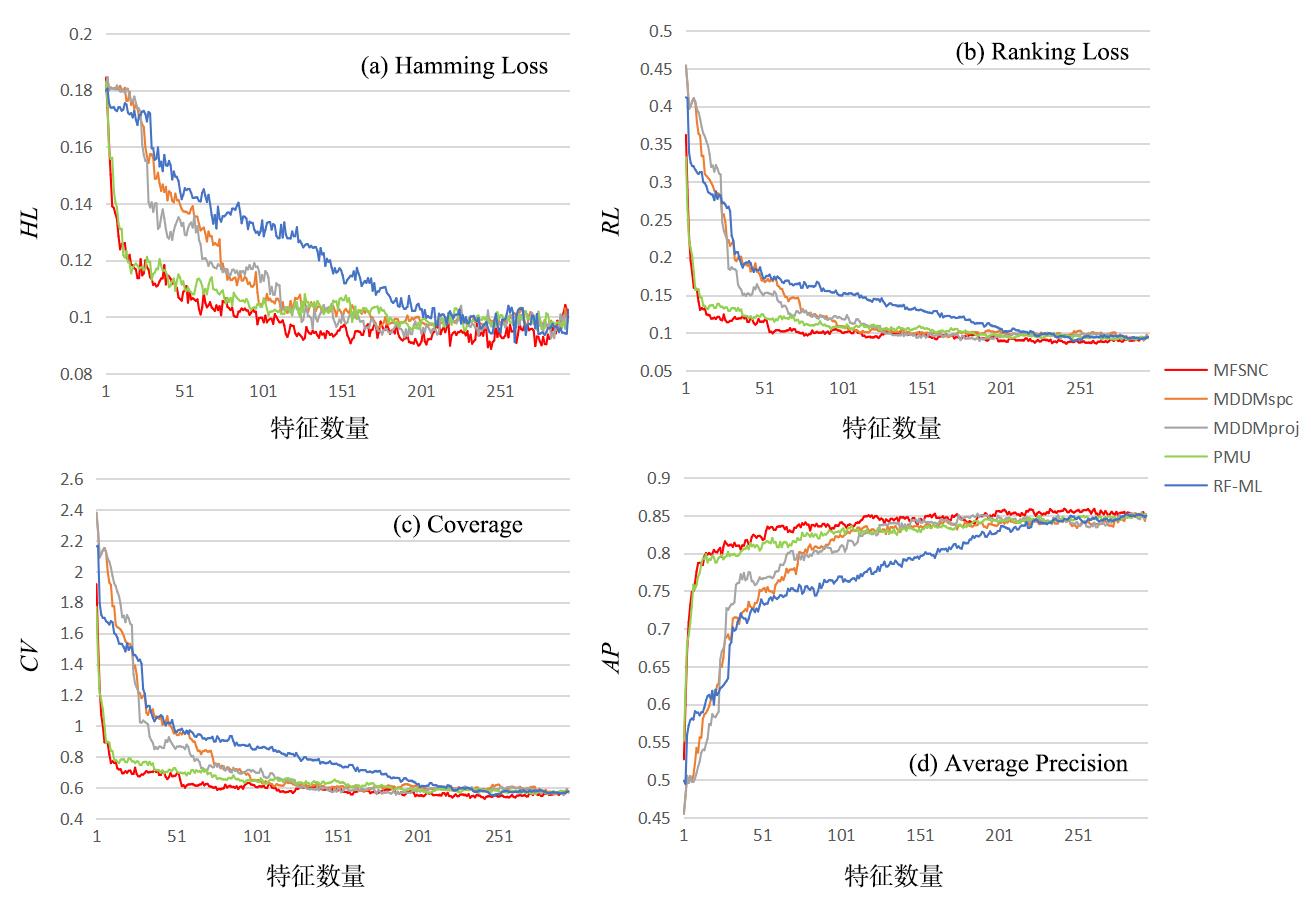
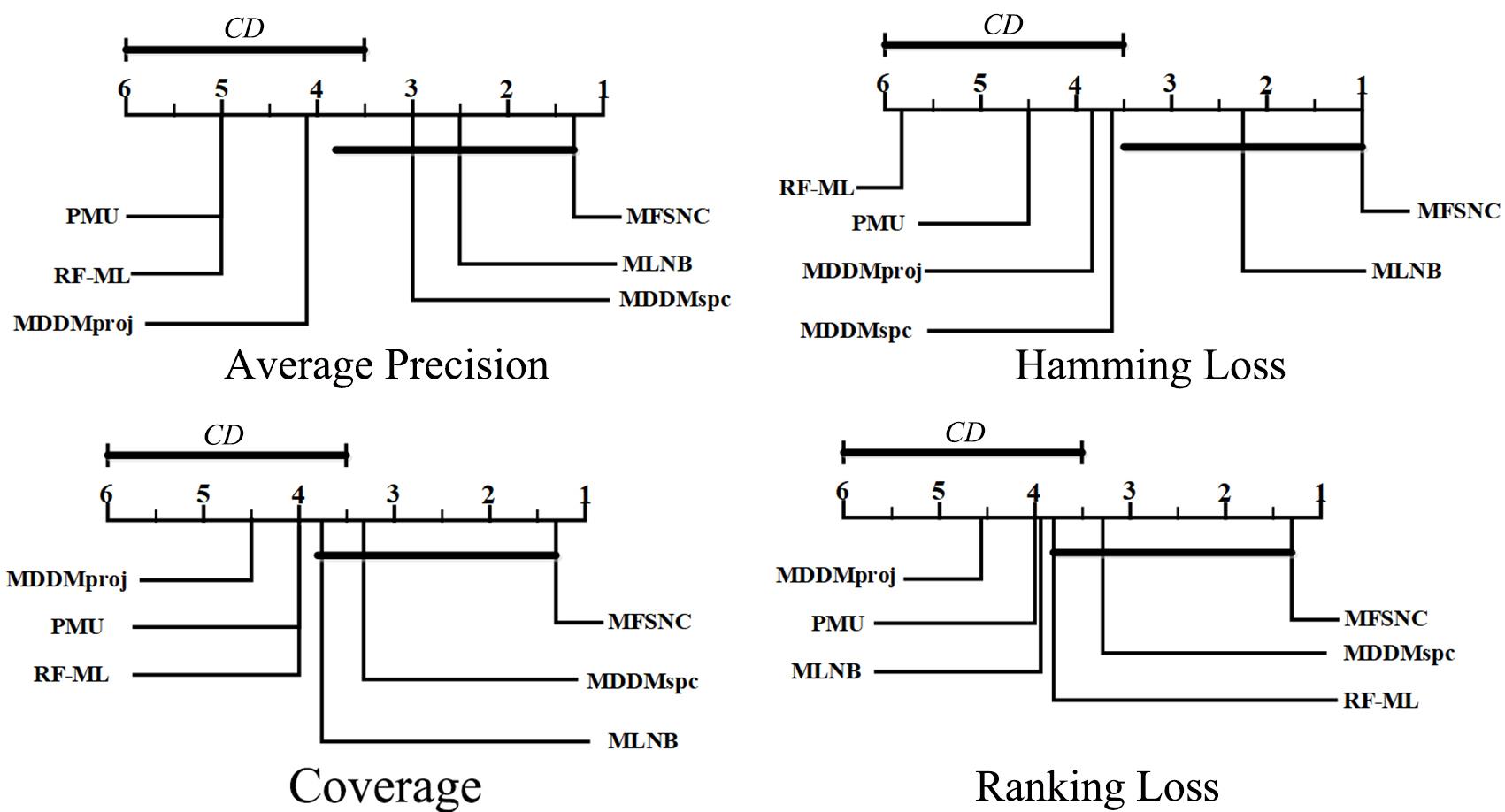
多标记学习广泛应用于图像分类、疾病诊断等领域,然而特征的高维性给多标记分类算法带来时间负担、过拟合和性能低等问题.基于多粒度邻域一致性设计相应的多标记特征选择算法:首先利用标记空间和特征空间邻域一致性来粒化所有样本,并基于多粒度邻域一致性观点定义新的多标记邻域信息熵和多标记邻域互信息;其次,基于邻域互信息构建一个评价候选特征质量的目标函数用于评价每个特征的重要性;最后通过多个指标验证了所提算法的有效性.
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | Boutell M R,Luo J B,Shen X P,et al. Learning multi?label scene classification. Pattern Recognition,2004,37(9):1757-1771. |
| 2 | Zhang P,Liu G X,Gao W F. Distinguishing two types of labels for multi?label feature selection. Pattern Recognition,2019(95):72-82. |
| 3 | Wold H. Estimation of principal components and related models by iterative least squares∥Krishnajah P R. Multivariate analysis. New York:Academic Press,1966:391-420. |
| 4 | Hotelling H. Relations between two sets of variates∥Kotz S,Johnson N L. Breakthroughs in statistics. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1992:162-190. |
| 5 | Fukunaga K. Introduction to statistical pattern recognition. The 2nd Edition. New York:Academic Press,1990,592. |
| 6 | Gharroudi O,Elghazel H,Aussem A. A comparison of multi?label feature selection methods using the random forest paradigm∥Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2014:95-106. |
| 7 | Gu Q Q,Li Z H,Han J W. Correlated multi?label feature selection∥Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. New York,NY,USA:ACM,2011:1087-1096. |
| 8 | Slavkov I,Karcheska J,Kocev D,et al. Relieff for hierarchical multi?label classification∥Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on New Frontiers in Mining Complex Patterns. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2013:148-161. |
| 9 | Zhang L J,Hu Q H,Duan J,et al. Multi?label feature selection with fuzzy rough sets∥Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2014:121-128. |
| 10 | Ding C,Peng H C. Minimum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology,2005,3(2):185-205. |
| 11 | Lee J,Kim D W. Mutual information?based multi?label feature selection using interaction information. Expert Systems with Applications,2015,42(4):2013-2025. |
| 12 | Li Y W,Lin Y J,Liu J H,et al. Feature selection for multi?label learning based on kernelized fuzzy rough sets. Neurocomputing,2018(318):271-286. |
| 13 | Lin Y J,Hu Q H,Liu J H,et al. Multi?label feature selection based on neighborhood mutual information. Applied Soft Computing,2016(38):244-256. |
| 14 | Zhang M L,Pe?a J M,Robles V. Feature selection for multi?label naive bayes classification. Information Sciences,2009,179(19):3218-3229. |
| 15 | Zhang Y,Zhou Z H. Multilabel dimensionality reduction via dependence maximization. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data,2010,4(3):1-21. |
| 16 | Lee J,Kim D W. Feature selection for multi?label classification using multivariate mutual information. Pattern Recognition Letters,2013,34(3):349-357. |
| 17 | Spola?r N,Cherman E A,Monard M C,et al. ReliefF for multi?label feature selection∥2013 Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems. Fortaleza,Brazil:IEEE,2013:6-11. |
| 18 | Friedman M. A comparison of alternative tests of significance for the problem of m rankings. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1940,11(1):86-92. |
| 19 | Dunn O J. Multiple comparisons among means. Journal of the American statistical Association,1961,56(293):52-64. |
| [1] | 李苓玉, 刘治平. 基于机器学习的自发性早产生物标记物发现[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(5): 767-774. |
| [2] | 刘琼, 代建华, 陈姣龙. 区间值数据的代价敏感特征选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 121-129. |
| [3] | 郑文彬, 李进金, 张燕兰, 廖淑娇. 基于矩阵的多粒度粗糙集粒度约简方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 141-149. |
| [4] | 李佳佳, 丁伟, 王伯伟, 聂秀山, 崔超然. 基于随机森林的民俗体育对身体指标影响评估方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 59-67. |
| [5] | 任睿,张超,庞继芳. 有限理性下多粒度q⁃RO模糊粗糙集的最优粒度选择及其在并购对象选择中的应用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 452-460. |
| [6] | 程玉胜,陈飞,庞淑芳. 标记倾向性的粗糙互信息k特征核选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 19-29. |
| [7] | 陈超逸,林耀进,唐莉,王晨曦. 基于邻域交互增益信息的多标记流特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 30-40. |
| [8] | 刘亮,何庆. 基于改进蝗虫优化算法的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 41-50. |
| [9] | 刘 素, 刘惊雷. 基于特征选择的CP-nets结构学习[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 14-28. |
| [10] | 陈海娟,冯 翔,虞慧群. 基于预测算子的GSO特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1206-1215. |
| [11] | 陈琳琳1*,陈德刚2. 一种基于核对齐的分类器链的多标记学习算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 725-. |
| [12] | 温 欣1,李德玉1,2*,王素格1,2. 一种基于邻域关系和模糊决策的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 733-. |
| [13] | 靳义林1,2*,胡 峰1,2. 基于三支决策的中文文本分类算法研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 794-. |
| [14] | 王一宾1,2,程玉胜1,2*,裴根生1. 结合均值漂移的多示例多标记学习改进算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(2): 422-. |
| [15] | 董利梅,赵 红*,杨文元. 基于稀疏聚类的无监督特征选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(1): 107-. |
|
||