南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 19–29.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.01.003
标记倾向性的粗糙互信息k特征核选择
- 1. 安庆师范大学计算机与信息学院,安庆,246011
2. 安徽省高校智能感知与计算重点实验室,安庆,246011
k⁃Kernel feature selection of tendentious labels based on rough mutual information
Yusheng Cheng1,2( ),Fei Chen1,Shufang Pang1
),Fei Chen1,Shufang Pang1
- 1. School of Computer and Information,Anqing Normal University,Anqing,246011,China
2. The University Key Laboratory of Intelligent Perception and Computing of Anhui Province,Anqing,246011,China
摘要:
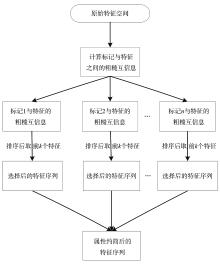
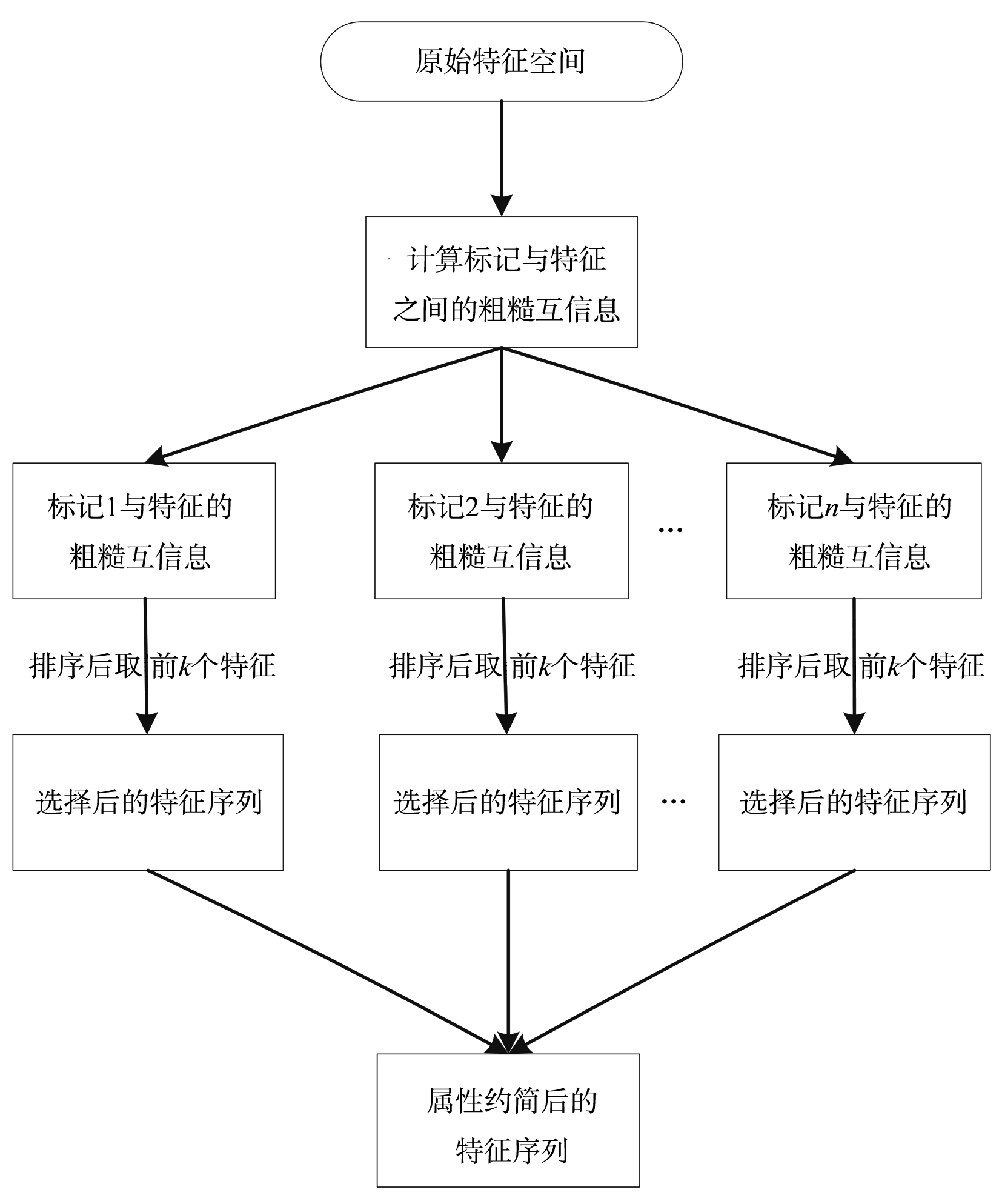
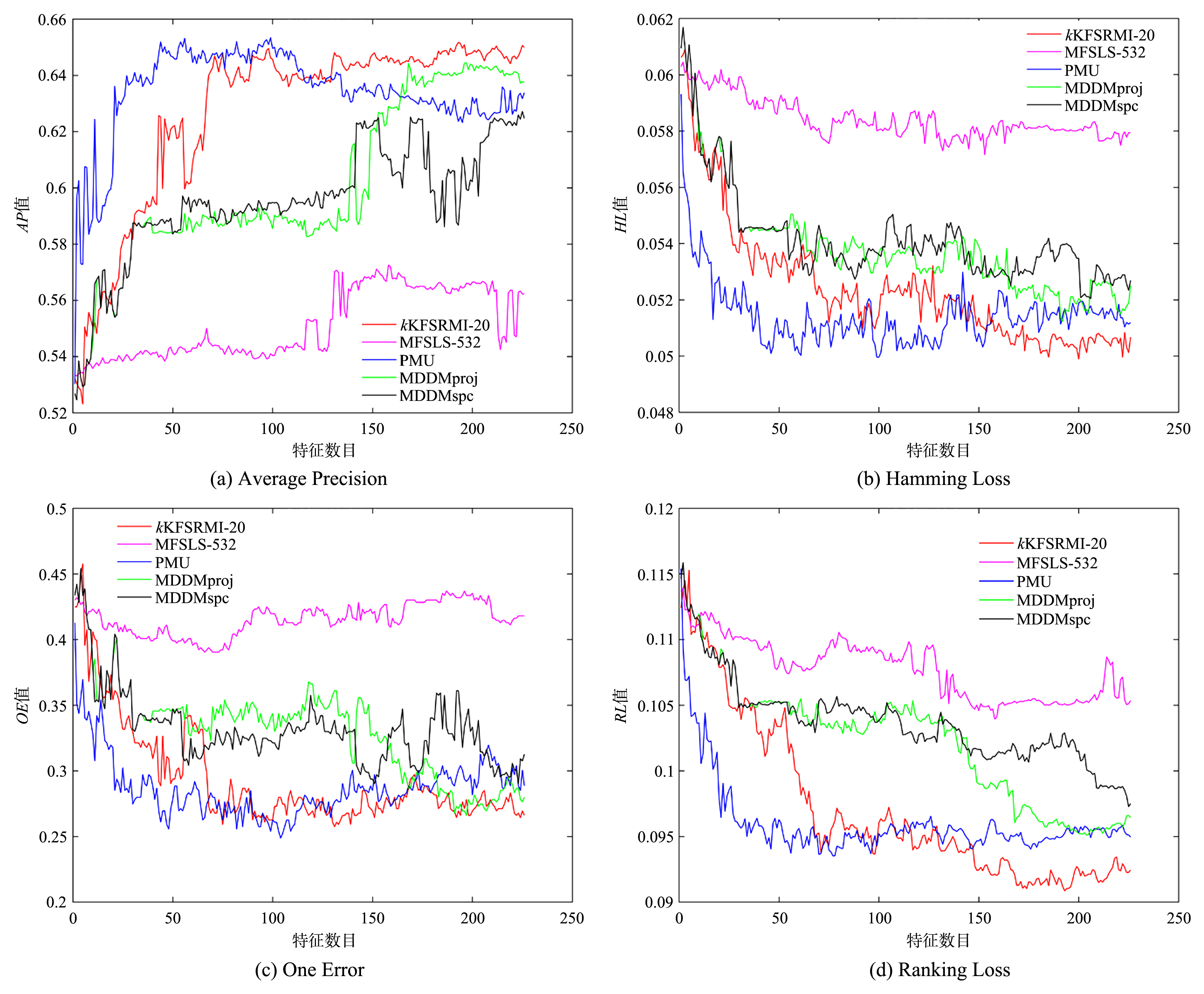
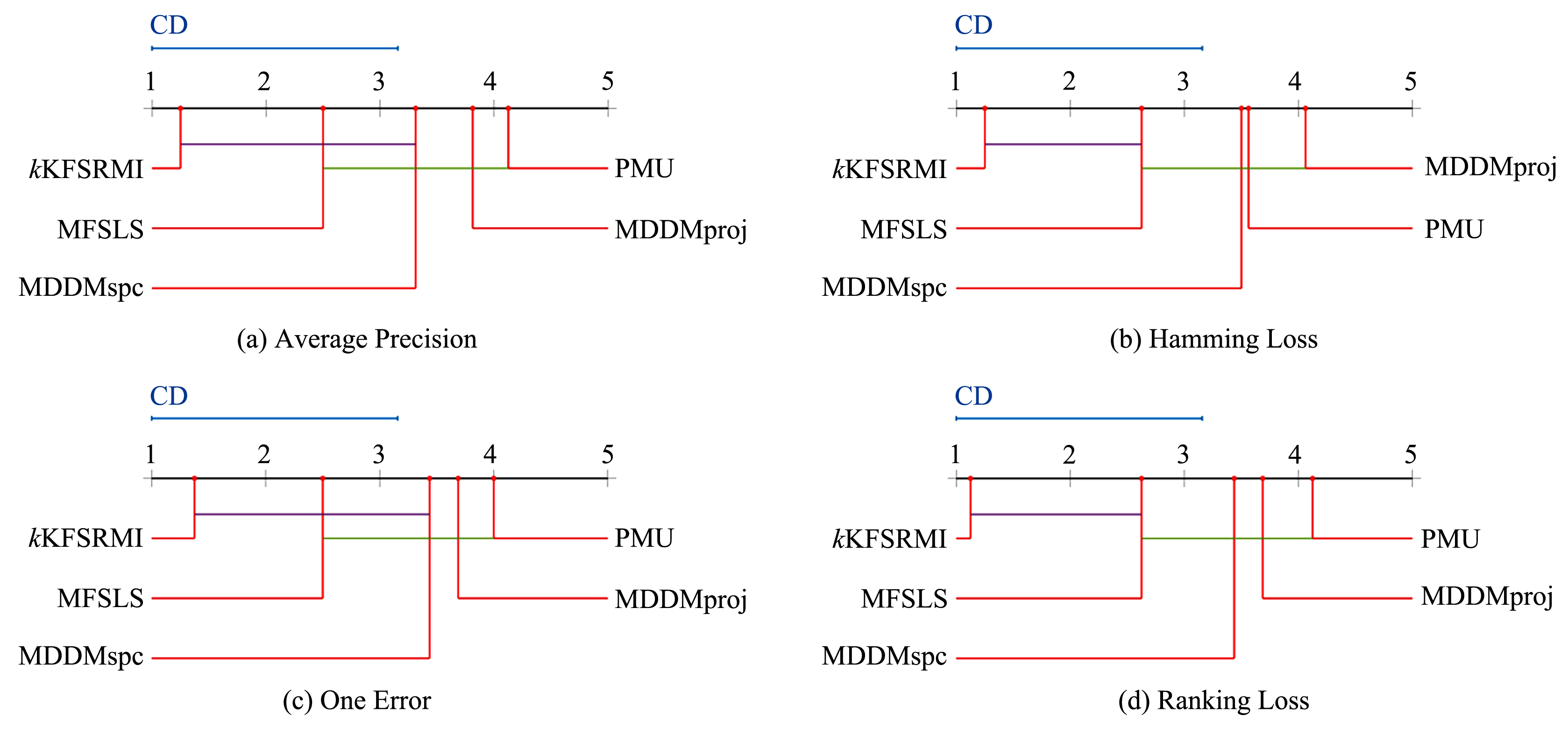
针对多标记学习算法中特征描述粒度导致的标记倾向性问题,大多数研究者从特征与所有标记之间的关联性入手,通过求解得出若干重要特征,并由此构造相应的特征子空间.这种做法会导致有些特征与某个标记有很强的相关性,但与整个标记空间的相关性却并不大,这样的特征丢失易造成分类器精度下降.如果将整个标记空间换成部分标记空间甚至单个标记空间来计算与特征之间的关联性,并把关联性很强的标记分开进行特征选择,就会降低算法的时间开销,提高算法的效率.同时,基于互信息的多标记学习算法多数采用传统熵的方法进行特征选择,由于传统熵不具有补的性质,计算方法较为复杂.引入粗糙熵的度量方法,提出基于粗糙互信息的多标记倾向性k特征核选择算法,实验和统计假设检验都证明该算法是有效的.
中图分类号:
- TP18
| 1 | Zhang M L,Zhou Z H. A review on multi?label learning algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering,2014,26(8):1819-1837. |
| 2 | 王一宾,裴根生,程玉胜. 弹性网络核极限学习机的多标记学习算法. 智能系统学报,2019,14(4):831-842. |
| Wang Y B,Pei G S,Cheng Y S.Multi?label learning algorithm of an elastic net kernel extreme learning machine. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2019,14(4):831-842. | |
| 3 | 李峰,苗夺谦,张志飞等. 一种标记粒化集成的多标记学习算法. 小型微型计算机系统,2018,39(6):1121-1125. |
| Li F,Miao D Q,Zhang Z F,et al. Label?granulated ensemble method for multi?label learning. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems,2018,39(6):1121-1125. | |
| 4 | 余鹰,王乐为,吴新念等. 基于改进卷积神经网络的多标记分类算法. 智能系统学报,2019,14(3):566-574. |
| Yu Y,Wang L W,Wu X M,et al. A multi?label classification algorithm based on an improved convolutional neural network. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2019,14(3):566-574. | |
| 5 | Geng X. Label distribution learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering,2016,28(7):1734-1748. |
| 6 | 刘海峰,姚泽清,苏展. 基于词频的优化互信息文本特征选择方法. 计算机工程,2014,40(7):179-182. |
| Liu H F,Yao Z Q,Su Z.Optimization mutual information text feature selection method based on word frequency. Computer Engineering,2014,40(7):179-182. | |
| 7 | 张辉宜,谢业名,袁志祥等. 一种基于概率的卡方特征选择方法. 计算机工程,2016,42(8):194-198,205. |
| Zhang H Y,Xie Y M,Yuan Z X,et al. A method of CHI-square feature selection based on probability. Computer Engineering,2016,42(8):194-198,205. | |
| 8 | 孙广路,宋智超,刘金来等. 基于最大信息系数和近似马尔科夫毯的特征选择方法. 自动化学报,2017,43(5):795-805. |
| Sun G L,Song Z C,Liu J L,et al. Feature selection method based on maximum information coefficient and approximate Markov blanket. Acta Automatica Sinica,2017,43(5):795-805. | |
| 9 | 赖学方,贺兴时. 最小冗余最大分离准则特征选择方法. 计算机工程与应用,2017,53(12):70-75. |
| Lai X F,He X S.Method based on minimum redundancy and maximum separability for feature selection. Computer Engineering and Applications,2017,53(12):70-75. | |
| 10 | 张振海,李士宁,李志刚等. 一类基于信息熵的多标签特征选择算法. 计算机研究与发展,2013,50(6):1177-1184. |
| Zhang Z H,Li S N,Li Z G,et al. Multi?label feature selection algorithm based on information entropy. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2013,50(6):1177-1184. | |
| 11 | 刘景华,林梦雷,王晨曦等. 基于局部子空间的多标记特征选择算法. 模式识别与人工智能,2016,29(3):240-251. |
| Liu J H,Lin M L,Wang C X,et al. Multi?label feature selection algorithm based on local subspace. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence,2016,29(3):240-251. | |
| 12 | Lee J,Kim D W. Feature selection for multi?label classification using multivariate mutual information. Pattern Recognition Letters,2013,34(3):349-357. |
| 13 | 王晨曦,林耀进,唐莉等. 基于信息粒化的多标记特征选择算法. 模式识别与人工智能,2018,31(2):123-131. |
| Wang C X,Lin Y J,Tang L,et al. Multi?label feature selection based on information granulation. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence,2018,31(2):123-131. | |
| 14 |
钱文彬,黄琴,王映龙等. 多标记不完备数据的特征选择算法. 计算机科学与探索,2019,doi:10.3778/j.issn.1673?9418.1807067.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673?9418.1807067 |
|
Qian W B,Huang Q,Wang Y L,et al. Feature selection algorithm in multi?label incomplete data. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology,2019,doi:10.3778/j.issn.1673?9418.1807067.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673?9418.1807067 |
|
| 15 | 李志欣,卓亚琦,张灿龙等. 多标记学习研究综述. 计算机应用研究,2014,31(6):1601-1605. |
| Li Z X,Zhuo Y Q,Zhang C L,et al. Survey on multi?label learning. Application Research of Computers,2014,31(6):1601-1605. | |
| 16 | Liang J Y,Chin K S,Dang C Y,et al. A new method for measuring uncertainty and fuzziness in rough set theory. International Journal of General Systems,2002,31(4):331-342. |
| 17 | 程玉胜,张佑生,胡学钢. 基于边界域的知识粗糙熵与粗集粗糙熵. 系统仿真学报,2007,19(9):2008-2011. |
| Cheng Y H,Zhang Y S,Hu X G.Entropy of knowledge and rough set based on boundary region. Journal of System Simulation,2007,19(9):2008-2011. | |
| 18 | Mi J S,Leung Y,Wu W Z. An uncertainty measure in partition?based fuzzy rough sets. International Journal of General Systems,2005,34(1):77-90. |
| 19 | Zhang M L,Zhou Z H. ML?KNN:a lazy learning approach to multi?label learning. Pattern Recognition,2007,40(7):2038-2048. |
| 20 | Zhang Y,Zhou Z H. Multilabel dimensionality reduction via dependence maximization. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data,2010,4(3):Article No. 14. |
| 21 | Dem?ar J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2006,7:1-30. |
| [1] | 陈超逸,林耀进,唐莉,王晨曦. 基于邻域交互增益信息的多标记流特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 30-40. |
| [2] | 刘亮,何庆. 基于改进蝗虫优化算法的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 41-50. |
| [3] | 刘 素, 刘惊雷. 基于特征选择的CP-nets结构学习[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 14-28. |
| [4] | 陈海娟,冯 翔,虞慧群. 基于预测算子的GSO特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1206-1215. |
| [5] | 陈琳琳1*,陈德刚2. 一种基于核对齐的分类器链的多标记学习算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 725-. |
| [6] | 温 欣1,李德玉1,2*,王素格1,2. 一种基于邻域关系和模糊决策的特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 733-. |
| [7] | 靳义林1,2*,胡 峰1,2. 基于三支决策的中文文本分类算法研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 794-. |
| [8] | 王一宾1,2,程玉胜1,2*,裴根生1. 结合均值漂移的多示例多标记学习改进算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(2): 422-. |
| [9] | 董利梅,赵 红*,杨文元. 基于稀疏聚类的无监督特征选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(1): 107-. |
| [10] | 崔 晨,邓赵红*,王士同. 面向单调分类的简洁单调TSK模糊系统[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(1): 124-. |
| [11] | 李 婵,杨文元*,赵 红. 联合依赖最大化与稀疏表示的无监督特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 775-. |
| [12] | 姚 晟1,2*,徐 风1,2,赵 鹏1,2,刘政怡1,2,陈 菊1,2. 基于改进邻域粒的模糊熵特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 802-. |
| [13] | 蔡亚萍,杨 明* . 一种利用局部标记相关性的多标记特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(4): 693-. |
| [14] | 谢娟英*,屈亚楠,王明钊 . 基于密度峰值的无监督特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(4): 735-. |
| [15] | 梁新彦1,2,钱宇华1,2*,郭 倩2,成红红1,2. 面向多标记学习的局部粗糙集[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(2): 270-. |
|