南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 30–40.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.01.004
基于邻域交互增益信息的多标记流特征选择算法
- 1. 闽南师范大学计算机学院,漳州,363000
2. 数据科学与智能应用福建省教育厅重点实验室,漳州,363000
Streaming multi⁃label feature selection based on neighborhood interaction gain information
Chaoyi Chen1,Yaojin Lin1,2( ),Li Tang1,2,Chenxi Wang1,2
),Li Tang1,2,Chenxi Wang1,2
- 1. School of Computer Science,Minnan Normal University,Zhangzhou,363000,China
2. Key Laboratory of;Data Science and Intelligence Application,Department of Education of Fujian Province,Zhangzhou,363000,China
摘要:
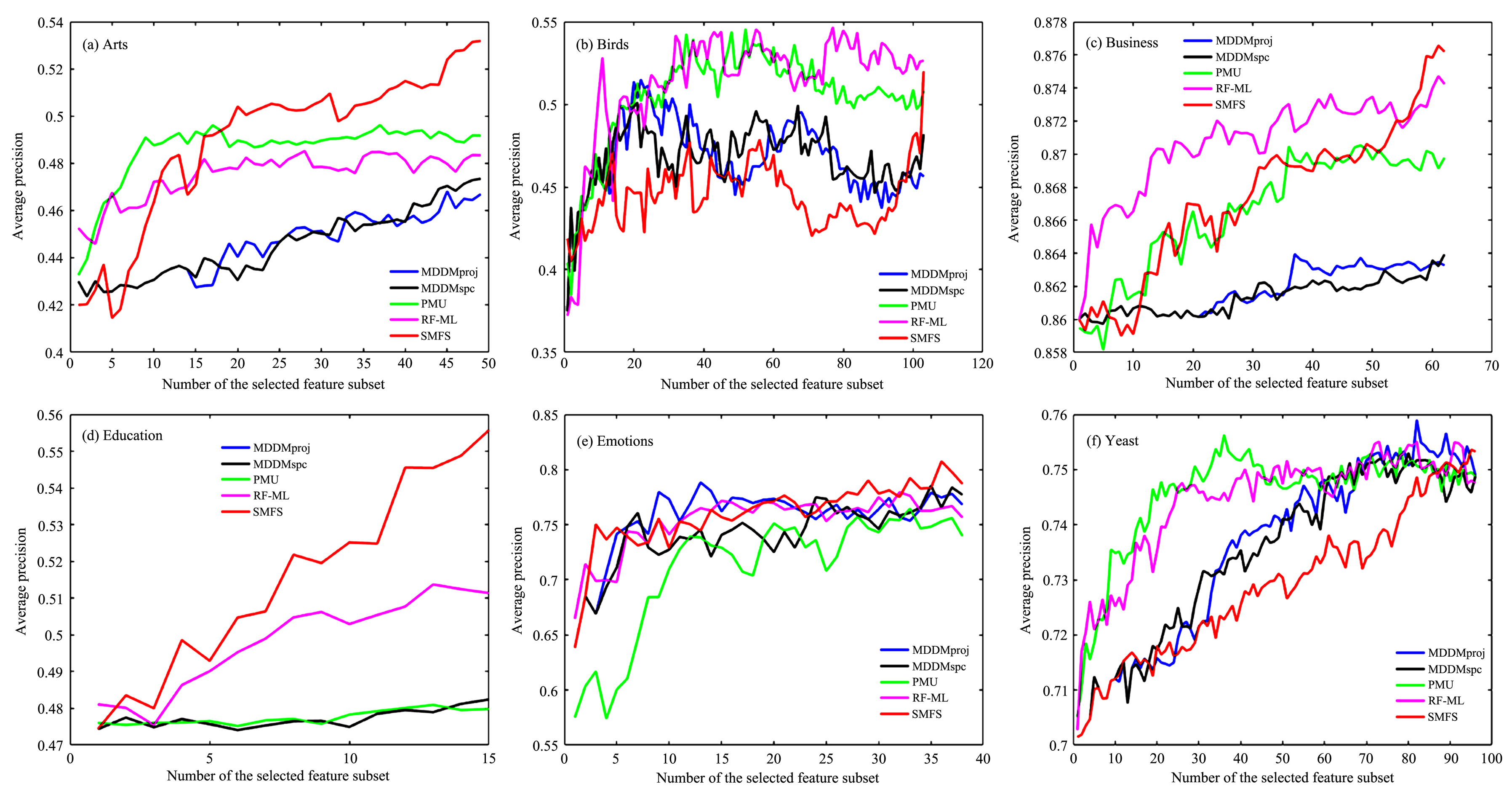
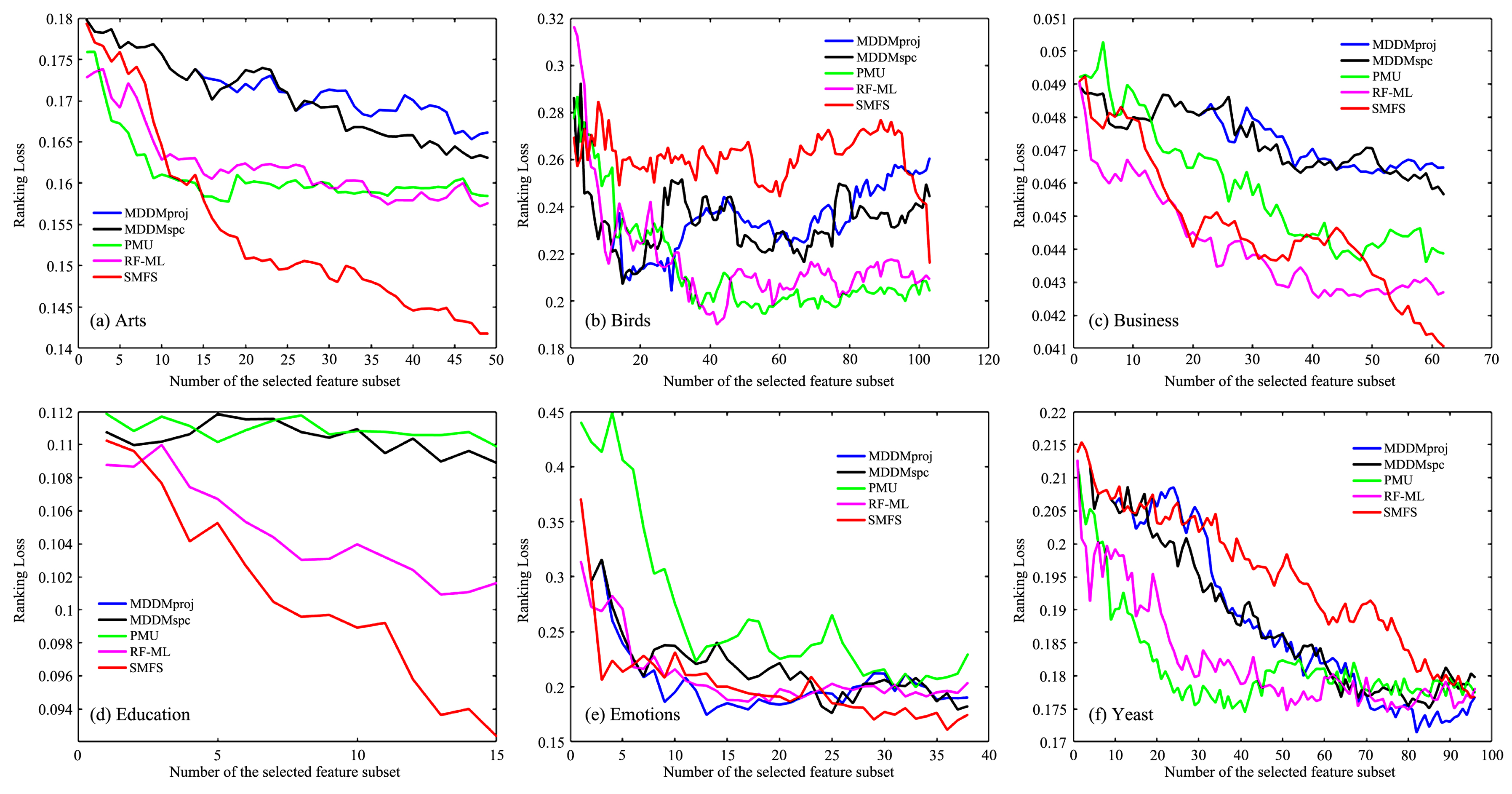
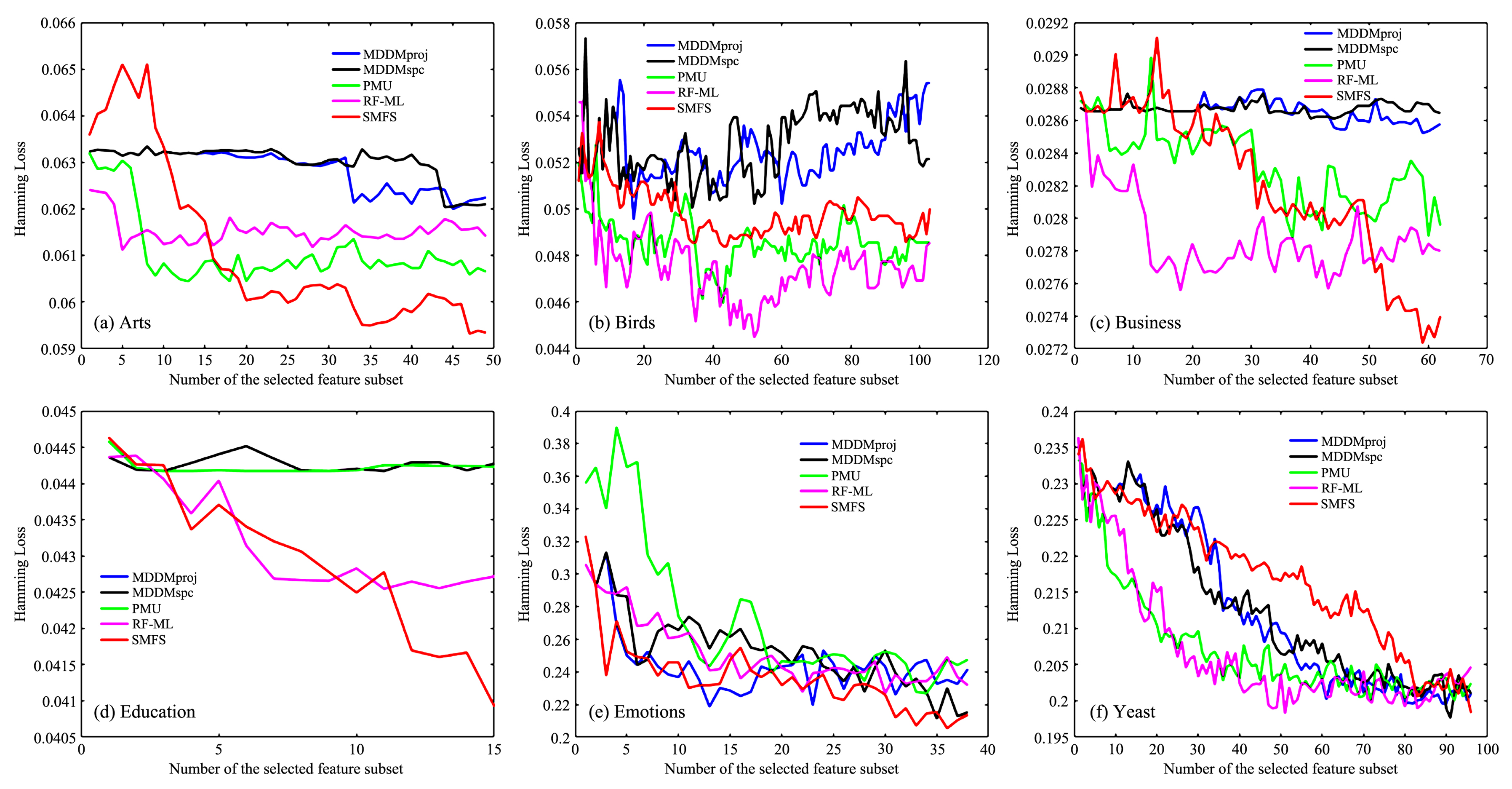
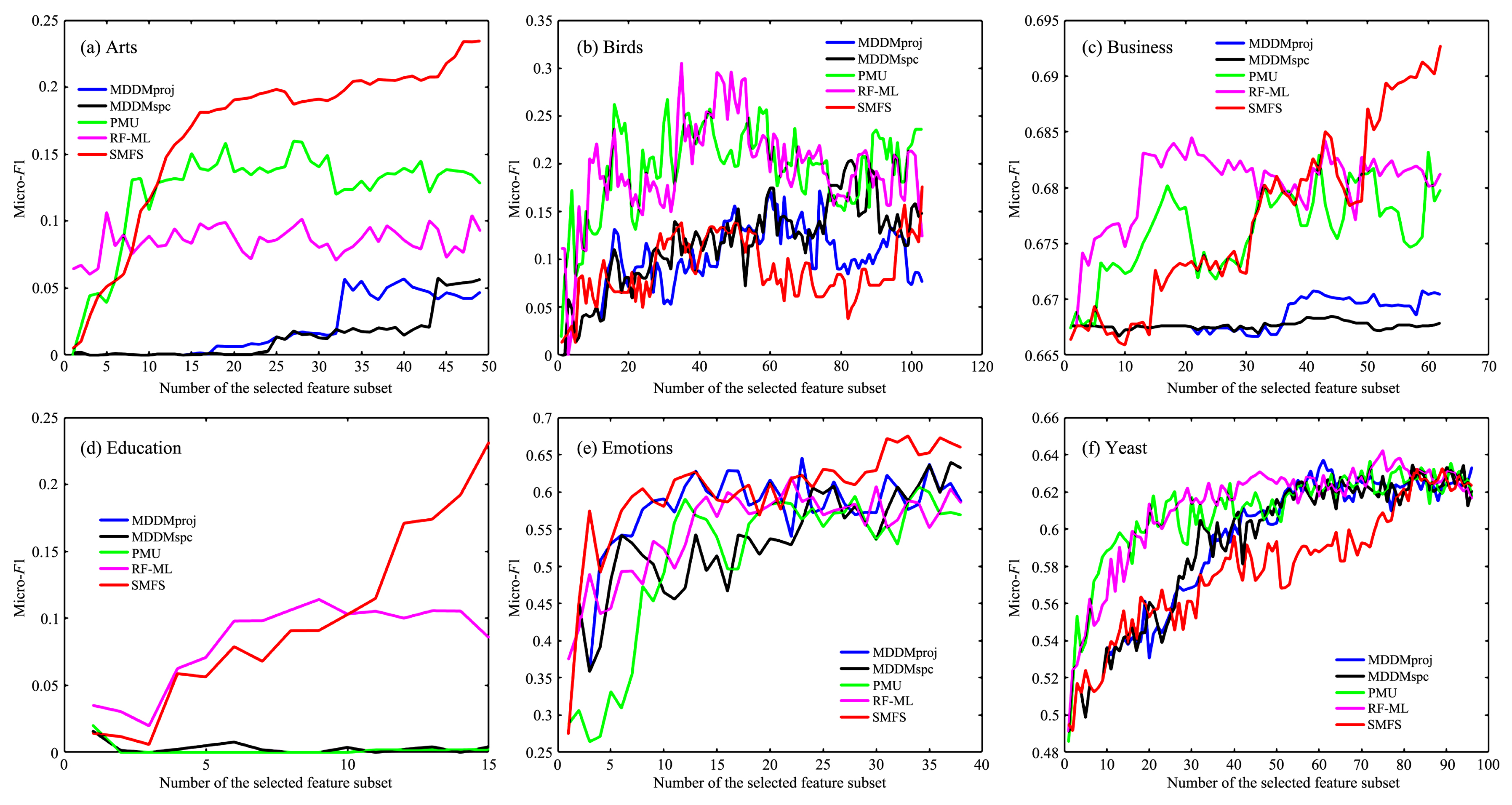
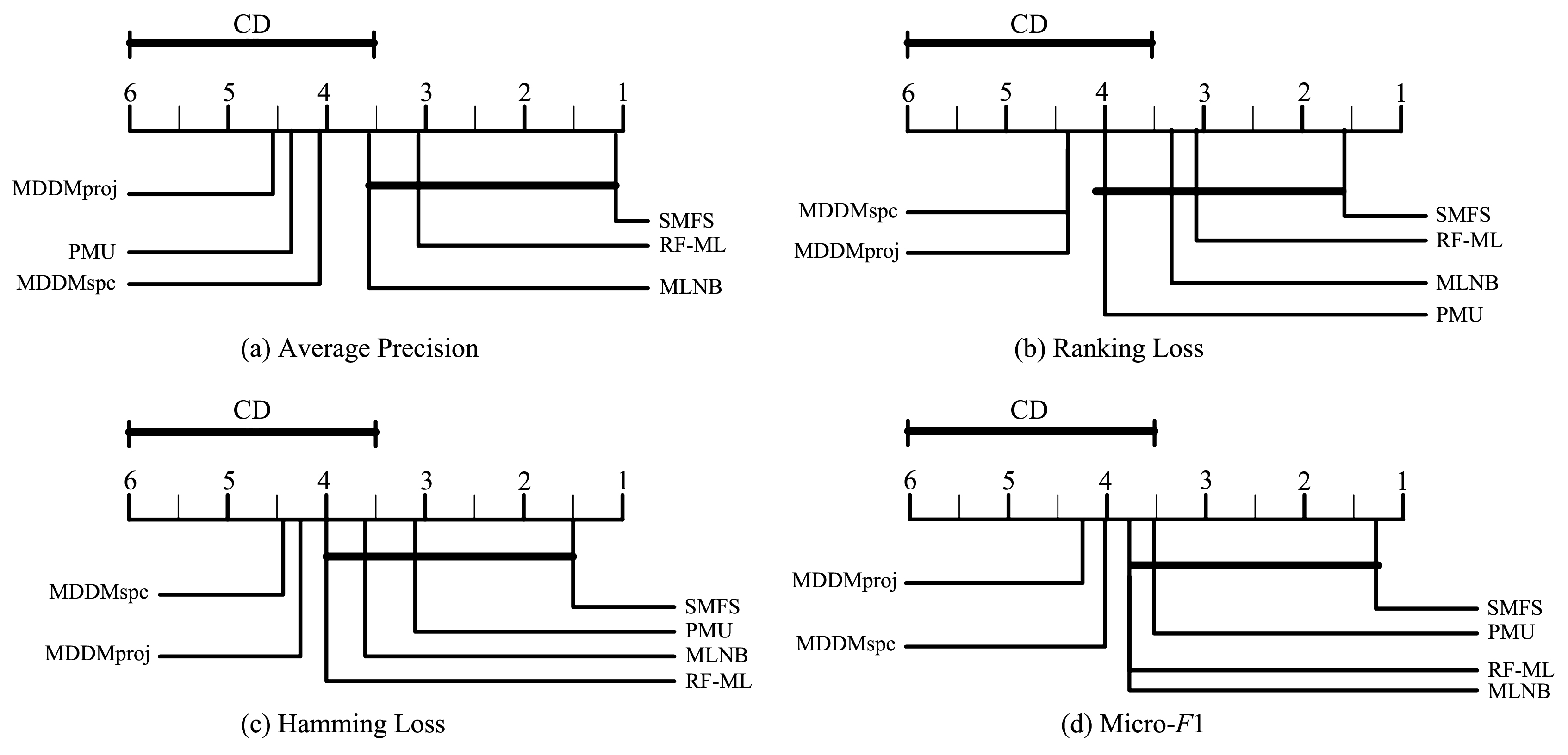
现有的多标记特征选择一般假设特征空间是固定已知的,然而实际应用中很多特征是需要在提取过程中实时地进行筛选.为此,提出基于邻域交互增益信息的多标记在线流特征选择算法.首先,基于多标记邻域互信息和邻域交互增益信息提出在线相关性分析与在线冗余性分析两种策略来评价特征;其次,基于邻域交互增益信息构建了在线流多标记特征选择的目标优化函数;最后,在六个多标记数据集和四个评价指标上,实验结果证明了该算法的有效性和稳定性.
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Boutell M R,Luo J B,Shen X P,et al. Learning multi?label scene classification. Pattern Recognition,2004,37(9):1757-1771. |
| 2 | Lewis D D,Yang Y M,Rose T G,et al. RCV1:a new benchmark collection for text categorization research. The Journal of Machine Learning Research,2004,5(2):361-397. |
| 3 | Elisseeff A,Weston J. A kernel method for multi?labelled classification∥Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems:Natural and Synthetic. Cambridge,MA,USA:MIT Press,2001. |
| 4 | Trohidis K,Tsoumakas G,Kalliris G,et al. Multi?label classification of music by emotion. EURASIP Journal on Audio,Speech,and Music Processing,2011,2011(1):4. |
| 5 | 段洁,胡清华,张灵均等. 基于邻域粗糙集的多标记分类特征选择算法. 计算机研究与发展,2015,52(1):56-65. |
| Duan J,Hu Q H,Zhang L J,et al. Feature selection for multi?label classification based on neighborhood rough set. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2015,52(1):56-65. | |
| 6 | Hotelling H. Relations between two sets of variates. Biometrika,1936,28(3-4):321-377. |
| 7 | Zhang Y,Zhou Z H. Multilabel dimensionality reduction via dependence maximization. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data,2010,4(3):14. |
| 8 | Yu K,Yu S P,Tresp V. Multi?label informed latent semantic indexing∥Proceedings of the 28th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.Salvador,Brazil:ACM,2005:258-265. |
| 9 | 许行,张凯,王文剑. 一种小样本数据的特征选择方法. 计算机研究与发展,2018,55(10):2321-2330. |
| Xu X,Zhang K,Wang W J.A feature selection method for small samples. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2018,55(10):2321-2330. | |
| 10 | Zhang L J,Hu Q H,Duan J,et al. Multi?label feature selection with fuzzy rough sets∥International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2014:121-128. |
| 11 | Lin Y J,Hu Q H,Liu J H,et al. Multi?label feature selection based on neighborhood mutual information. Applied Soft Computing,2016,38:244-256. |
| 12 | Hu L,Gao W F,Zhao K,et al. Feature selection considering two types of feature relevancy and feature interdependency. Expert Systems with Applications,2018,93:423-434. |
| 13 | 程玉胜,李雨,王一宾等. 动态滑动窗口加权互信息流特征选择. 南京大学学报(自然科学),2018,54(5):974-985. |
| Cheng Y S,Li Y,Wang Y B,et al. Streaming feature selection with weighted fuzzy mutual information based on dynamic sliding window. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science),2018,54(5):974-985. | |
| 14 | Lin Y J,Hu Q H,Liu J H,et al. Streaming feature selection for multilabel learning based on fuzzy mutual information. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,2017,25(6):1491-1507. |
| 15 | Liu J H,Lin Y J,Li Y W,et al. Online multi?label streaming feature selection based on neighborhood rough set. Pattern Recognition,2018,84:273-287. |
| 16 | Lin Y J,Hu Q H,Liu J H,et al. Multi?label fea?ture selection based on max?dependency and min?redundancy. Neurocomputing,2015,168:92-103. |
| 17 | Kwak N,Choi C H. Input feature selection for classification problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,2002,13(1):143-159. |
| 18 | Zhang M L,Pe?a J M,Robles V. Feature selection for multi?label naive Bayes classification. Information Sciences,2009,179(19):3218-3229. |
| 19 | Lee J,Kim D W. Feature selection for multi?label classification using multivariate mutual information. Pattern Recognition Letters,2013,34(3):349-357. |
| 20 | Spola?r N,Cherman E A,Monard M C,et al. ReliefF for multi?label feature selection∥2013 Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems (BRACIS). Fortaleza,Brazil:IEEE,2013:6-11. |
| 21 | Friedman M. A comparison of alternative tests of significance for the problem of m rankings. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1940,11(1):86-92. |
| 22 | Dunn O J. Multiple comparisons among means. Journal of the American Statistical Association,1961,56(293):52-64. |
| [1] | 程玉胜,陈飞,庞淑芳. 标记倾向性的粗糙互信息k特征核选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 19-29. |
| [2] | 陈琳琳1*,陈德刚2. 一种基于核对齐的分类器链的多标记学习算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 725-. |
| [3] | 王一宾1,2,程玉胜1,2*,裴根生1. 结合均值漂移的多示例多标记学习改进算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(2): 422-. |
| [4] | 蔡亚萍,杨 明* . 一种利用局部标记相关性的多标记特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(4): 693-. |
| [5] | 梁新彦1,2,钱宇华1,2*,郭 倩2,成红红1,2. 面向多标记学习的局部粗糙集[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(2): 270-. |
| [6] | 吕静,何志芬. 一种基于正则化最小二乘的多标记分类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(1): 139-147. |
|