南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 1–8.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.01.001
• • 下一篇
一种基于用户结构和属性的无监督用户对齐方法
- 计算智能重庆市重点实验室,重庆邮电大学,重庆,400065
An unsupervised user alignment method based on user structure and attribute
Dongming Yu,Yuan Li,Zhixing Li,Guoyin Wang( )
)
- Chongqing Key Laboratory of Computational Intelligence,Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Chongqing,400065,China
摘要:
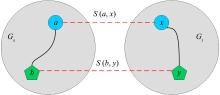
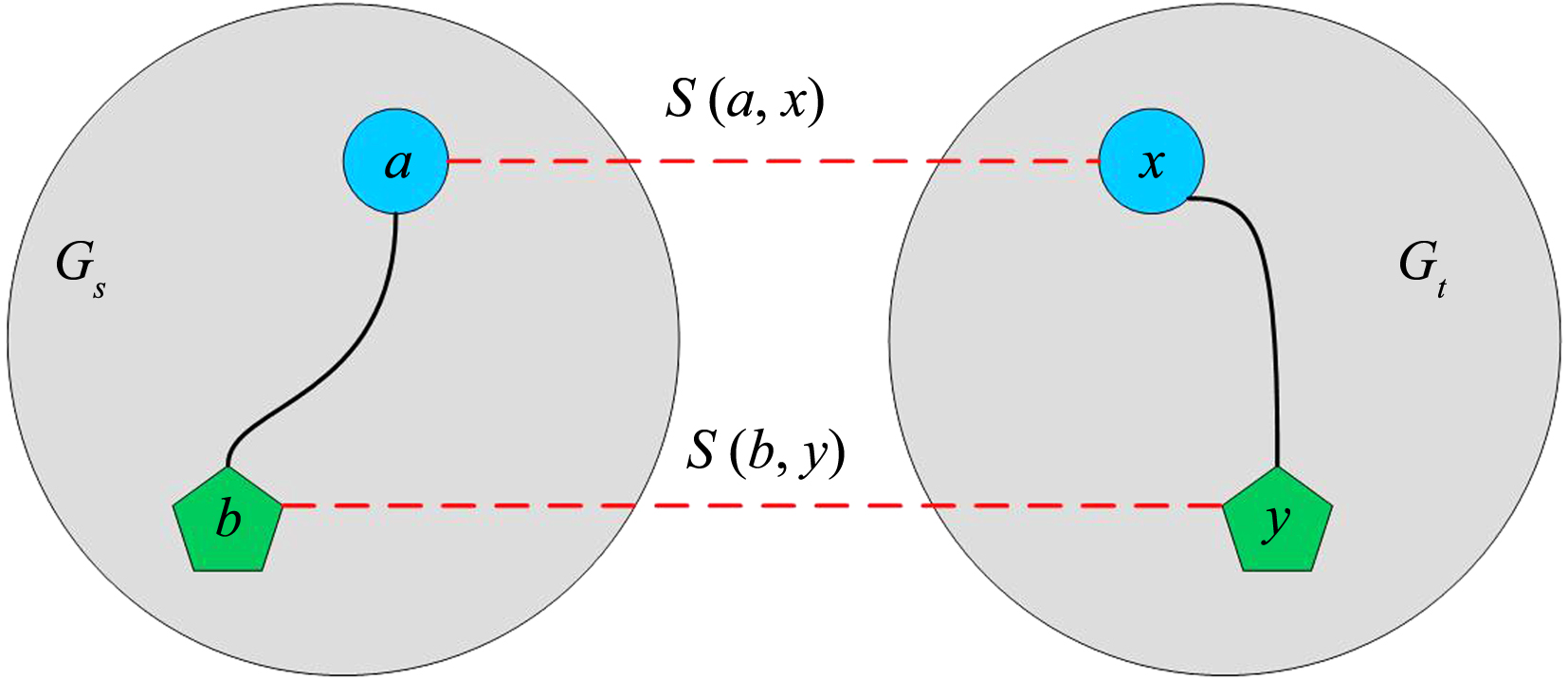
随着互联网应用的蓬勃发展,一个人在不同的社交网络平台上都拥有账户是很常见的.如何在多个社交网络上找到同一个人的账户,对许多应用是很重要的问题,也被称为用户对齐问题.在用户对齐问题上,目前有两个主要的挑战:首先,收集手工对齐的用户对作为训练数据的代价非常大,但传统的有监督方法往往需要大量的标注数据才能获得较好的效果;其次,不同网络中的用户的结构和属性往往不太相同,进一步增加了用户对齐的难度.提出一种无监督用户对齐方法SPUAL(Soft Principle for User Alignment),设计了一种新颖的基于用户的属性与结构的软对齐一致性原则,通过无监督方法计算用户对是否服从此原则来推断用户对是否对齐.在几个公共数据集上的实验表明,该方法的性能比目前最先进的无监督方法都有明显提高.
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Zhang Y T,Tang J,Yang Z L,et al. Cosnet:connecting heterogeneous social networks with local and global consistency∥Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.Sydney,Australia:ACM,2015:1485-1494. |
| 2 | Chen Z,Yu X,Song B,et al. Community?based network alignment for large attributed network∥Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.Singapore:ACM,2017:587-596. |
| 3 | Manners H N,Elmsallati A,Guzzi P H,et al. Performing local network alignment by ensembling global aligners∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). Kansas City,MO,USA:IEEE,2017:1316-1323. |
| 4 | Smalter A,Huan J,Lushington G. Gpm:a graph pattern matching kernel with diffusion for chemical compound classification∥2008 8th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering.Athens,Greece:IEEE,2008:1-6. |
| 5 | Bayati M,Gerritsen M,Gleich D F,et al. Algorithms for large,sparse network alignment problems∥2009 9th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining.Miami,FL,USA:IEEE,2009:705-710. |
| 6 | Koutra D,Tong H,Lubensky D. Big?Align:Fast bipartite graph alignment∥2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). Dallas,TX,USA:IEEE,2013. |
| 7 | Zhang S,Tong H H. Final:Fast attributed network alignment∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.San Francisco,CA,USA:ACM,2016:1345-1354. |
| 8 | Zhang S,Tong H,Tang J,et al. iNEAT:Incomplete network alignment∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining.New Orleans,LA,USA:IEEE,2017:1189-1194. |
| 9 | Goga O,Perito D,Lei H,et al. Large?scale correlation of accounts across social networks. Technical Report. Berkeley:University of California at Berkeley,2013:TR?13?002. |
| 10 | Liu S Y,Wang S H,Zhu F D. HYDRA:Large?scale social identity linkage via heterogeneous behavior modeling∥Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data.Snowbird,UT,USA:ACM,2014. |
| 11 | Zhou X P,Liang X,Du X Y,et al. Structure based user identification across social networks. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2017,30(6):1178-1191. |
| 12 | Liu L,Cheung W K,Li X,et al. Aligning users across social networks using network embedding∥Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence.New York,NY,USA:AAAI Press,2016. |
| 13 | Zhang J,Chen B,Wang X,et al. Mego2vec:embedding matched ego networks for user alignment across social networks∥Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.Torino,Italy:ACM,2018:327-336. |
| 14 | Page L,Brin S,Motwani R,et al. The PageRank citation ranking:bringing order to the web. Technical Report. Stanford InfoLab,1999. |
| 15 | Liao C S,Lu K,Baym M,et al. IsoRankN:Spectral methods for global alignment of multiple protein networks. Bioinformatics,2009,25(12):i253-i258. |
| 16 | Andersen R,Chung F R K,Lang K J. Local graph partitioning using pageRank vectors∥2006 47th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS'06). Berkeley,CA,USA:IEEE,2006. |
| 17 | Bayati M,Shah D,Sharma M. Maximum weight matching via max?product belief propagation∥Proceedings of International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT 2005). Adelaide,Australia:IEEE,2005. |
| 18 | Zhang J W,Yu P S. Multiple anonymized social networks alignment∥2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining.Atlantic City,NJ,USA:IEEE,2015:599-608. |
| 19 | Zhong E H,Fan W,Wang J W,et al. ComSoc:adaptive transfer of user behaviors over composite social network∥ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.Beijing,China:ACM,2012. |
| 20 | Heimann M,Shen H M,Safavi T,et al. Regal:representation learning?based graph alignment∥Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.Torino,Italy:ACM,2018:117-126. |
| 21 | Klau G W. A new graph?based method for pairwise global network alignment. BMC Bioinformatics,2009,10(S1):S59. |
| 22 | Kollias G,Mohammadi S,Grama A. Network similarity decomposition (NSD):a fast and scalable approach to network alignment. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2012,24(12):2232-2243. |
| 23 |
Zheng Z D,Zheng L,Yang Y. Pedestrian alignment network for large?scale person re?identification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,2018,doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2018.
doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2018 |
|
2873599.
doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2018 |
| [1] | 陈俊芬,赵佳成,韩洁,翟俊海. 基于深度特征表示的Softmax聚类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 533-540. |
| [2] | 吕国俊,曹建军,郑奇斌,常宸,翁年凤. 基于结构保持对抗网络的跨模态实体分辨[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(2): 197-205. |
| [3] | 王伯伟, 聂秀山, 马林元, 尹义龙. 基于语义相似度的无监督图像哈希方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 41-48. |
| [4] | 靳义林1,2*,胡 峰1,2. 基于三支决策的中文文本分类算法研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 794-. |
| [5] | 董利梅,赵 红*,杨文元. 基于稀疏聚类的无监督特征选择[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(1): 107-. |
| [6] | 李 凡1,2,赵 姝1,2*,陈 洁1,2,张燕平1,2. 基于加权中介中心性的结构洞占据者方法获取[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 756-. |
| [7] | 李 婵,杨文元*,赵 红. 联合依赖最大化与稀疏表示的无监督特征选择方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 775-. |
| [8] | 宾 晟*,孙更新. 基于多子网复合复杂网络模型的多关系社交网络重要节点发现算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(2): 378-. |
| [9] | 张燕平1,2张顺1,2钱付兰1,2严远亭1,2. 一种局部和全局用户影响力相结合的社交推荐算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(4): 858-865. |
|