南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 452–460.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.04.003
有限理性下多粒度q⁃RO模糊粗糙集的最优粒度选择及其在并购对象选择中的应用
- 1.山西转型综改示范区成果转化有限公司,太原,030032
2.计算智能与中文信息处理教育部重点实验室(山西大学),太原,030006
3.山西大学计算机与信息技术学院,太原,030006
Optimal granularity selections of multigranulation q⁃RO fuzzy rough sets under bounded rationality and their applications in merger and acquisition target selections
Rui Ren1,Chao Zhang2,3( ),Jifang Pang3
),Jifang Pang3
- 1.Achievement Transformation Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanxi Transformation and Comprehensive Reform Demonstration Zone,Taiyuan,030032,China
2.Key Laboratory of Computational Intelligence and Chinese Information Processing of Ministry of Education(Shanxi University),Taiyuan,030006,China
3.School of Computer and Information Technology,Shanxi University,Taiyuan,030006,China
摘要:
有限理性通常指决策者困顿于信息处理能力有限的自然状态,该状态是决策者在实际决策情境中需要面对的常态,因而有必要研究有限理性下的决策问题.多粒度粗糙集在多属性群决策分析领域的优势在于运算效率高,并能结合决策风险,然而多数基于多粒度粗糙集的多属性群决策方法并未考虑有限理性这一实际情境.以q?RO(q?Rung Orthopair)模糊集为背景,首先提出乐观与悲观多粒度q?RO模糊粗糙集模型;接着在并购对象选择的背景下,依据交互式多属性决策(Portuguese of Interactive and Multi?criteria Decision Making,TODIM)法来处理有限理性下的决策信息,发展多粒度q?RO模糊粗糙集的最优粒度选择机制并建立相应的多属性群决策方法;最后结合并购对象选择的实际算例验证了所建立模型与方法的有效性.
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Simon H A. Administrative behavior. New York:Free Press,1957:72-87. |
| 2 | Simon H A. Bounded rationality and organizational learning. Organization Science,1991,2(1):125-134. |
| 3 | Peng Y,Lu Q. Complex dynamics analysis for a duopoly Stackelberg game model with bounded rationality. Applied Mathematics and Computation,2015,271:259-268. |
| 4 | Liu D H,Lv W,Li H Y,et al. Bargaining model of labor disputes considering social mediation and bounded rationality. European Journal of Operational Research,2017,262(3):1064-1071. |
| 5 | Liang D C,Zhang Y R J,Xu Z S,et al. Pythagorean fuzzy vikor approaches based on todim for evaluating internet banking website quality of Ghanaian banking industry. Applied Soft Computing,2019,78:583-594. |
| 6 | Liang D C,Wang M W,Xu Z S,et al. Risk appetite dual hesitant fuzzy three?way decisions with todim. Information Sciences,2020,507:585-605. |
| 7 | Qian Y H,Liang J Y,Yao Y Y,et al. MGRS:a multi?granulation rough set. Information Sciences,2010,180(6):949-970. |
| 8 | Qian Y H,Li S Y,Liang J Y,et al. Pessimistic rough set based decisions:a multigranulation fusion strategy. Information Sciences,2014,264:196-210. |
| 9 | Qian Y H,Zhang H,Sang Y L,et al. Multigranulation decision:theoretic rough sets. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2014,55(1):225-237. |
| 10 | Qian Y H,Liang X Y,Lin G P,et al. Local multigranulation decision?theoretic rough sets. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2017,82:119-137. |
| 11 | Zhang C,Li D Y,Liang J Y. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic rough set over two universes model and its applications. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics,2018,9(4):577-588. |
| 12 |
Zhan J M,Sun B Z,Alcantud J C R. Covering based multigranulation (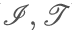 )?fuzzy rough set models and applications in multi?attribute group decision?making. Information Sciences,2019,476:290-318. )?fuzzy rough set models and applications in multi?attribute group decision?making. Information Sciences,2019,476:290-318.
|
| 13 | Zhang C,Li D Y,Liang J Y. Interval?valued hesitant fuzzy multi?granularity three?way decisions in consensus processes with applications to multi?attribute group decision making. Information Sciences,2020,511:192-211. |
| 14 | Zhang C,Li D Y,Liang J Y. Multi?granularity three?way decisions with adjustable hesitant fuzzy linguistic multigranulation decision?theoretic rough sets over two universes. Information Sciences,2020,507:665-683. |
| 15 | Sun B Z,Ma W M,Li B J,et al. Three?way decisions approach to multiple attribute group decision making with linguistic information?based decision?theoretic rough fuzzy set. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,2018,93:424-442. |
| 16 | Sun B Z,Zhou X M,Lin N N. Diversified binary relation?based fuzzy multigranulation rough set over two universes and application to multiple attribute group decision making. Information Fusion,2020,55:91-104. |
| 17 | Yager R R. Generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,2017,25(5):1222-1230. |
| 18 | Atanassov K T. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,1986,20(1):87-96. |
| 19 | Yager R R,Abbasov A M. Pythagorean membership grades,complex numbers,and decision making. International Journal of Intelligent Systems,2013,28(5):436-452. |
| 20 | Yager R R,Alajlan N. Approximate reasoning with generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. Information Fusion,2017,38:65-73. |
| 21 |
Liu P D,Chen S M,Wang P. Multiple?attribute group decision?making based on q?rung orthopair fuzzy power maclaurin symmetric mean operators. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics:Systems,2018:1-16,doi:10.1109/TSMC.2018.2852948.
doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2852948 |
| 22 | Darko A P,Liang D C. Some q?rung orthopair fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making with modified EDAS method. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,2020,87:103259. |
| 23 | Peng X D,Liu L. Information measures for q?rung orthopair fuzzy sets. International Journal of Intelligent Systems,2019,34(8):1795-1834. |
| 24 | Gomes L F A M,Lima M M P P. Todim:basic and application to multicriteria ranking of projects with environmental impacts. Foundations of Computing and Decision Sciences,1992,16(3):113-127. |
| 25 | Zhang C,Li D Y,Ren R. Pythagorean fuzzy multigranulation rough set over two universes and its applications in merger and acquisition. International Journal of Intelligent Systems,2016,31(9):921-943. |
| 26 | 宋鹏,梁吉业,曹付元. 基于邻域粗糙集的企业财务危机预警指标选择. 经济管理,2009,31(8):130-135. |
| Song P,Liang J Y,Cao F Y. Index selection of enterprise's financial crisis early warning based on neighborhood rough set. Economic Management Journal,2009,31(8):130-135. | |
| 27 | 张超,李德玉. 考虑关联性与优先关系的区间犹豫模糊图决策. 计算机研究与发展,2019,54(11):2438-2447. |
| Zhang C,Li D Y. Interval?valued hesitant fuzzy graphs decision making with correlations and prioritization relationships. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2019,54(11):2438-2447. | |
| 28 | Zhang C,Li D Y,Kang X P,et al. Neutrosophic fusion of rough set theory:An overview. Computers in Industry,2020,115:103117. |
| [1] | 孟慧丽*,马媛媛,徐久成. 基于信息量的悲观多粒度粗糙集粒度约简[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 343-348. |
| [2] | 莫京兰1,2,吕跃进2,李金海3. 不完备序信息系统的模型扩展及其属性约简[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 430-437. |
| [3] | 王丽娟 1.2**,杨习贝1.2,杨静宇1,吴陈2 . 一种新的不完备多粒度粗糙集*[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(4): 436-444. |
|
