南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 460–470.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2023.03.009
基于多粒度信息编码和联合优化的篇章级服务事件序列抽取方法
- 1.浙江工业大学计算机科学与技术学院,杭州,310023
2.浙江中烟工业有限责任公司信息中心,杭州,310009
Document⁃level service event sequence extraction based on multi⁃granularity information encoding and joint optimization
Qinnan Cheng1, Zhiqiang Mo1, Bin Cao1( ), Jing Fan1, Yuxiang Shan2
), Jing Fan1, Yuxiang Shan2
- 1.College of Computer Science & Technology, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, 310023, China
2.Information Center, China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial Co. , Ltd. , Hangzhou, 310009, China
摘要:
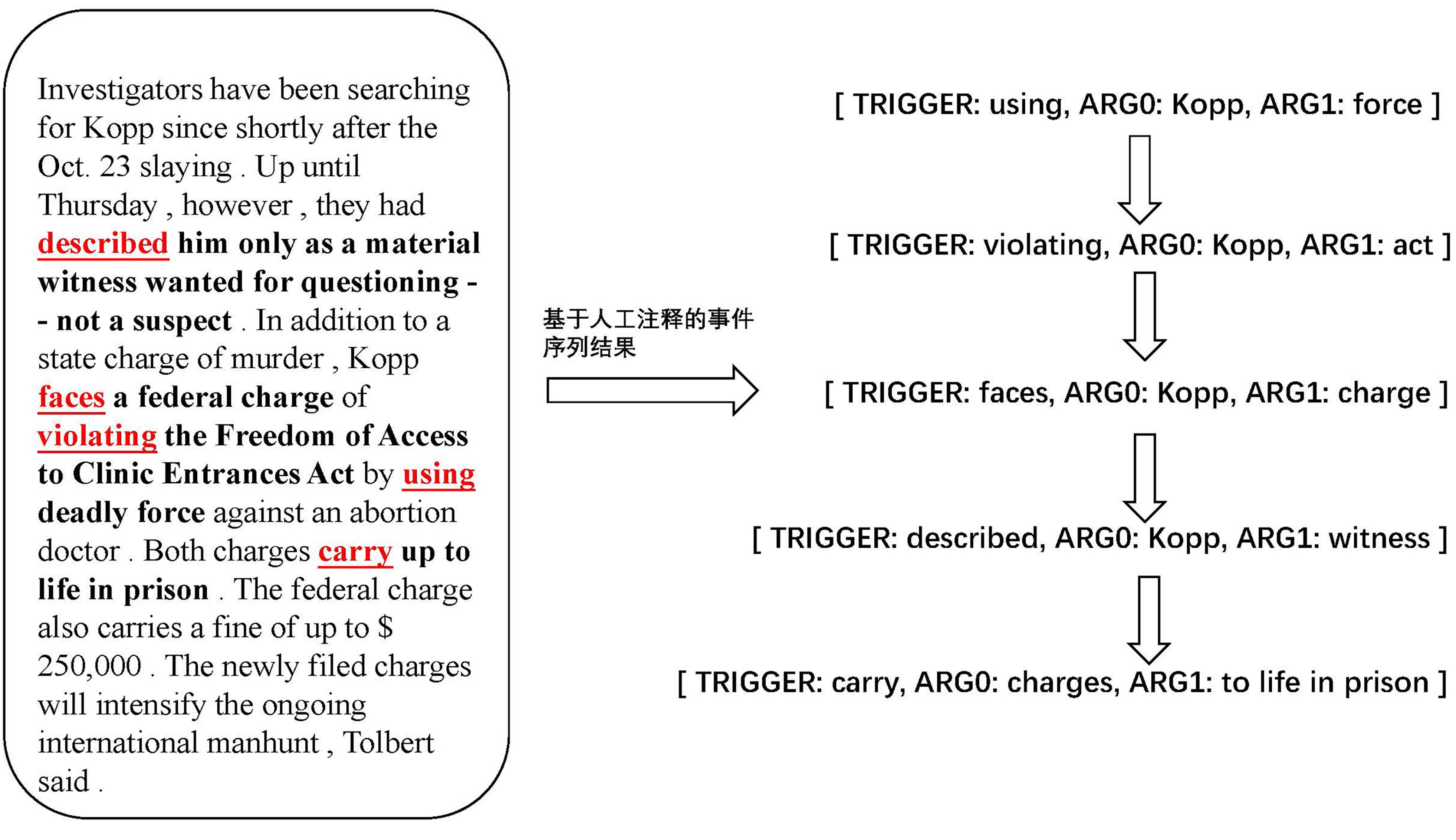
篇章级别的服务事件序列抽取任务旨在发现给定服务的相关文本中所有服务事件的顺序序列关系,构建得到一组按照服务事件发生顺序排列的服务事件集合,其研究可以广泛应用于知识图谱构建、自动问答等任务.与该任务相关的现有工作分过程抽取和事件时序关系抽取两类:过程抽取相关研究默认事件真实发生的顺序与文本描述的顺序一致,忽略了许多非过程性文本中事件发生的顺序与文本描述顺序不一致的情况;.事件时序关系抽取的相关研究往往关注事件对之间的时序关系判断,无法建模所有事件的顺序序列关系.针对以上问题,提出一种基于多粒度信息编码和联合优化的篇章级服务事件序列抽取方法,使用多粒度信息编码模块获得服务文本中具有丰富语义信息的服务事件向量表示,再利用联合优化模块提取服务事件之间的顺序序列关系,得到篇章级别的服务事件序列.由于没有公开数据集可以直接用于服务事件序列抽取任务的评估,抽取基于事件时序关系抽取的公开数据集TimeBank (TB),AQUAINT (AQ),Platinum (PL)和MATRES中的数据,构建了可用于篇章级服务事件序列抽取任务评估的数据集,实验结果证明了提出方法的有效性.
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Strassel S, Mitchell A. Multilingual resources for entity extraction∥Proceedings of the ACL 2003 Workshop on Multilingual and Mixed?Language Named Entity Recognition. Sapporo,Japan:Association for Computational Linguistics,2003:49-56. |
| 2 | Manshadi M, Swanson R, Gordon A S. Learning a probabilistic model of event sequences from internet weblog stories∥Proceedings of the 21st International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference. Coconut Grove,FL,USA:AAAI Press,2008:159-164. |
| 3 | Jeblee S, Hirst G. Listwise temporal ordering of events in clinical notes∥Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Health Text Mining and Information Analysis. Brussels,Belgium:Association for Computational Linguistics,2018:177-182. |
| 4 | Feng W F, Zhuo H H, Kambhampati S. Extracting action sequences from texts based on deep reinforcement learning∥Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm,Sweden:AAAI Press,2018:4064-4070. |
| 5 | Qian C, Wen L J, Kumar A,et al. An approach for process model extraction by multi?grained text classification∥The 32nd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2020:268-282. |
| 6 | Han R J, Ning Q, Peng N Y. Joint event and temporal relation extraction with shared representations and structured prediction∥Proceedings of 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Hong Kong,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:434-444. |
| 7 | Ning Q, Subramanian S, Roth D. An improved neural baseline for temporal relation extraction∥Proceedings of 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Hong Kong,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:6203-6209. |
| 8 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K,et al. BERT:Pre?training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding∥Proceedings of 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Volume 1. Long and Short Papers. Minneapolis,MI,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:4171-4186. |
| 9 | Graves A. Long short?term memory∥Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2012:37-45. |
| 10 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N,et al. Attention is all you need∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach,CA,USA:Curran Associates Inc.,2017:6000-6010. |
| 11 | Pustejovsky J, Hanks P, Sauri R,et al. The timebank corpus. Corpus Linguistics,2003:40. |
| 12 | Graff D. The AQUAINT corpus of English news text. Philadelphia:Linguistic Data Consortium,2002. |
| 13 | UzZaman N, Llorens H, Derczynski L,et al. Semeval?2013 task 1:Tempeval?3:Evaluating time expressions,events,and temporal relations∥The 2nd Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics,Volume 2:Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Atlanta,GE,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2013:1-9. |
| 14 | Ning Q, Wu H, Roth D. A multi?axis annotation scheme for event temporal relations∥Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Volume 1:Long Papers. Melbourne,Australia:Association for Computational Linguistics,2018:1318-1328. |
| 15 | Walter K, Minor M, Bergmann R. Workflow extraction from cooking recipes∥Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Case?Based Reasoning Workshops. London,UK:Springer,2011:207-216. |
| 16 | Schumacher P, Minor M. Extracting control?flow from text∥Proceedings of 2014 IEEE 15th International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration. Redwood City,CA,USA:IEEE,2014:203-210. |
| 17 | Chen D L, Mooney R J. Learning to interpret natural language navigation instructions from observations∥Proceedings of the 25th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco,CA,USA:AAAI Press,2011:859-865. |
| 18 | Chen D. Fast online lexicon learning for grounded language acquisition∥Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Volume 1:Long Papers. Jeju Island,Korea:Association for Computational Linguistics,2012:430-439. |
| 19 | Kim J, Mooney R. Adapting discriminative reranking to grounded language learning∥Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Volume 1:Long Papers. Sofia,Bulgaria:Association for Computational Linguistics,2013:218-227. |
| 20 | Zhang Z Q, Webster P, Uren V,et al. Automatically extracting procedural knowledge from instructional texts using natural language processing∥Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation. Istanbul,Turkey:European Language Resources Association,2012:520-527. |
| 21 | Leopold H, Van Der Aa H, Reijers H A. Identifying candidate tasks for robotic process automation in textual process descriptions∥The 19th International Conference on Business Process Modeling,Development and Support. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2018:67-81. |
| 22 | 倪维健,韦振胜,曾庆田,等.面向自然过程文本的案例信息抽取.计算机集成制造系统,2018,24(7):1680-1689. |
| Ni W J, Wei Z S, Zeng Q T,et al. Case information extraction from natural procedure text. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems,2018,24(7):1680-1689. | |
| 23 | Mei H, Bansal M, Walter M R. Listen,attend,and walk:Neural mapping of navigational instructions to action sequences∥Proceedings of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Phoenix,AZ,USA:AAAI Press,2016:2772-2778. |
| 24 | Mani I, Verhagen M, Wellner B,et al. Machine learning of temporal relations∥Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and the 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Sydney,Australia:Association for Computational Linguistics,2006:753-760. |
| 25 | Chambers N, Wang S, Jurafsky D. Classifying temporal relations between events∥Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics Companion Volume,Proceedings of the Demo and Poster Sessions. Prague,Czech Republic:Association for Computa?tional Linguistics,2007:173-176. |
| 26 | Mirza P, Tonelli S. Classifying temporal relations with simple features//Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Gothenburg,Sweden:Association for Computational Linguistics,2014:308-317. |
| 27 | Bethard S. ClearTK?timeML:A minimalist approach to tempEval 2013∥The 2nd Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics,Volume 2:Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Atlanta,GE,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2013:10-14. |
| 28 | Chambers N, Cassidy T, McDowell B,et al. Dense event ordering with a multi?pass architecture. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics,2014(2):273-284. |
| 29 | Tourille J, Ferret O, Névéol A,et al. LIMSI?COT at SemEval?2016 Task 12:Temporal relation identification using a pipeline of classifiers∥Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. San Diego,CA,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2016:1136-1142. |
| 30 | Cheng F, Miyao Y. Classifying temporal relations by bidirectional LSTM over dependency paths∥Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Volume 2:Short Papers. Vancouver,Canada:Association for Computational Linguistics,2017:1-6. |
| 31 | Cao Z, Qin T, Liu T Y,et al. Learning to rank:From pairwise approach to listwise approach∥Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. Corvalis,OR,USA:ACM,2007:129-136. |
| 32 | Do Q, Lu W, Roth D. Joint inference for event timeline construction∥Proceedings of 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning. Jeju Island,Korea:Association for Computational Linguistics,2012:677-687. |
| [1] | 谭嘉辰, 董永权, 张国玺. SSM: 基于孪生网络的糖尿病视网膜眼底图像分类模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(3): 425-434. |
| [2] | 曲皓, 狄岚, 梁久祯, 刘昊. 双端输入型嵌套融合多尺度信息的织物瑕疵检测[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(3): 398-412. |
| [3] | 张绎凡, 李婷, 葛洪伟. 多样性诱导的潜在嵌入多视图聚类[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(3): 388-397. |
| [4] | 杨京虎, 段亮, 岳昆, 李忠斌. 基于子事件的对话长文本情感分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(3): 483-493. |
| [5] | 仲兆满, 熊玉龙, 黄贤波. 基于异构集成学习的多元文本情感分析研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(3): 471-482. |
| [6] | 周业瀚, 沈子钰, 周清, 李云. 基于生成式对抗网络的自监督多元时间序列异常检测方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 256-262. |
| [7] | 宋雨, 肖玉柱, 宋学力. 基于伪标签回归和流形正则化的无监督特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 263-272. |
| [8] | 冯海, 马甲林, 许林杰, 杨宇, 谢乾. 融合标签嵌入和知识感知的多标签文本分类方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 273-281. |
| [9] | 卞苏阳, 严云洋, 龚成张, 冷志超, 祝巧巧. 基于CXANet⁃YOLO的火焰检测方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 295-301. |
| [10] | 崔凡, 强继朋, 朱毅, 李云. 基于ChineseBert的中文拼写纠错方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 302-312. |
| [11] | 宋耀莲, 殷喜喆, 杨俊. 基于时空特征学习Transformer的运动想象脑电解码方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | 操东林, 崔超然, 杨潇. 基于深度强化学习的国内金融市场投资比较研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 333-342. |
| [13] | 刘佳慧, 袁卫华, 曹家伟, 张涛, 张志军. 基于用户特征聚类与服务质量预测的推荐方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(1): 120-133. |
| [14] | 崔瑞华, 綦小龙, 刘艳芳, 林玲. 面向概念漂移数据流的在线集成自适应算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(1): 134-144. |
| [15] | 陈瑞, 徐金东, 刘兆伟, 阎维青, 王璇, 宋永超, 倪梦莹. 基于模糊空谱特征的高光谱图像分类[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(1): 145-154. |
|
||