南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 302–312.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2023.02.013
基于ChineseBert的中文拼写纠错方法
- 扬州大学信息工程学院,扬州,225127
Chinese spelling correction method based on ChineseBert
Fan Cui, Jipeng Qiang( ), Yi Zhu, Yun Li
), Yi Zhu, Yun Li
- School of Information Engineering,Yangzhou University,Yangzhou,225127,China
摘要:
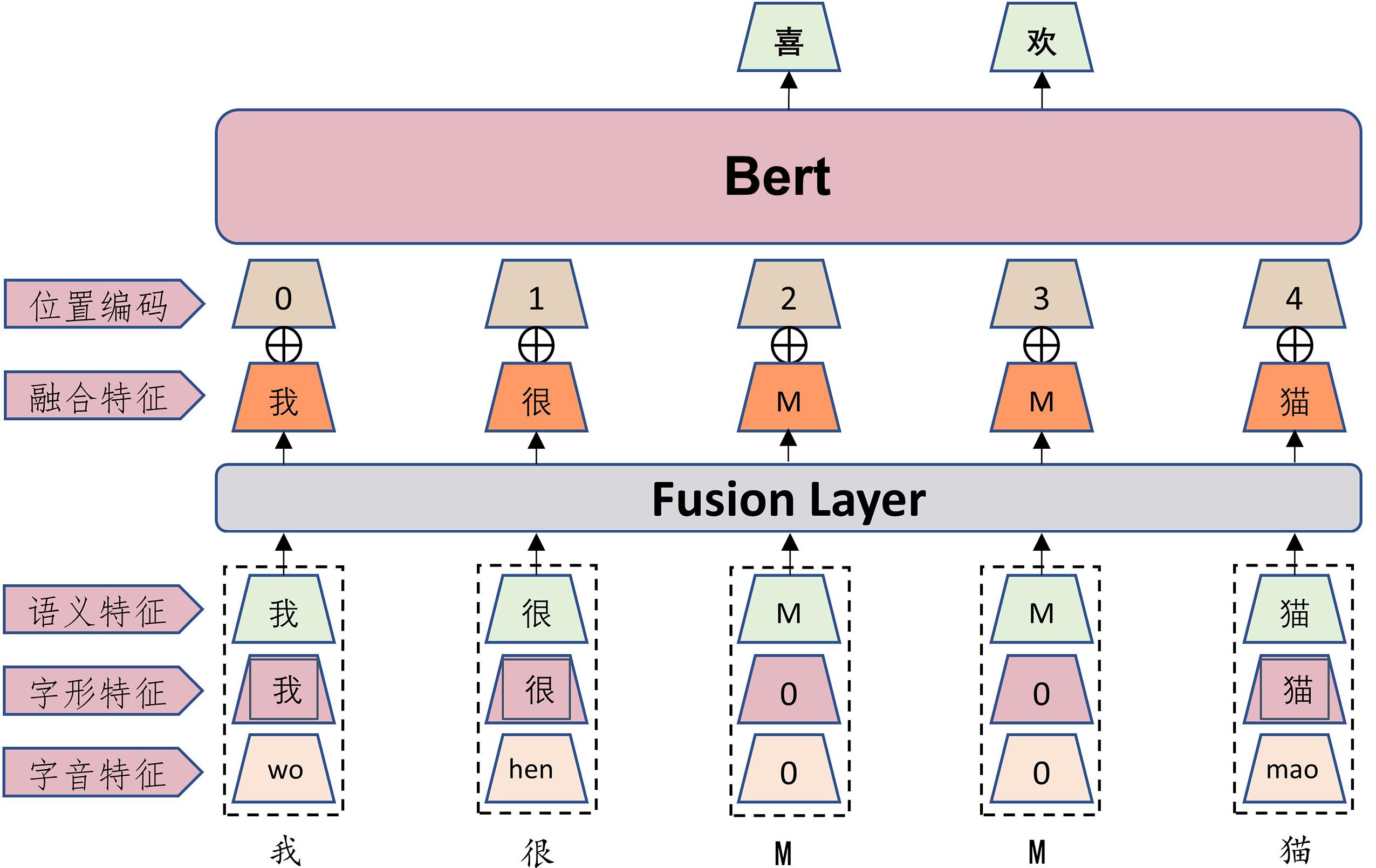
中文拼写错误主要集中在拼音相似和字形相似两个方面,而通用的预训练语言模型只考虑文本的语义信息,忽略了中文的拼音和字形特征.最新的中文拼写纠错(Chinese Spelling Correction,CSC)方法在预训练模型的基础上利用额外的网络来融入拼音和字形特征,但和直接微调预训练模型相比,改进的模型没有显著提高模型的性能,因为由小规模拼写任务语料训练的拼音和字形特征,和预训练模型获取的丰富语义特征相比,存在严重的信息不对等现象.将多模态预训练语言模型ChineseBert应用到CSC问题上,由于ChineseBert已将拼音和字形信息放到预训练模型构建阶段,基于ChineseBert的CSC方法不仅无须构建额外的网络,还解决了信息不对等的问题.由于基于预训练模型的CSC方法普遍不能很好地处理连续错误的问题,进一步提出SepSpell方法.首先利用探测网络检测可能错误的字符,再对可能错误的字符保留拼音特征和字形特征,掩码对应的语义信息进行预测,这样能降低预测过程中错误字符带来的干扰,更好地处理连续错误问题.在三个官方评测数据集上进行评估,提出的两个方法都取得了非常不错的结果.
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | Gao J F, Li X L, Micol D,et al. A large scale ranker?based system for search query spelling correction∥Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Beijing,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2010:358-366. |
| 2 | Hong Y Z, Yu X G, He N,et al. FASPell:A fast,adaptable,simple,powerful Chinese spell checker based on DAE?decoder paradigm∥Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Noisy User?generated Text. HongKong,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:160-169. |
| 3 | Burstein J, Chodorow M. Automated essay scoring for nonnative English speakers∥Proceedings of a Symposium on Computer Mediated Language Assessment and Evaluation in Natural Language Processing. College Park,Maryland:Association for Computational Linguistics,1999:68-75. |
| 4 | Xie W J, Huang P J, Zhang X R,et al. Chinese spelling check system based on N?gram model∥Proceedings of the 8th SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing. Beijing,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2015:128-136. |
| 5 | Yeh J F, Li S F, Wu M R,et al. Chinese word spelling correction based on n?gram ranked inverted index list∥Proceedings of the 7th SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing. Nagoya,Japan:Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing,2013:43-48. |
| 6 | Yu J J, Li Z H. Chinese spelling error detection and correction based on language model,pronunciation,and shape∥Proceedings of The 3rd CIPS?SIGHAN Joint Conference on Chinese Language Processing. Wuhan,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2014:220-223. |
| 7 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K,et al. Bert:Pre?training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding∥Proceedings of 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies,Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers). Minneapolis,MI,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:4171-4186. |
| 8 | Cui Y M, Che W X, Liu T,et al. Pre?training with whole word masking for Chinese BERT. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2021(29):3504-3514. |
| 9 | Liu C L, Lai M H, Tien K W,et al. Visually and phonologically similar characters in incorrect Chinese words:Analyses,identification,and applications. ACM Transactions on Asian Language Information Processing,2011,10(2):10. |
| 10 | Cheng X Y, Xu W D, Chen K L,et al. SpellGCN:Incorporating phonological and visual similarities into language models for Chinese spelling check∥Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Seatle,Washington DC,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2020:871-881. |
| 11 | Xu H D, Li Z L, Zhou Q Y,et al. Read,listen,and see:Leveraging multimodal information helps Chinese spell checking∥Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Bangkok, Thailand:Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:716-728. |
| 12 | Huang L, Li J J, Jiang W W,et al. PHMOSpell:Phonological and morphological knowledge guided Chinese spelling check∥Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1:Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand:Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:5958-5967. |
| 13 | Sun Z J, Li X Y, Sun X F,et al. ChineseBERT:Chinese pretraining enhanced by glyph and pinyin information∥Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1:Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand:Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:2065-2075. |
| 14 | Wang B X, Che W X, Wu D Y,et al. Dynamic connected networks for Chinese spelling check∥Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Bangkok, Thailand:Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:2437-2446. |
| 15 | Clark K, Luong M T, Le Q V,et al. Electra:Pre?training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators∥The 8th International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa,Ethiopia:OpenReview.net,2020,. |
| 16 | Wu S H, Liu C L, Lee L H. Chinese spelling check evaluation at SIGHAN bake?off 2013∥Proceedings of the 7th SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing. Nagoya,Japan:Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing,2013:35-42. |
| 17 | Yu L C, Lee L H, Tseng Y H,et al. Overview of SIGHAN 2014 bake?off for Chinese spelling check∥Proceedings of the 3rd CIPS?SIGHAN Joint Conference on Chinese Language Processing. Wuhan,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2014:126-132. |
| 18 | Tseng Y H, Lee L H, Chang L P,et al. Introduction to SIGHAN 2015 bake?off for Chinese spelling check∥Proceedings of the 8th SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing. Beijing,China:Association for Computational Linguistics,2015:32-37. |
| 19 | Rao G Q, Gong Q, Zhang B l,et al. Overview of NLPTEA?2018 share task Chinese grammatical error diagnosis∥/Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications. Melbourne,Australia:Association for Computational Linguistics,2018:42-51. |
| 20 | Fu R J, Pei Z Q, Gong J F,et al. Chinese grammatical error diagnosis using statistical and prior knowledge driven features with probabilistic ensemble enhancement∥Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications. Melbourne,Australia:Association for Computational Linguistics,2018:52-59. |
| 21 | Wang D M, Song Y, Li J,et al. A hybrid approach to automatic corpus generation for Chinese spelling check∥Proceedings of 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Brussels,Belgium:Association for Computational Linguistics,2018:2517-2527. |
| 22 | Wang D M, Tay Y, Zhong L. Confusionset?guided pointer networks for Chinese spelling check∥Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Florence,Italy:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:5780-5785. |
| 23 | Zhang S H, Huang H R, Liu J C,et al. Spelling error correction with soft?masked BERT∥Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Seatle,Washington DC,USA:Association for Computational Linguistics,2020:882-890. |
| 24 | Guo Z, Ni Y, Wang K Q,et al. Global attention decoder for Chinese spelling error correction∥Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Bangkok, Thailand: Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:1419-1428. |
| 25 | Wang S, Shang L. Improve Chinese spelling check by reevaluation∥The26th Pacific?Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2022:237-248. |
| [1] | 朱伟,张帅,辛晓燕,李文飞,王骏,张建,王炜. 结合区域检测和注意力机制的胸片自动定位与识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 591-600. |
| [2] | 罗春春,郝晓燕. 基于双重注意力模型的微博情感倾向性分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(2): 236-243. |
| [3] | 韩普,刘亦卓,李晓艳. 基于深度学习和多特征融合的中文电子病历实体识别研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 942-951. |
| [4] | 范 君, 业巧林, 业 宁. 基于线性鉴别的无参数局部保持投影算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(2): 211-220. |
| [5] | 阚建飞, 任永峰, 翟继友, 董学育, 霍 瑛. 基于稀疏模型和Gabor小波字典的跟踪算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 85-91. |
| [6] | 严云洋, 瞿学新, 朱全银, 李 翔, 赵 阳. 基于离群点检测的分类结果置信度的度量方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 102-109. |
|
||