南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 21–28.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.01.003
基于深度主动学习的甲状腺癌病理图像分类方法
- 1.西安电子科技大学电子工程学院, 西安, 710071
2.空军军医大学基础医学院病理学教研室, 西安, 710071
3.空军军医大学生物医学工程系, 西安, 710071
Papillary thyroid carcinoma pathological image classification based on deep active learning
Meng Zhang1, Bing Han1( ), Zhe Wang2, Fusheng You3, Haoran Li1
), Zhe Wang2, Fusheng You3, Haoran Li1
- 1.School of Electronic Engineering,Xidian University,Xi'an,710071,China
2.Teaching and Research Section of Pathology,School of Basic Medicine,Air Force Medical University,Xi'an,710071,China
3.School of Biomedical Engineering,Air Force Medical University,Xi'an,710071,China
摘要:
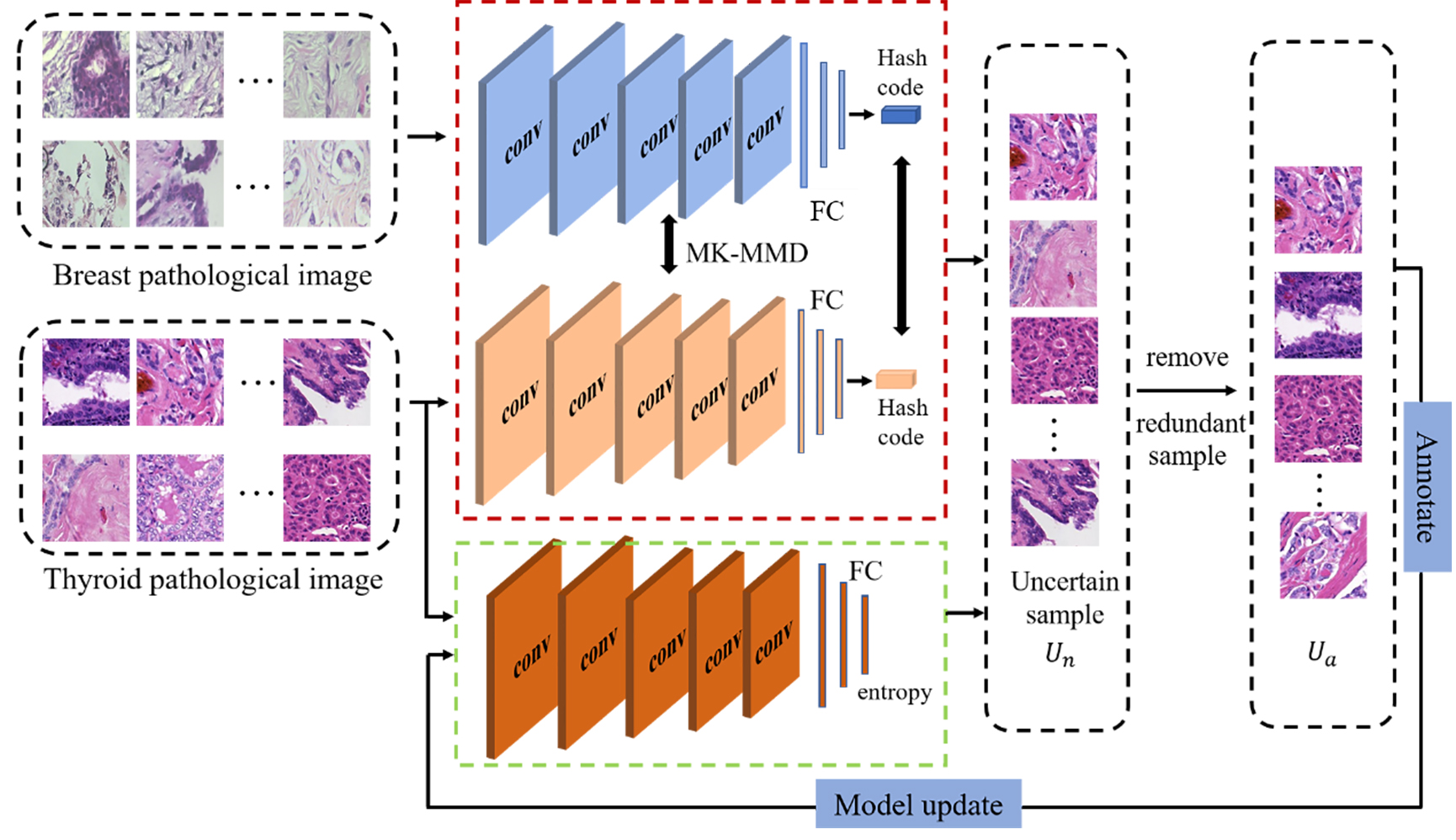
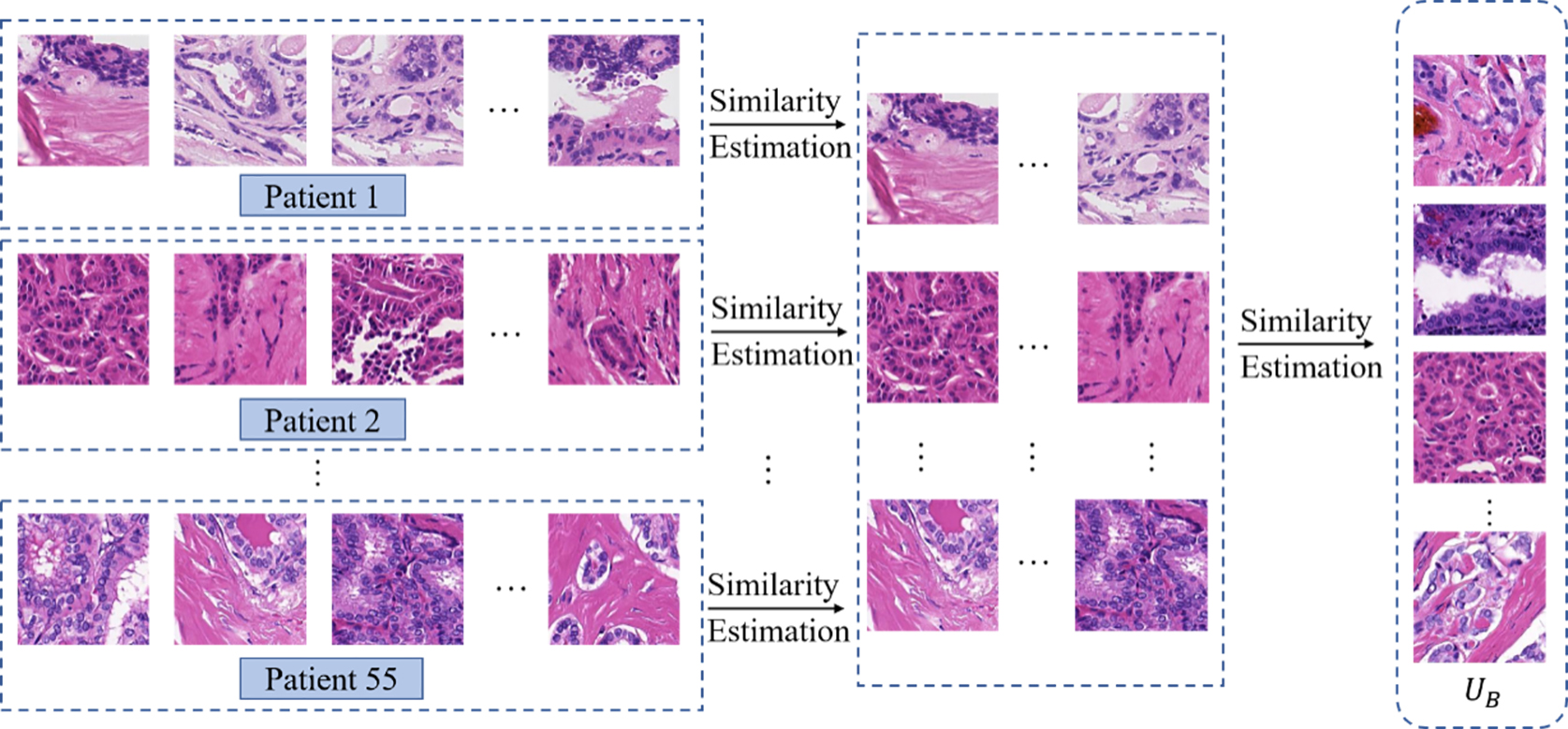
甲状腺癌是内分泌系统最常见的恶性肿瘤,甲状腺病理图像对于甲状腺癌的分级、预后和后续治疗有重要的指导作用.近年来,深度学习在病理图像分类分级中表现出色,然而,为了获得良好的分类性能,这些方法往往需要大量的标注数据.众所周知,医学图像的手动注释非常繁琐、耗时,并且需要领域知识的指导.为了降低标注成本,提出一种将卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Networks,CNN)和主动学习相结合的分类方法,无须标记所有数据,仅选择少量样本进行标注.此方法利用CNN提取病理图像的特征,进而使用该特征计算未标注样本的不确定性和相似性,选择“有价值”的样本;然后由病理学家对选定的样本进行标注,并不断微调网络以增强模型的分类性能.在甲状腺病理图像上的实验结果表明,该方法能够在不牺牲最终分类准确率的情况下降低标记成本.
中图分类号:
- TP183
| 1 | Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global,regional,and national cancer incidence,mortality,years of life lost,years lived with disability,and disability?adjusted life?years for 32 cancer groups,1990 to 2015:a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncology,2017,3(4):524-548. |
| 2 | 黄庆文,陈伊,李华贵. 甲状腺癌CT、B超诊断与病理诊断对照分析研究. 中外医疗,2017,36(28):179-180,183. |
| Huang Q W,Chen Y,Li H G,et al. Comparative analysis of CT diagnosis,B ultrasound diagnosis and patho?logical diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma. China Foreign Medical Treatment,2017,36(28):179-180,183. | |
| 3 | 陈健. 精确病理诊断在甲状腺癌精准医疗中的意义. 中国肿瘤临床,2017,44(4):181-185. |
| Chen J. Accurate pathological diagnosis of thyroid cancer in the era of precision medicine. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology,2017,44(4):181-185. | |
| 4 | 王伟. 甲状腺乳头状癌颈部转移淋巴结清扫研究进展. 硕士学位论文. 蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2015. |
| Wang W. Research progress in metastatic cervical lymph node dissection of thyroid papillary carcinoma. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bengbu:Bengbu Medical College,2015. | |
| 5 | Venkateswara H,Eusebio J,Chakraborty S,et al. Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:5018-5027. |
| 6 | Abe N,Mamitsuka H. Query learning strategies using boosting and bagging∥Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Machine Learning. San Francisco,CA,USA:Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.,1998,388:1-9. |
| 7 | Ebert S,Fritz M,Schiele B. RALF:a reinforced active learning formulation for object class recognition∥2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence,RI,USA:IEEE,2012:3626-3633. |
| 8 | Huang S J,Jin R,Zhou Z H. Active learning by querying informative and representative examples∥Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook,NY,USA:Curran Associates Inc.,2010:892-900. |
| 9 | Tang Y P,Huang S J. Self?paced active learning:Query the right thing at the right time∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2019,33:5117-5124. |
| 10 | Wang D,Shang Y. A new active labeling method for deep learning∥2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Beijing,China:IEEE,2014:112-119. |
| 11 | Li J M. Notice of removal:active learning for hyperspectral image classification with a stacked autoencoders based neural network∥2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Phoenix,AZ,USA:IEEE,2016:1062-1065. |
| 12 | Stark F,Hazirba? C,Triebel R,et al. CAPTCHA recognition with active deep learning∥German Conference on Pattern Recognition Workshop. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2015:94-101. |
| 13 | Al Rahhal M M,Bazi Y,AlHichri H,et al. Deep learning approach for active classification of electrocardiogram signals. Information Sciences,2016,345:340-354. |
| 14 | Zhou Z W,Shin J,Zhang L,et al. Fine?tuning convolutional neural networks for biomedical image analysis:actively and incrementally∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:7340-7349. |
| 15 | Yang L,Zhang Y Z,Chen J X,et al. Suggestive annotation:a deep active learning framework for biomedical image segmentation∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer?Assisted Intervention. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2017:399-407. |
| 16 | Camelyon. . |
| 17 | Zhou Z W,Shin J,Feng R B,et al. Integrating active learning and transfer learning for carotid intima?media thickness video interpretation. Journal of Digital Imaging,2019,32(2):290-299. |
| 18 | Vedaldi A,Lenc K. MatConvNet:convolutional neural networks for MATLAB∥The 23rd ACM International Conference. Brisbane,Australia:ACM, 2015:689-692. |
| 19 | Lewis D D,Gale W A. A sequential algorithm for training text classifiers∥Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1994:3-12. |
| [1] | 曾宪华, 陆宇喆, 童世玥, 徐黎明. 结合马尔科夫场和格拉姆矩阵特征的写实类图像风格迁移[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 1-9. |
| [2] | 余方超, 方贤进, 张又文, 杨高明, 王丽. 增强深度学习中的差分隐私防御机制[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1): 10-20. |
| [3] | 潘越,王骏,李文飞,张建,王炜. 基于卷积神经网络的蛋白质折叠类型最小特征提取[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(5): 744-753. |
| [4] | 汪敏,赵飞,闵帆. 储层预测的代价敏感主动学习算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 561-569. |
| [5] | 朱伟,张帅,辛晓燕,李文飞,王骏,张建,王炜. 结合区域检测和注意力机制的胸片自动定位与识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 591-600. |
| [6] | 李康,谢宁,李旭,谭凯. 基于卷积神经网络和几何优化的统计染色体核型分析方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 116-124. |
| [7] | 李子龙,周勇,鲍蓉. AdaBoost图像到类距离学习的图像分类方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [8] | 张银芳,于洪,王国胤,谢永芳. 一种用于数据流自适应分类的主动学习方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 67-73. |
| [9] | 柴变芳,魏春丽,曹欣雨,王建岭. 面向网络结构发现的批量主动学习算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 1020-1029. |
| [10] | 韩普,刘亦卓,李晓艳. 基于深度学习和多特征融合的中文电子病历实体识别研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 942-951. |
| [11] | 张家精,夏巽鹏,陈金兰,倪友聪. 基于张量分解和深度学习的混合推荐算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 952-959. |
| [12] | 钟琪,冯亚琴,王蔚. 跨语言语料库的语音情感识别对比研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(5): 765-773. |
| [13] | 王蔚, 胡婷婷, 冯亚琴. 基于深度学习的自然与表演语音情感识别[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 660-666. |
| [14] | 黄 帷,闵 帆*,任 杰. 基于协同过滤加权预测的主动学习缺失值填补算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 758-. |
| [15] | 曹冬寅,王 琼*,张兴敢. 基于稀疏重构残差和随机森林的集成分类算法 [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(6): 1127-. |
|
||