南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 669–679.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2023.04.013
基于多维注意力机制的单通道语音增强方法
姚瑶1, 杨吉斌1( ), 张雄伟1(
), 张雄伟1( ), 陈乐乐1, 范君怡2
), 陈乐乐1, 范君怡2
- 1.陆军工程大学指挥控制工程学院,南京,210007
2.中国科学院声学研究所东海研究站,上海,201815
Single⁃channel speech enhancement based on multi⁃dimensional attention mechanism
Yao Yao1, Jibin Yang1( ), Xiongwei Zhang1(
), Xiongwei Zhang1( ), Lele Chen1, Junyi Fan2
), Lele Chen1, Junyi Fan2
- 1.School of Command and Control Engineering,Army Engineering University,Nanjing, 210007,China
2.Shanghai Acoustics Laboratory,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai,201815, China
摘要:
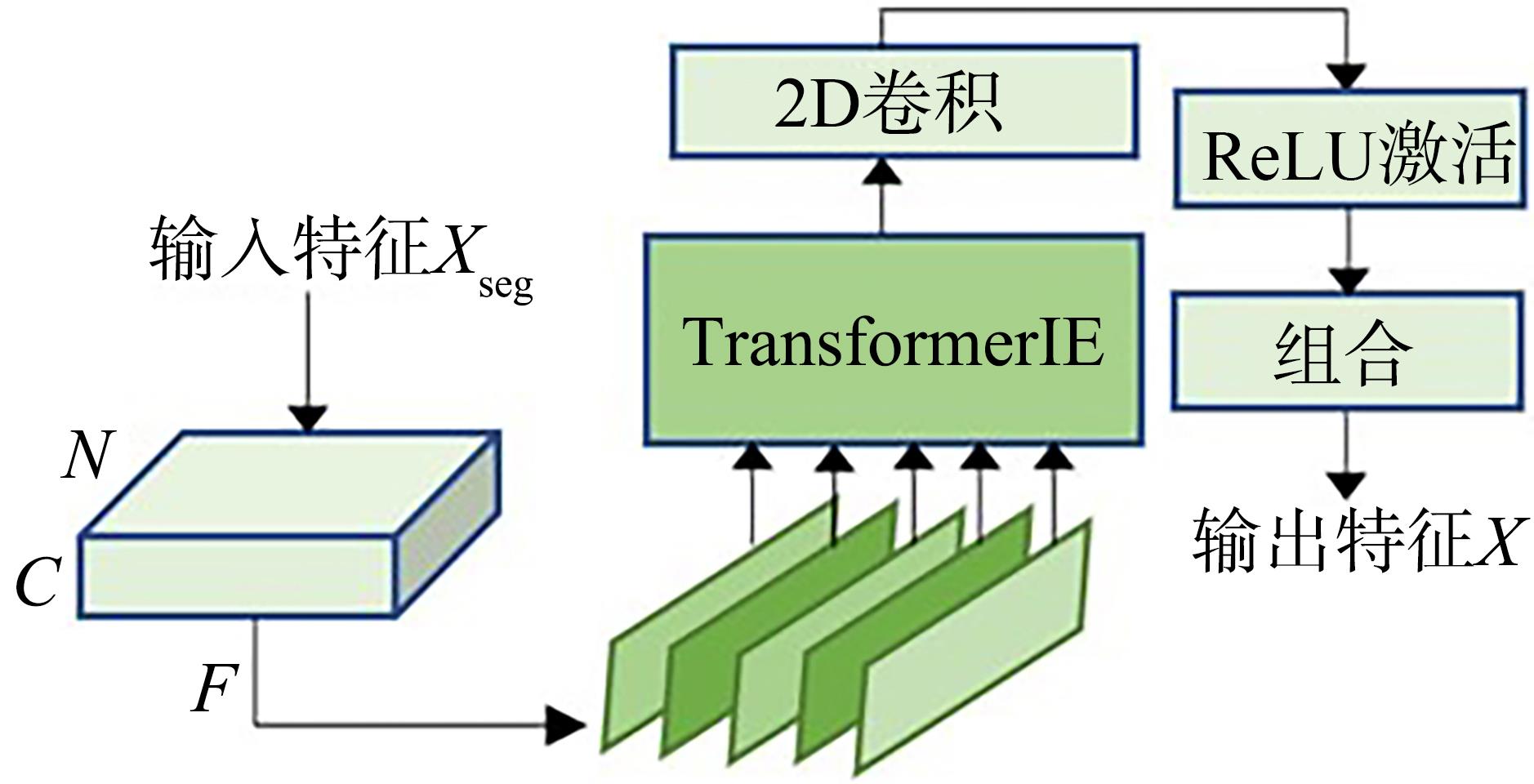
基于深度学习的单通道语音增强技术能有效改善语音增强的质量,但在低信噪比环境下,语音增强的效果不能令人满意.为了改善低信噪比下单通道语音增强的质量,提出一种多维注意力机制(Multi?Dimensional Attention Mechanism,MDAM),通过将通道注意力和全局、局部时间注意力进行级联,充分挖掘深度神经网络各通道间语音特征的长短时相关性.在此基础上,设计了基于多维注意力机制的时域语音增强网络MDAM?Net,采用跳跃连接的编解码结构获取深层语音特征,并采用MDAM充分关注干净语音特征在网络通道间、时间方向上全局与局部范围的变化差异,可以更好地建模语音特征的上下文联系.仿真实验的结果表明,在保持较低模型参数量条件下,MDAM?Net在VoiceBank?DEMAND公开数据集上增强语音的PESQ(Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality)评分可以达到3.25.在低信噪比条件下,增强语音质量显著优于已有的单通道语音增强模型.
中图分类号:
- TN912
| 1 | Sun Z Y, Li Y D, Jiang H J,et al. A supervised speech enhancement method for smartphone?based binaural hearing aids. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems,2020,14(5):951-960. |
| 2 | 徐勇. 基于深层神经网络的语音增强方法研究. 博士学位论文. 合肥:中国科学技术大学,2015. |
| Xu Y. Research on deep neural network based speech enhancement. Ph.D. Dissertation. Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China,2015. | |
| 3 | 魏泉水. 基于深度神经网络的语音增强算法研究. 硕士学位论文. 南京:南京大学,2016. |
| Wei Q S. Research on speech enhancement algorithm based on deep neural network. Master Dissertation. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2016. | |
| 4 | 叶文政. 基于深度学习的极低信噪比语音增强方法. 硕士学位论文. 成都:电子科技大学,2021. |
| Ye W Z. Extremely low signal?to?noise ratio speech enhancement method based on deep learning. Master Dissertation. Chengdu:University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,2021. | |
| 5 | Hao X, Su X D, Wang Z Y,et al. UNetGAN:A robust speech enhancement approach in time domain for extremely low signal?to?noise ratio condition∥The 20th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Graz,Austria:ISCA,2019:1786-1790. |
| 6 | Weninger F, Hershey J R, Le Roux J,et al. Discriminatively trained recurrent neural networks for single?channel speech separation∥2014 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing. Atlanta,GA,USA:IEEE,2014:577-581. |
| 7 | Pandey A, Wang D L. TCNN:Temporal convolutional neural network for real?time speech enhancement in the time domain∥2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Brighton,UK:IEEE,2019:6875-6879. |
| 8 | Macartney C, Weyde T. Improved speech enhance?ment with the wave?U?Net. 2018,arXiv:. |
| 9 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N,et al. Attention is all you need∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach,CA,USA:Curran Associates Inc.,2017:6000-6010. |
| 10 | Kim J, El?Khamy M, Lee J. T?GSA:Transformer with gaussian?weighted self?attention for speech enhancement//2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Barcelona,Spain:IEEE,2020:6649-6653. |
| 11 | Giri R, Isik U, Krishnaswamy A. Attention Wave?U?Net for speech enhancement∥2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics. New Paltz,NY,USA:IEEE,2019:249-253. |
| 12 | Pandey A, Wang D L. Dense CNN with self?attention for time?domain speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2021(29):1270-1279. |
| 13 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y,et al. CBAM:Convolutional block attention module∥Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2018:3-19. |
| 14 | Tolooshams B, Giri R, Song A H,et al. Channel?attention dense U?Net for multichannel speech enhancement∥2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Barcelona,Spain:IEEE,2020:836-840. |
| 15 | Park H J, Kang B H, Shin W,et al. MANNER:Multi?view attention network for noise erasure∥2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Singapore:IEEE,2022:7842-7846. |
| 16 | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze?and?excitation networks∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Confe?rence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City,UT,USA:IEEE,2018:7132-7141. |
| 17 | Sperber M, Niehues J, Neubig G,et al. Self?attentional acoustic models∥The 19th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communi?cation Association. Hyderabad,India:ISCA,2018:3723-3727. |
| 18 | Pandey A, Wang D L. On cross?corpus genera?lization of deep learning based speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2020(28):2489-2499. |
| 19 | Valentini-Botinhao C, Wang X, Takaki S,et al. Investigating RNN?based speech enhancement methods for noise?robust text?to?speech∥The 9th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop. Sunnyvale,CA,USA:ISCA,2016:146-152. |
| 20 | Veaux C, Yamagishi J, King S. The voice bank corpus:Design,collection and data analysis of a large regional accent speech database∥2013 International Conference Oriental COCOSDA Held Jointly with 2013 Conference on Asian Spoken Language Research and Evaluation. Gurgaon,India:IEEE,2013:1-4. |
| 21 | Thiemann J, Ito N, Vincent E. The diverse environments multi?channel acoustic noise database:A database of multichannel environmental noise recordings. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2013,133(S5):3591. |
| 22 | Rix A W, Beerends J G, Hollier M P,et al. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ):A new method for speecn quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs∥Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing. Salt Lake City,Utah,USA:IEEE,2001:749-752. |
| 23 | Taal C H, Hendriks R C, Heusdens R,et al. An algorithm for intelligibility prediction of time–frequency weighted noisy speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2011,19(7):2125-2136. |
| 24 | Hu Y, Loizou P C. Evaluation of objective quality measures for speech enhancement. IEEE Tran?sactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2008,16(1):229-238. |
| 25 | Pascual S, Bonafonte A, Serrà J. SEGAN:Speech enhancement generative adversarial network∥The 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Stockholm,Sweden:ISCA,2017:3642-3646. |
| 26 | Soni M H, Shah N, Patil H A. Time?frequency masking?based speech enhancement using generative adversarial network∥2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Calgary,AB,Canada:IEEE,2018:5039-5043. |
| 27 | Fu S W, Liao C F, Tsao Y,et al. MetricGAN:Generative adversarial networks based black?box metric scores optimization for speech enhancement∥The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach,CA,USA:PMLR,2019:2031-2041. |
| 28 | Yin D C, Luo C, Xiong Z W,et al. PHASEN:A phase?and?harmonics?aware speech enhancement network∥Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York,NY,USA:AAAI,2020:9458-9465. |
| 29 | Zhang Q Q, Nicolson A, Wang M J,et al. DeepMMSE:A deep learning approach to MMSE?based noise power spectral density estimation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2020(28):1404-1415. |
| 30 | Defossez A, Synnaeve G, Adi Y. Real time speech enhancement in the waveform domain∥The 21st Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Shanghai,China:ISCA,2020:3291-3295. |
| 31 | Wang K, He B B, Zhu W P. TSTNN:Two?stage transformer based neural network for speech enhancement in the time domain∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Toronto,Canada:IEEE,2021:7098-7102. |
| 32 | Kong Z F, Ping W, Dantrey A,et al. Speech denoising in the waveform domain with self?attention∥2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Singapore:IEEE,2022:7867-7871. |
| 33 | 范君怡,杨吉斌,张雄伟,等. U?net网络中融合多头注意力机制的单通道语音增强. 声学学报,2022,47(6):703-716. |
| Fan J Y, Yang J B, Zhang X W,et al. Monaural speech enhancement using U?net fused with multi?head self?attention. Acta Acustica,2022,47(6):703-716. |
| [1] | 谭嘉辰, 董永权, 张国玺. SSM: 基于孪生网络的糖尿病视网膜眼底图像分类模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(3): 425-434. |
| [2] | 宋耀莲, 殷喜喆, 杨俊. 基于时空特征学习Transformer的运动想象脑电解码方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 313-321. |
| [3] | 唐伟佳, 张华, 侯志荣. 基于空间卷积融合的中文文本匹配方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(5): 868-875. |
| [4] | 井花花, 晏涛, 刘渊. 融合全局和局部特征的光场图像空间超分辨率算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(2): 298-308. |
|
||