南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 115–134.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.01.012
• • 上一篇
开放集识别研究综述
- 天津大学智能与计算学部,天津,300350
A survey on open set recognition
- College of Intelligence and Computing,Tianjin University,Tianjin,300350,China
摘要:
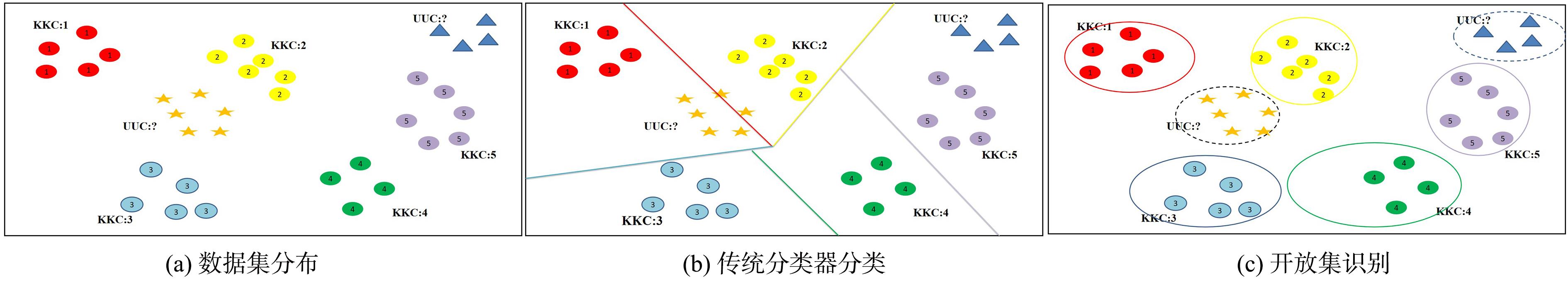
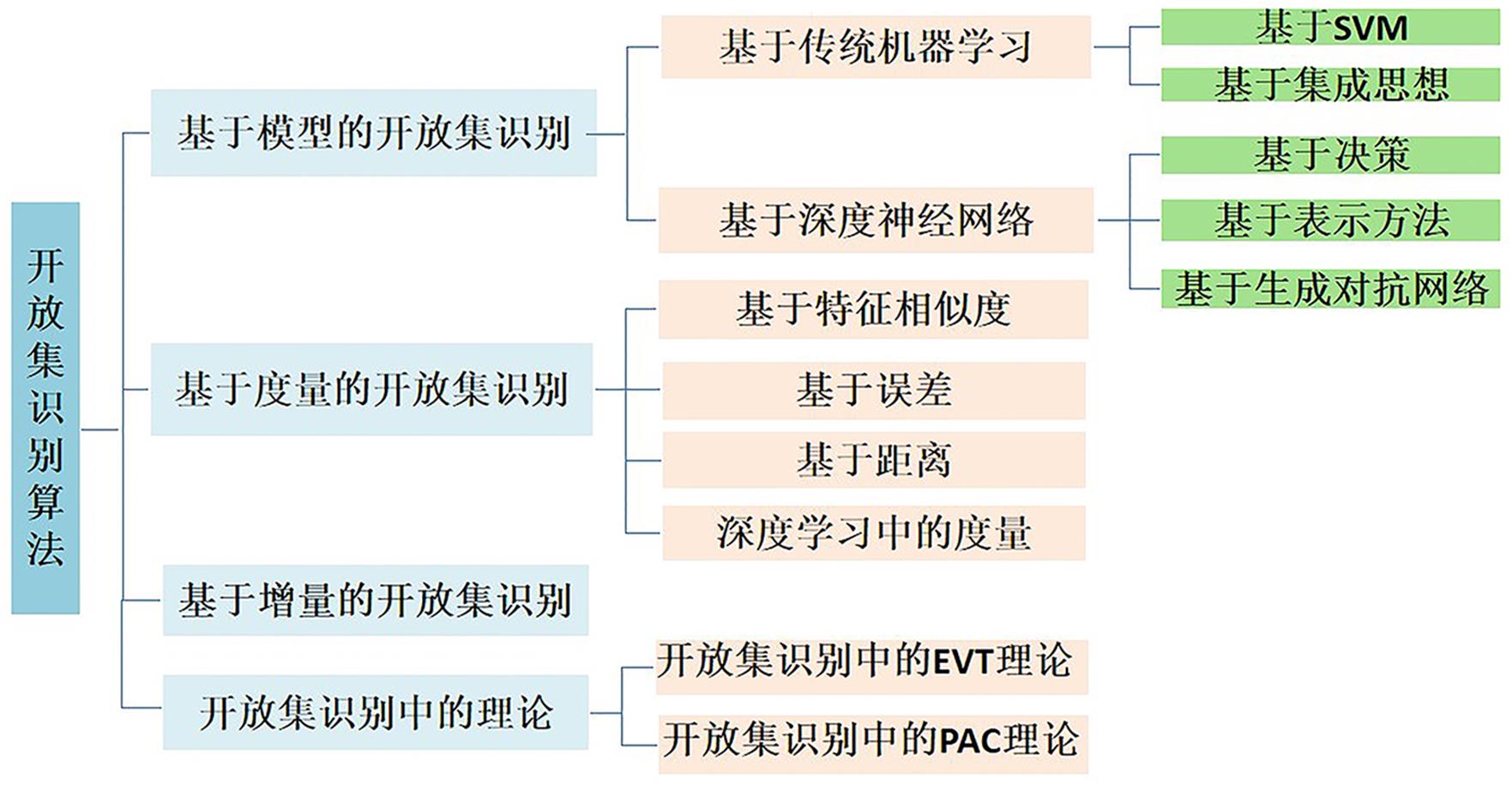
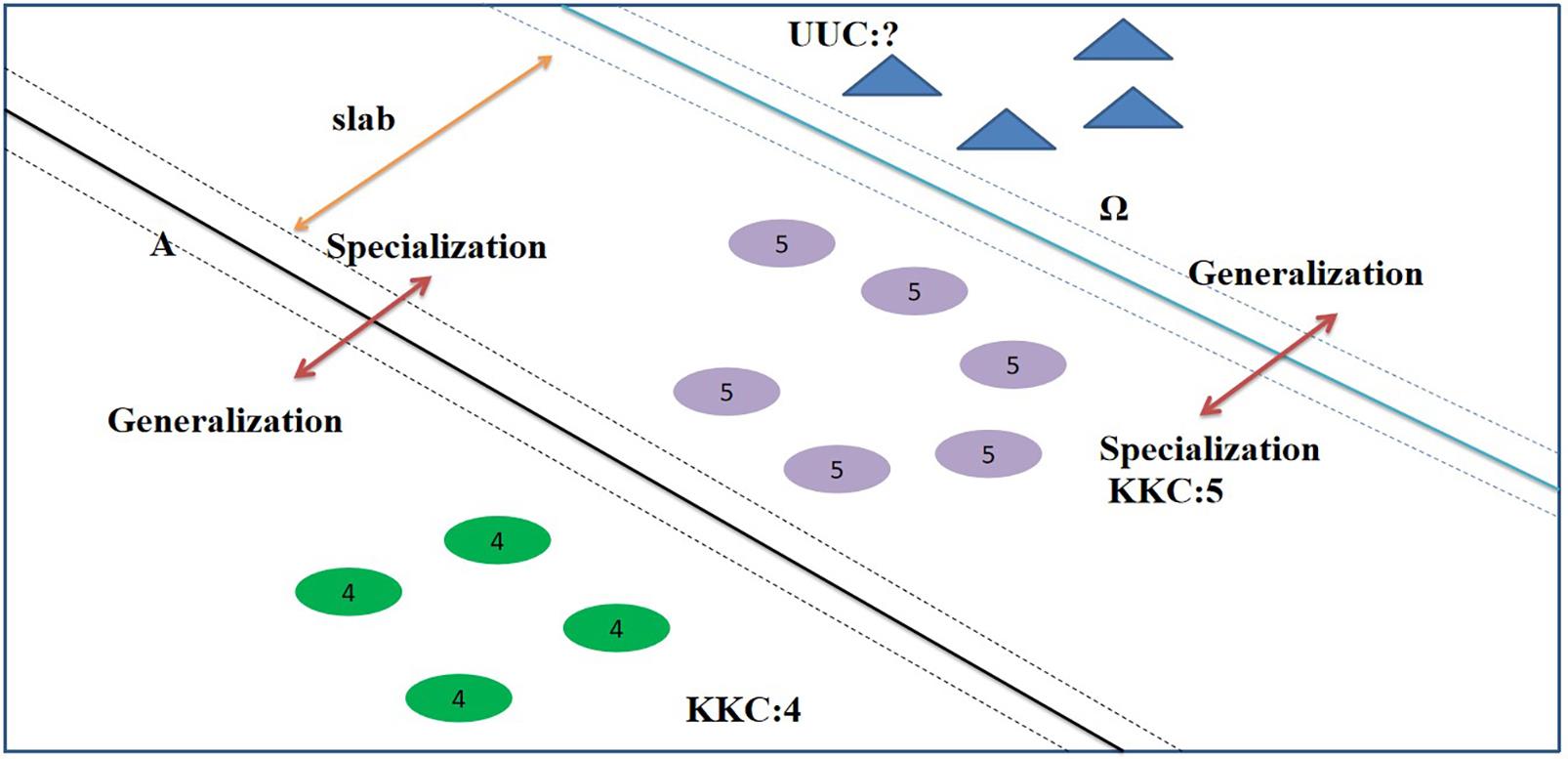
传统机器学习方法和深度神经网络在训练模型的过程中都需要大量标记样本作为支撑,然而标记大量样本是一个耗费巨大的过程,并且真实场景变化莫测,获得所有类别的标记样本是不现实的.因此,研究者开始突破标记样本的限制,提出一种更符合现实的场景——开放集识别(Open Set Recognition,OSR).OSR要求建立的模型不仅能分类训练过程中出现的类别,还可以有效地处理未见过的类别.近年来,OSR迅速发展成为热点领域,大量的工作围绕OSR展开.对现有的OSR工作进行总结:首先,从定义上将OSR与其他相关工作进行区分;其次,按照模型建立、度量选择、增量特点对OSR算法进行总结,并介绍了OSR的两种理论;最后展望了OSR未来的发展方向.
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | Shaout A,Kaja N,Awad S. A smart traffic sign recognition system∥2015 11th International Computer Engineering Conference. Cairo,Egypt:IEEE,2015:157-162. |
| 2 | Chellappa R,Wilson C L,Sirohey S. Human and machine recognition of faces:A survey. Proceedings of the IEEE,1995,83(5):705-741. |
| 3 | Daugman J. Face and gesture recognition:Overview. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1997,19(7):675-676. |
| 4 | Zhao W,Chellappa R,Phillips P J,et al. Face recognition:A literature survey. ACM Computing Surveys,2003,35(4):399-458. |
| 5 | Krizhevsky A,Sutskever I,Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks∥Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe,Nevada:Curran Associates Inc.,2012:1097-1105. |
| 6 | Gregor K,Danihelka I,Graves A,et al. DRAW:A recurrent neural network for image generation∥Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille,France:JMLR.org,2015:1462-1471. |
| 7 | Palatucci M,Pomerleau D,Hinton G,et al. Zero?shot learning with semantic output codes∥Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver,Canada:Curran Associates Inc.,2009:1410-1418. |
| 8 | Phillips P J,Grother P,Micheals R. Evaluation methods in face recognition∥Li S Z,Jain A K. Handbook of face recognition. Springer London,2011:551-574. |
| 9 | Li F Y,Wechsler H. Open set face recognition using transduction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2005,27(11):1686-1697. |
| 10 | Scheirer W J,de Rezende Rocha A,Sapkota A,et al. Toward open set recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2013,35(7):1757-1772. |
| 11 | Geng C X,Huang S J,Chen S C. Recent advances in open set recognition:A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2021,43(10):3614-3631. |
| 12 | Scheirer W J,Jain L P,Boult T E. Probability models for open set recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2014,36(11):2317-2324. |
| 13 | Dhamija A R,Günther M,Boult T E. Reducing network agnostophobia∥Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal,Canada:Curran Associates Inc.,2018:9157-9168. |
| 14 | Zhang H,Patel V M. Sparse representation?based open set recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(8):1690-1696. |
| 15 | Yang Y,Hou C P,Lang Y,et al. Open?set human activity recognition based on micro?Doppler signatures. Pattern Recognition,2019(85):60-69. |
| 16 | Geng C X,Chen S C. Collective decision for open set recognition. 2020,arXiv:. |
| 17 | Cardoso D O,Gama J,Fran?a F M G. Weightless neural networks for open set recognition. Machine Learning,2017,106(9-10):1547-1567. |
| 18 | Romera?Paredes B,Torr P H S. An embarrassingly simple approach to zero?shot learning∥Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille,France:JMLR.org,2015:2152-2161. |
| 19 | Kodirov E,Xiang T,Gong S G. Semantic autoencoder for zero?shot learning∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:4447-4456. |
| 20 | Bucher M,Herbin S,Jurie F. Improving semantic embedding consistency by metric learning for zero?shot classiffication∥Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam,The Netherlands:Springer,2016:730-746. |
| 21 | Norouzi M,Mikolov T,Bengio S,et al. Zero?shot learning by convex combination of semantic embeddings. 2014,arXiv:. |
| 22 | Zhang Z M,Saligrama V. Zero?shot learning via semantic similarity embedding∥Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago,Chile:IEEE,2015:4166-4174. |
| 23 | Zhang L,Xiang T,Gong S G. Learning a deep embedding model for zero?shot learning∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:3010-3019. |
| 24 | Frome A,Corrado G S,Shlens J,et al. DeViSE:A deep visual?semantic embedding model∥Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe,Nevada:Curran Associates Inc.,2013:2121-2129. |
| 25 | Akata Z,Perronnin F,Harchaoui Z,et al. Label?embedding for attribute?based classification∥Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland,OR,USA:IEEE,2013:819-826. |
| 26 | Chao W L,Changpinyo S,Gong B Q,et al. An empirical study and analysis of generalized zero?shot learning for object recognition in the wild∥Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam,The Netherlands:Springer,2016:52-68. |
| 27 | Jain L P,Scheirer W J,Boult T E. Multi?class open set recognition using probability of inclusion∥Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich,Switzerland:Springer,2014:393-409. |
| 28 | Bodesheim P,Freytag A,Rodner E,et al. Kernel null space methods for novelty detection∥Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland,OR,USA:IEEE,2013:3374-3381. |
| 29 | Tax D M J,Duin R P W. Growing a multi?class classifier with a reject option. Pattern Recognition Letters,2008,29(10):1565-1570. |
| 30 | Bendale A,Boult T. Towards open world recognition∥Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston,MA,USA:IEEE,2015:1893-1902. |
| 31 | Cortes C,Vapnik V. Support?vector networks. Machine Learning,1995,20(3):273-297. |
| 32 | Cevikalp H. Best fitting hyperplanes for classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(6):1076-1088. |
| 33 | Cevikalp H,Triggs B. Polyhedral conic classifiers for visual object detection and classification∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:4114-4122. |
| 34 | Kotz S,Nadarajah S. Extreme value distributions:Theory and applications. London:Impenial College Press,2000. |
| 35 | Scherreik M D,Rigling B D. Open set recognition for automatic target classification with rejection. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems,2016,52(2):632-642. |
| 36 | Gershman S J,Blei D M. A tutorial on Bayesian nonparametric models. Journal of Mathematical Psychology,2012,56(1):1-12. |
| 37 | Vareto R,Silva S,Costa F,et al. Towa rds open?set face recognition using hashing functions∥2017 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics. Denver,CO,USA:IEEE,2017:634-641. |
| 38 | Dong H Z,Fu Y W,Sigal L,et al. Learning to separate domains in generalized zero?shot and open set learning:A probabilistic perspective. 2021,arXiv:. |
| 39 | Neira M A C,Júnior P R M,Rocha A,et al. Data?fusion techniques for open?set recognition problems. IEEE Access,2018(6):21242-21265. |
| 40 | Matan O,Kiang R K,Stenard C E,et al. Handwritten character recognition using neural network architectures∥Proceedings of the 4th USPS Advanced Technology Conference. Washington DC,USA,1990:1003-1011. |
| 41 | Nguyen A,Yosinski J,Clune J. Deep neural networks are easily fooled:High confidence predictions for unrecognizable images∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston,MA,USA:IEEE,2015:427-436. |
| 42 | Goodfellow I J,Shlens J,Szegedy C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. 2015,arXiv:1412. 6572. |
| 43 | Szegedy C,Zaremba W,Sutskever I,et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks. 2014,arXiv:1312. 6199. |
| 44 | Bendale A,Boult T E. Towards open set deep networks∥Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,NV,USA:IEEE,2016:1563-1572. |
| 45 | Mensink T,Verbeek J,Perronnin F,et al. Distance?based image classification:Generalizing to new classes at near?zero cost. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2013,35(11):2624-2637. |
| 46 | Ristin M,Guillaumin M,Gall J,et al. Incremental learning of NCM forests for large?scale image classification∥Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus,OH,USA:IEEE,2014:3654-3661. |
| 47 | Rozsa A,Günther M,Boult T E. Adversarial robustness:Softmax versus openmax. 2017,arXiv:. |
| 48 | Venkataram V M. Open set text classification using neural networks. Master Dissertation. Colorado Springs:University of Colorado Colorado Springs,2018. |
| 49 | Shu L,Xu H,Liu B. DOC:Deep open classification of text documents. 2017,arXiv:. |
| 50 | Yang H M,Zhang X Y,Yin F,et al. Convolutional prototype network for open set recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2020,doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2020. 3045079. |
| 51 | Zhang H J,Li A,Guo J,et al. Hybrid models for open set recognition∥European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow,UK:Springer,2020:102-117. |
| 52 | Yoshihashi R,Shao W,Kawakami R,et al. Classification?reconstruction learning for open?set recognition∥Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,CA,USA:IEEE,2019:4011-4020. |
| 53 | Hassen M,Chan P K. Learning a neural?network?based representation for open set recognition. 2018,arXiv:. |
| 54 | Sun X,Yang Z N,Zhang C,et al. Conditional gaussian distribution learning for open set recognition∥Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle,WA,USA:IEEE,2020:13477-13486. |
| 55 | Perera P,Morariu V I,Jain R,et al. Generative?discriminative feature representations for openset recognition∥Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle,WA,USA:IEEE,2020:11811-11820. |
| 56 | Ge Z Y,Demyanov S,Chen Z T,et al. Generative OpenMax for multi?class open set classification. 2017,arXiv:. |
| 57 | Neal L,Olson M,Fern X,et al. Open set learning with counterfactual images∥Proceedings of the European Conference on 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich,Germany:Springer,2018:620-635. |
| 58 | Yu Y,Qu W Y,Li N,et al. Open?category classification by adversarial sample generation. 2017,arXiv:. |
| 59 | Ditria L,Meyer B J,Drummond T. OpenGAN:Open set generative adversarial networks∥Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision. 2020. |
| 60 | Fei G L,Liu B. Breaking the closed world assumption in text classification∥Proceedings of 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. San Diego,CA,USA:ACL,2016:506-514. |
| 61 | Fei G L,Liu B. Social media text classification under negative covariate shift∥Proceedings of 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Lisbon,Portugal:ACL,2015:2347-2356. |
| 62 | Wright J,Ma Y,Mairal J,et al. Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE,2010,98(6):1031-1044. |
| 63 | Peng J T,Li L Q,Tang Y Y. Maximum likelihood estimation?based joint sparse representation for the classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2019,30(6):1790-1802. |
| 64 | Wright J,Yang A Y,Ganesh A,et al. Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2009,31(2):210-227. |
| 65 | Cevikalp H,Yavuz H S. Fast and accurate face recognition with image sets∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:1564-1572. |
| 66 | Júnior P R M,De Souza R M,de O Werneck R,et al. Nearest neighbors distance ratio open?set classifier. Machine Learning,2017,106(3):359-386. |
| 67 | Meyer B J,Drummond T. The importance of metric learning for robotic vision:Open set recognition and active learning∥2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Montreal,Canada:IEEE,2019:2924-2931. |
| 68 | Schroff F,Kalenichenko D,Philbin J. FaceNet:A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering∥Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway,NJ,USA:IEEE,2015:815-823. |
| 69 | Song H O,Xiang Y,Jegelka S,et al. Deep metric learning via lifted structured feature embedding∥Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,NV,USA:IEEE,2016:4004-4012. |
| 70 | Sohn K. Improved deep metric learning with multi?class N?pair loss objective∥Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Proceedings Systems. Barcelona,Spain:Curran Associates Inc.,2016:1857-1865. |
| 71 | Kumar B G V,Carneiro G,Reid I. Learning local image descriptors with deep siamese and triplet convolutional networks by minimizing global loss functions∥Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,NV,USA:IEEE,2016:5385-5394. |
| 72 | Song H O,Jegelka S,Rathod V,et al. Learnable structured clustering framework for deep metric learning. 2017,arXiv:. |
| 73 | Harwood B,Kumar B G V,Carneiro G,et al. Smart mining for deep metric learning∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:2840-2848. |
| 74 | Meyer B J,Harwood B,Drummond T. Deep metric learning and image classification with nearest neighbour gaussian kernels∥2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Athens,Greece:IEEE,2018:151-155. |
| 75 | Shu Y,Shi Y M,Wang Y W,et al. P?ODN:Prototype based open deep network for open set recognition. 2020,arXiv:. |
| 76 | Chen G Y,Peng P X,Wang X Q,et al. Adversarial reciprocal points learning for open set recognition. 2021,arXiv:. |
| 77 | Chen G Y,Qiao L M,Shi Y M,et al. Learning open set network with discriminative reciprocal points. 2020,arXiv:. |
| 78 | De Rosa R,Mensink T,Caputo B. Online open world recognition. 2016,arXiv:. |
| 79 | Rudd E M,Jain L P,Scheirer W J,et al. The extreme value machine. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2018,40(3):762-768. |
| 80 | Günther M,Cruz S,Rudd E M,et al. Toward open?set face recognition∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu,HI,USA:IEEE,2017:573-582. |
| 81 | Henrydoss J,Cruz S,Rudd E M,et al. Incremental open set intrusion recognition using extreme value machine∥2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. Cancun,Mexico:IEEE,2017:1089-1093. |
| 82 | Oza P,Patel V M. Deep cnn?based multi?task learning for open?set recognition. 2019,arXiv:. |
| 83 | Mundt M,Pliushch I,Majumder S,et al. Open set recognition through deep neural network uncertainty:Does out?of?distribution detection require generative classifiers?∥Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Seoul,Korea (South):IEEE,2019:753-757. |
| 84 | Vignotto E,Engelke S. Extreme value theory for open set classification:GPD and GEV classifiers. 2019,arXiv:. |
| 85 | Liu S,Garrepalli R,Dietterich T G,et al. Open category detection with PAC guarantees∥Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm,Sweden,2018:3169-3178. |
| 86 | LeCun Y,Bottou L,Bengio Y,et al. Gradient?based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE,1998,86(11):2278-2324. |
| 87 | Netzer Y,Wang T,Coates A,et al. Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning.http:∥citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/showciting?doi=10.1.1.231.6173,2020-03-20. |
| 88 | Bilenko M,Basu S,Mooney R J. Integrating constraints and metric learning in semi?supervised clustering∥Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Machine Learning. Banff,Canada:ACM,2004:81-88. |
| 89 | Frey P W,Slate D J. Letter recognition using Holland?style adaptive classifiers. Machine Learning,1991,6(2):161-182. |
| 90 | Krizhevsky A. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Technical Report. Toronto:University of Toronto,2009. |
| 91 | Nene S A,Nayar S K,Murase H. Columbia object image library (COIL?20). Technical Report CUCS?005?96. Columbia University,1996. |
| 92 | Georghiades A S,Belhumeur P N,Kriegman D J. From few to many:Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2001,23(6):643-660. |
| 93 | Le Y,Yang X. Tiny ImageNet visual recognition challenge∥CS 231N. 2015. |
| 94 | Grif?n G,Holub A,Perona P. Caltech?256 object category dataset. Technical Report 7694. California Institute of Technology,2007. |
| 95 | Deng J,Dong W,Socher R,et al. ImageNet:A large?scale hierarchical image database∥Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami,FL,USA:IEEE,2009:248-255. |
| 96 | Dalal N,Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection∥2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego,CA,USA:IEEE,2005,1:886-893. |
| 97 | Sapkota A,Parks B,Scheirer W,et al. FACE?GRAB:Face recognition with general region assigned to binary operator∥2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition?Workshops. San Francisco,CA,USA:IEEE,2010:82-89. |
| 98 | Sokolova M,Lapalme G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Information Processing & Management,2009,45(4):427-437. |
| 99 | Sokolova M,Japkowicz N,Szpakowicz S. Beyond accuracy,F?score and ROC:A family of discriminant measures for performance evaluation∥Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Hobart,Australia:Springer,2006:1015-1021. |
| 100 | Cai W L,Chen S C,Zhang D Q. A multiobjective simultaneous learning framework for clustering and classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,2010,21(2):185-200. |
| 101 | Qian Q,Chen S C,Cai W L. Simultaneous clustering and classification over cluster structure representation. Pattern Recognition,2012,45(6):2227-2236. |
| 102 | Zhao B,Wu X,Feng J S,et al. Diversified visual attention networks for fine?grained object classification. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia,2017,19(6):1245-1256. |
| 103 | Qin S J. An overview of subspace identification. Computers & Chemical Engineering,2006,30(10-12):1502-1513. |
| 104 | Qu Y Y,Lin L,Shen F M,et al. Joint hierarchical category structure learning and large?scale image classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2017,26(9):4331-4346. |
| 105 | Pan S J,Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2010,22(10):1345-1359. |
| 106 | Busto P P,Gall J. Open set domain adaptation∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:754-763. |
| 107 | Saito K,Yamamoto S,Ushiku Y,et al. Open set domain adaptation by backpropagation∥Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich,Germany:Springer,2018:156-171. |
| 108 | 刘晓龙,王士同. 面向开放集图像分类的模糊域自适应方法. 计算机科学与探索,2021,15(3):515-523. |
| Liu X L,Wang S T. Fuzzy domain adaptation algorithm for open set image classification. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology,2021,15(3):515-523. | |
| 109 | 刘晓龙,王士同. 渐进式分离的开放集模糊域自适应方法. 计算机应用,2021,41(11):3127-3131. |
| Liu X L,Wang S T. Open?set fuzzy domain adaptation algorithm via progressive separation. Journal of Computer Applications,2021,41(11):3127-3131. | |
| 110 | Szepesvári C. Algorithms for reinforcement learning. Synthesis lectures on artificial intelligence and machine learning. San Franscisco,CA,USA:Morgan & Claypool,2010. |
| 111 | Shao R,Perera P,Yuen P C,et al. Open?set adversarial defense∥16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow,UK,USA,2020:682-698. |
| 112 | Yang Q,Liu Y,Chen T J,et al. Federated machine learning:Concept and applications. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology,2019,10(2):Article No. 12. |
| [1] | 刘小伟, 景运革. 一种有效更新多源数据约简的增量算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(6): 1083-1091. |
| [2] | 李苓玉, 刘治平. 基于机器学习的自发性早产生物标记物发现[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(5): 767-774. |
| [3] | 贾霄, 郭顺心, 赵红. 基于图像属性的零样本分类方法综述[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(4): 531-543. |
| [4] | 崔鹤, 刘昆, 瞿晓磊. 基于紫外⁃可见光谱和机器学习方法的溶解性有机质吸附预测模型研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(3): 356-363. |
| [5] | 王明钊, 程华, 王宇泽, 刘鹏. 基于精度可变乘法器的脉动阵列[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(6): 885-891. |
| [6] | 曹欣怡,李鹤,王蔚. 基于语料库的语音情感识别的性别差异研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(5): 758-764. |
| [7] | 阚 威, 李 云. 基于LSTM的脑电情绪识别模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 110-116. |
| [8] | 朱亚奇1,邓维斌1 ,2*. 一种基于不平衡数据的聚类抽样方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 421-429. |
| [9] | 朱亚奇1,邓维斌1,2*. 一种基于不平衡数据的聚类抽样方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 421-429. |
| [10] | 潘世超1,王文剑1,2**,郭虎升1. 基于概率密度估计的增量支持向量机算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(5): 603-610. |
| [11] | 张继1·2,王洪元1.2**. 一种基于增量半监督判别分析的跟踪方法*[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(4): 397-404. |
|
||