南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 94–102.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.01.010
多示例学习的两阶段实例选择和自适应包映射算法
- 1.西南石油大学计算机科学学院,成都,610500
2.西南石油大学人工智能研究院,成都,610500
Two⁃stage instance selection and adaptive bag mapping algorithm for multi⁃instance learning
Mei Yang1, Wenxi Zeng1, Yu Fang1, Fan Min1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Computer Science, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, 610500, China
2.Institute for Artificial Intelligence, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, 610500, China
摘要:
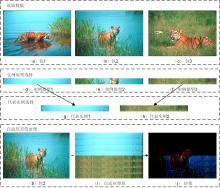
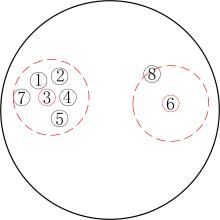
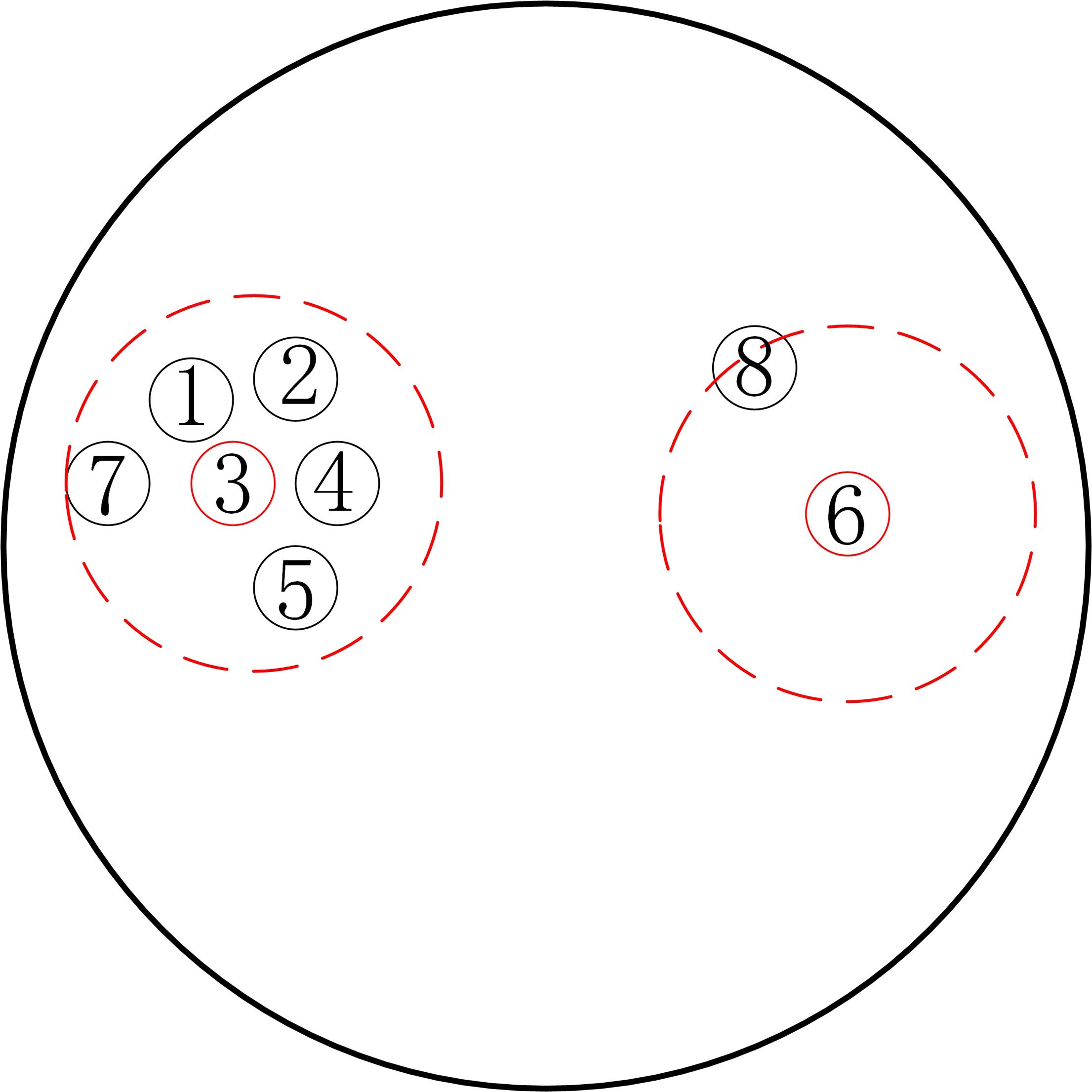
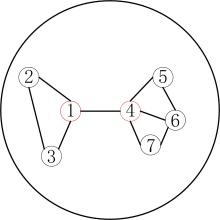
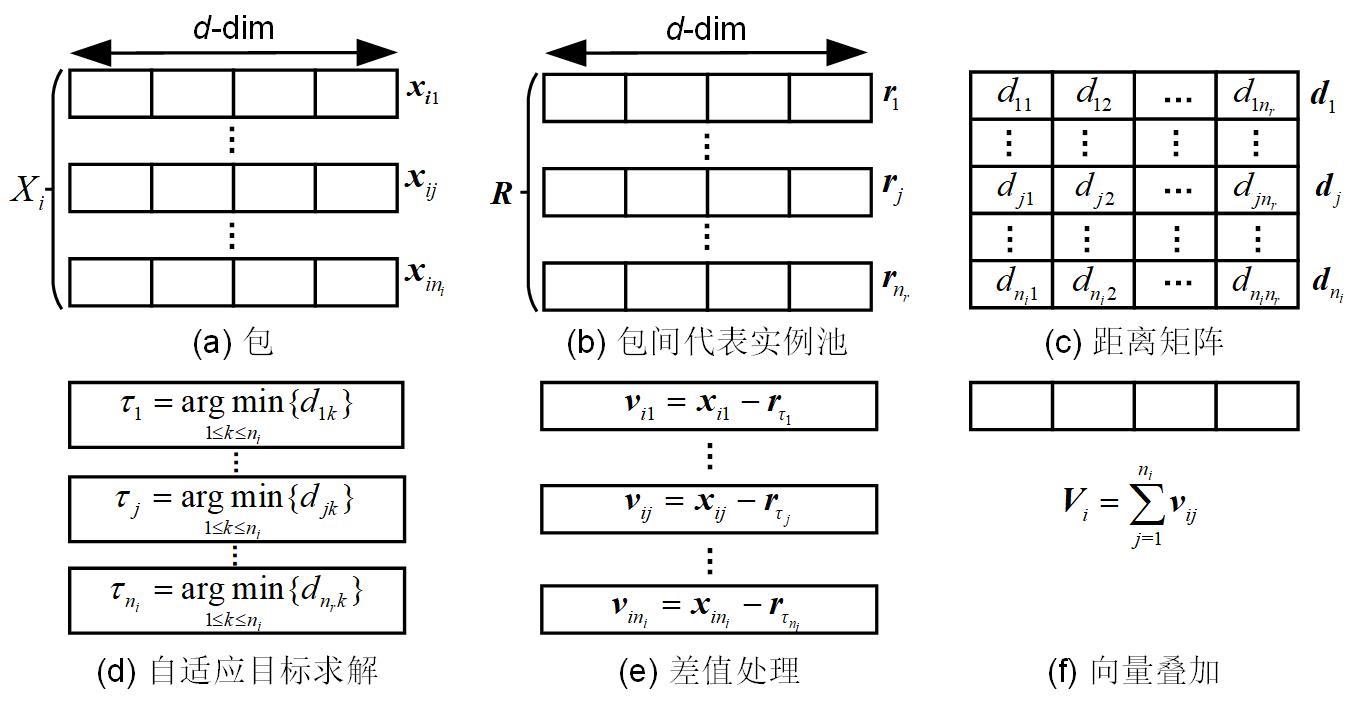
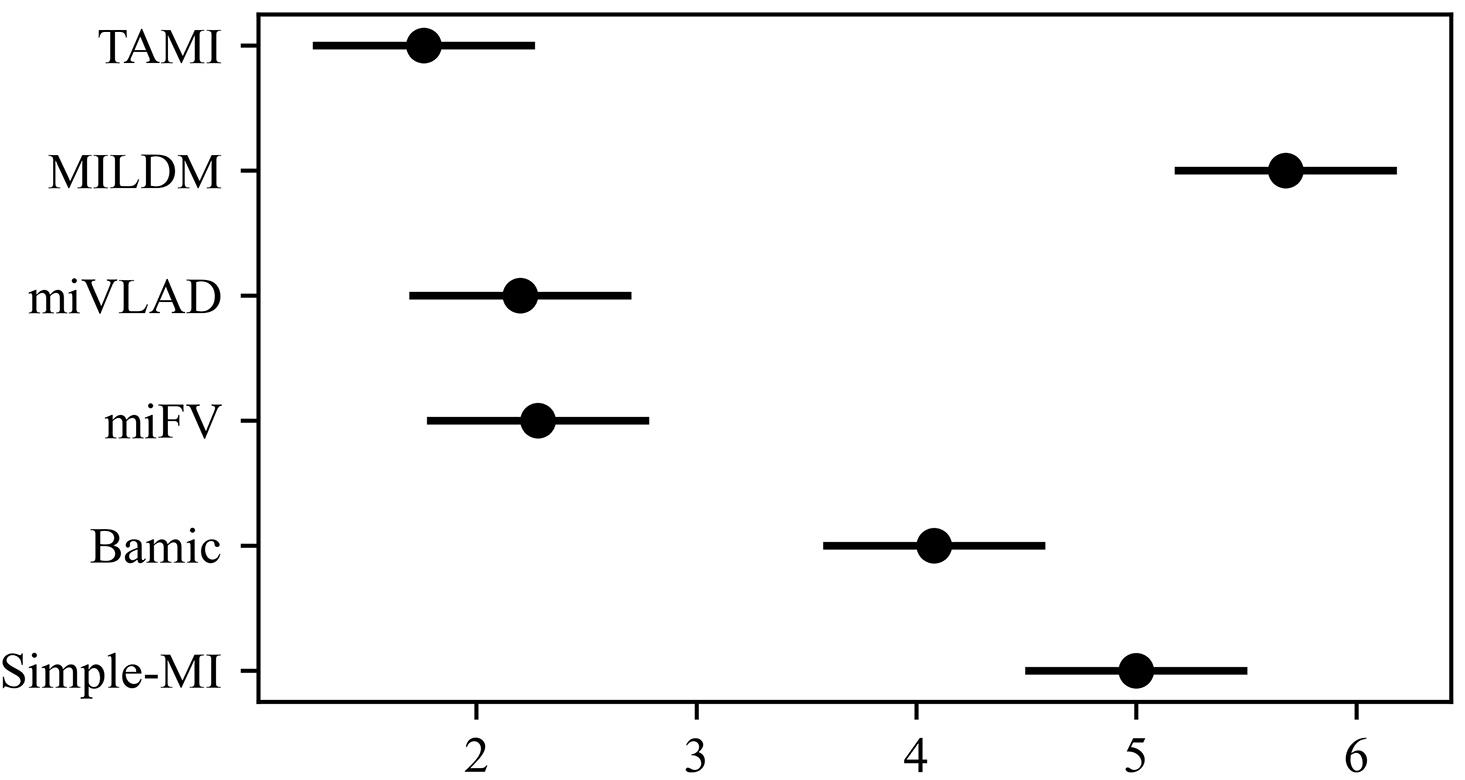
多示例学习(Multi?Instance Learning,MIL)研究对象的内部结构比单示例学习更加复杂.已有的MIL方法大都基于原始空间中的实例进行包映射,但这些方法通常忽略包的内部结构信息,难以保证所选实例与包在新特征空间中的关联性.提出一种多示例学习的两阶段实例选择和自适应包映射(TAMI)算法.首先,实例选择技术根据包中实例的密度值和关联性,挖掘包内结构特征,选取实例原型;其次,实例选择技术选取具有峰值密度的实例原型作为代表实例;最后,自适应包映射技术通过定义新的映射函数将包转换为单向量进行学习.实验利用显著性检验从统计学的角度验证了TAMI在图像检索、文本分类等基本数据集上的有效性.结果表明,TAMI在图像检索和医学图像数据集上取得了比其他MIL算法更好的效果,并在文本分类数据集上表现良好.
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | Dietterich T G,Lathrop R H,Lozano?Pérez T. Solving the multiple instance problem with axis?parallel rectangles. Artificial Intelligence,1997,89(1-2):31-71. |
| 2 | Maron O,Ratan A L. Multiple?instance learning for natural scene classification∥Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Machine Learning. San Francisco,CA,USA:IEEE,1998:341-349. |
| 3 | Song X F,Jiao L C,Yang S Y,et al. Sparse coding and classifier ensemble based multi?instance learning for image categorization. Signal Processing,2013,93(1):1-11. |
| 4 | Wei X S,Ye H J,Mu X,et al. Multi?instance learning with emerging novel class. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2019,33(5):2109-2120. |
| 5 | Zhu L,Zhao B,Gao Y. Multi?class multi?instance learning for lung cancer image classification based on bag feature selection∥2008 5th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery. Ji'nan,China:IEEE,2008:487-492. |
| 6 | Wang Z Y,Poon J,Sun S D,et al. Attention?based multi?instance neural network for medical diagnosis from incomplete and low quality data∥2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest,Hungary:IEEE,2019:1-8. |
| 7 | Andrews S,Tsochantaridis I,Hofmann T. Support vector machines for multiple?instance learning∥Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver,Canada:MIT Press,2002:561-568. |
| 8 | Zhou Z H,Sun Y Y,Li Y F. Multi?instance learning by treating instances as non?I.I.D. samples∥Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. New York,NY,USA:ACM,2009:1249-1256. |
| 9 | Angelidis S,Lapata M. Multiple instance learning networks for fine?grained sentiment analysis. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics,2018(6):17-31. |
| 10 | Zhang D,He J R,Lawrence R. MI2LS:Multi?instance learning from multiple informationsources∥Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York,NY,USA:ACM,2013:149-157. |
| 11 | Zhou Z H,Zhang M L. Solving multi?instance problems with classifier ensemble based on constructive clustering. Knowledge and Information Systems,2007,11(2):155-170. |
| 12 | Chen Y X,Bi J B,Wang J Z. MILES:Multiple?instance learning via embedded instance selection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2006,28(12):1931-1947. |
| 13 | Hong C,Wang M,Gao Y,et al. Image annotation by multiple?instance learning with discriminative feature mapping and selection. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics,2014,44(5):669-680. |
| 14 | Rodriguez A,Laio A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science,2014,344(6191):1492-1496. |
| 15 | Amores J. Multiple instance classification:Review,taxonomy and comparative study. Artificial Intelligence,2013(201):81-105. |
| 16 | Zhang M l,Zhou Z H. Multi?instance clustering with applications to multi?instance prediction. Applied Intelligence,2009,31(1):47-68. |
| 17 | Wei X S,Wu J X,Zhou Z H. Scalable multi?instance learning∥2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Shenzhen,China:IEEE,2014:1037-1042. |
| 18 | Xu B C,Ting K M,Zhou Z H. Isolation set?kernel and its application to multi?instance learning∥Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. New York,NY,USA:ACM,2019:941-949. |
| 19 | Wei X S,Wu X J,Zhou Z H. Scalable algorithms for multi?instance learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2017,28(4):975-987. |
| 20 | Wu J,Pan S R,Zhu X Q,et al. Multi?instance learning with discriminative bag mapping. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2018,30(6):1065-1080. |
| 21 | Zhang Y L,Zhou Z H. Multi?instance learning with key instance shift∥Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Main Track. Melbourne,Australia:IJCAI,2017:3441-3447. |
| 22 | Sánchez J,Perronnin F,Mensink T,et al. Image classification with the fisher vector:Theory and practice. International Journal of Computer Vision,2013,105(3):222-245. |
| 23 | Decencière E,Zhang X W,Cazuguel G,et al. Feedback on a publicly distributed image database:The messidor database. Image Analysis & Stereology,2014,33(3):231. |
| 24 | Kandemir M,Hamprecht F A. Computer?aided diagnosis from weak supervision:A benchmarking study. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics,2015(42):44-50. |
| 25 | Dem?ar J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. The Journal of Machine Learning Research,2006(7):1-30. |
| [1] | 李娜, 段友祥, 孙歧峰, 沈楠. 一种基于样本点距离突变的聚类方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(5): 775-784. |
| [2] | 林 銮,陆武萍,唐朝生,赵红崴,冷 挺,李胜杰. 基于计算机图像处理技术的松散砂性土微观结构定量分析方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1064-1074. |
| [3] | 朱庆峰1,2,葛洪伟1,2*. 快速特征映射优化的流形密度峰聚类[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 838-. |
| [4] | 王一宾1,2,程玉胜1,2*,裴根生1. 结合均值漂移的多示例多标记学习改进算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(2): 422-. |
| [5] | 杨 洁1,2,王国胤1*,庞紫玲1. 密度峰值聚类相关问题的研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 791-. |
| [6] | 曹蕴清1,2* ,曾祥华1,季 阳2,翟颖颖2,李 伟2. 激光晶化制备硅量子点/碳化硅多层膜pin结构的光伏特性探索[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(3): 399-. |
| [7] | 张栋冰*. 基于TOPHATPCNN的图像车辆目标检测方法研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(3): 590-. |
| [8] | 贾培灵1,樊建聪1,2*,彭延军1,2. 一种基于簇边界的密度峰值点快速搜索聚类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(2): 368-. |
| [9] | 蓝 君1,李义丰1,2*. 密度为零的零折射率声学超材料研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(1): 69-. |
| [10] | 汪 璐,贾修一*,顾雁囡. 三支决策贝叶斯网络分类器[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(5): 833-. |
| [11] | 谢娟英*,屈亚楠,王明钊 . 基于密度峰值的无监督特征选择算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(4): 735-. |
| [12] | 赵 洁1,2,林 锦2,吴剑锋1*,吴吉春1. 大连周水子地区海水入侵数值模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(3): 479-489. |
| [13] | 白莹12,薛山3,鲁善海4,朱愿福12,李荣富12, 阮晓红12*. 沙颍河流域平原区土壤氮空间分布特征及影响因素研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(1): 65-76. |
| [14] | 陈妮1,2,3,冯学智1,2,3*,肖鹏峰1,2,3, 贺广均1,2,3,4. 玛纳斯河流域春季雪层参数特性分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(5): 936-943. |
| [15] | 廖 娟 1* , 王 江 1 , 徐 亮 2 , 李 勃 1 , 陈启美 1 . 相机抖动场景下的运动前景检测算法 [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 219-226. |
|
||