南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 981–999.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.06.007
水星的火山活动历史
- 1.行星环境与宜居性研究实验室,中山大学大气科学学院,珠海,519082
2.中国科学院比较行星学卓越创新中心,合肥,230026
The history of volcanism on Mercury
Yichen Wang1, Zhiyong Xiao1,2( )
)
- 1.Planetary Environmental and Astrobiological Research Laboratory,School of Atmospheric Sciences,Sun Yat?sen University,Zhuhai,519082,China
2.CAS Center for Excellence in Comparative Planetary,Hefei,230026,China
摘要:
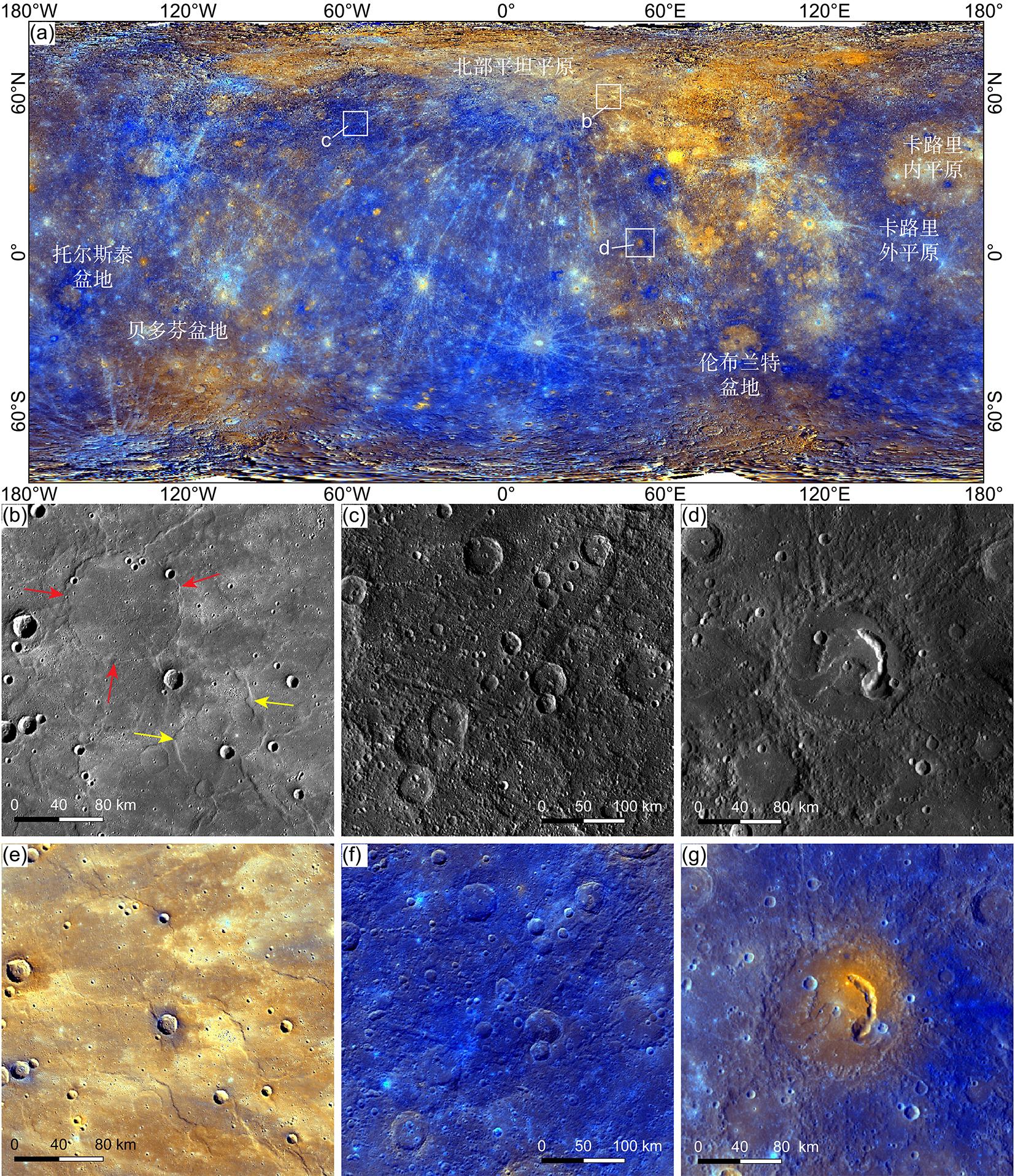
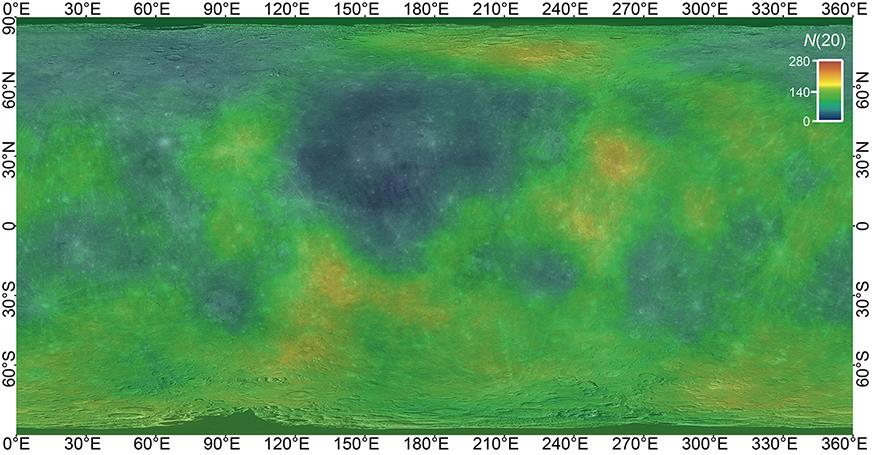
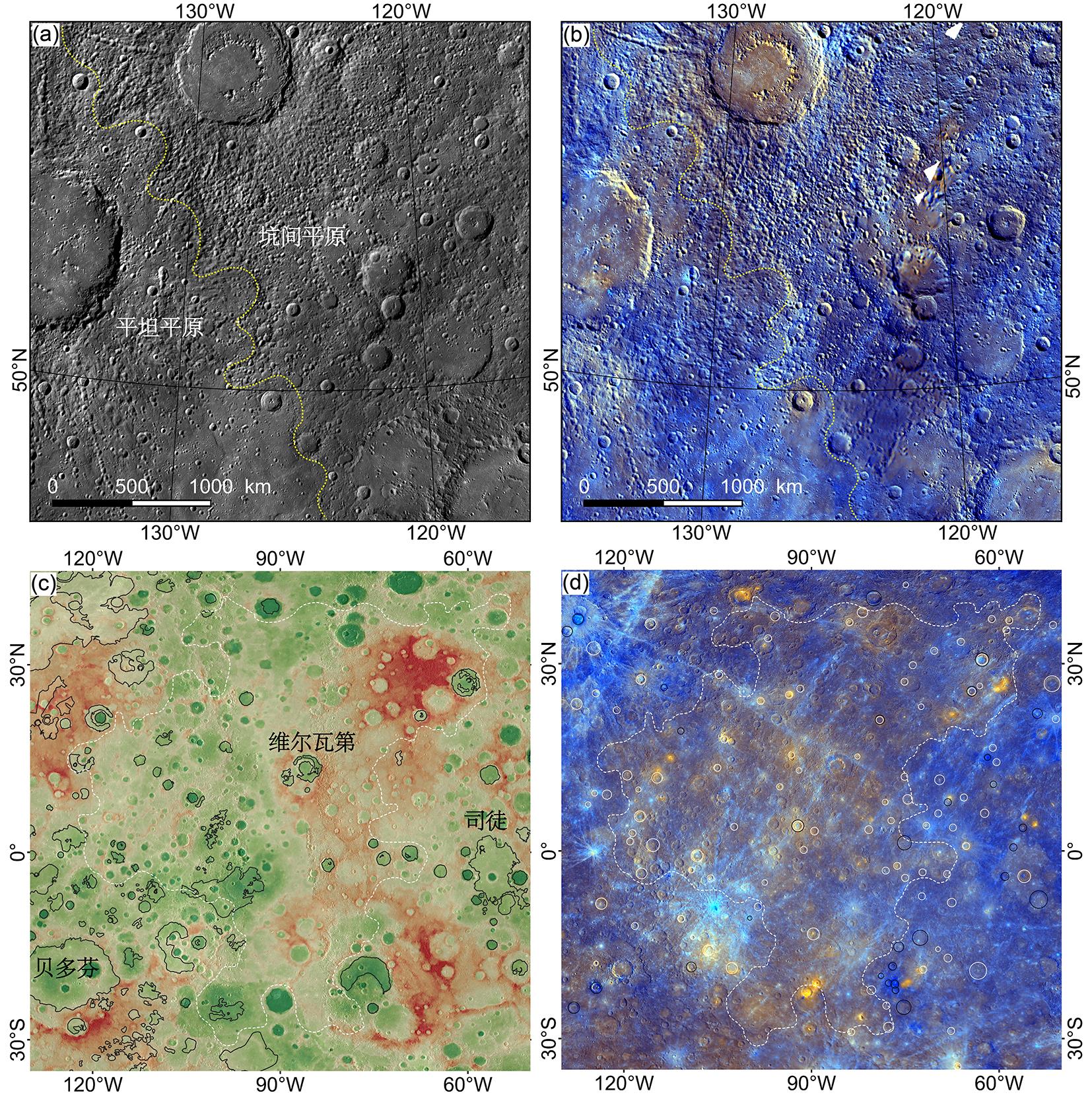
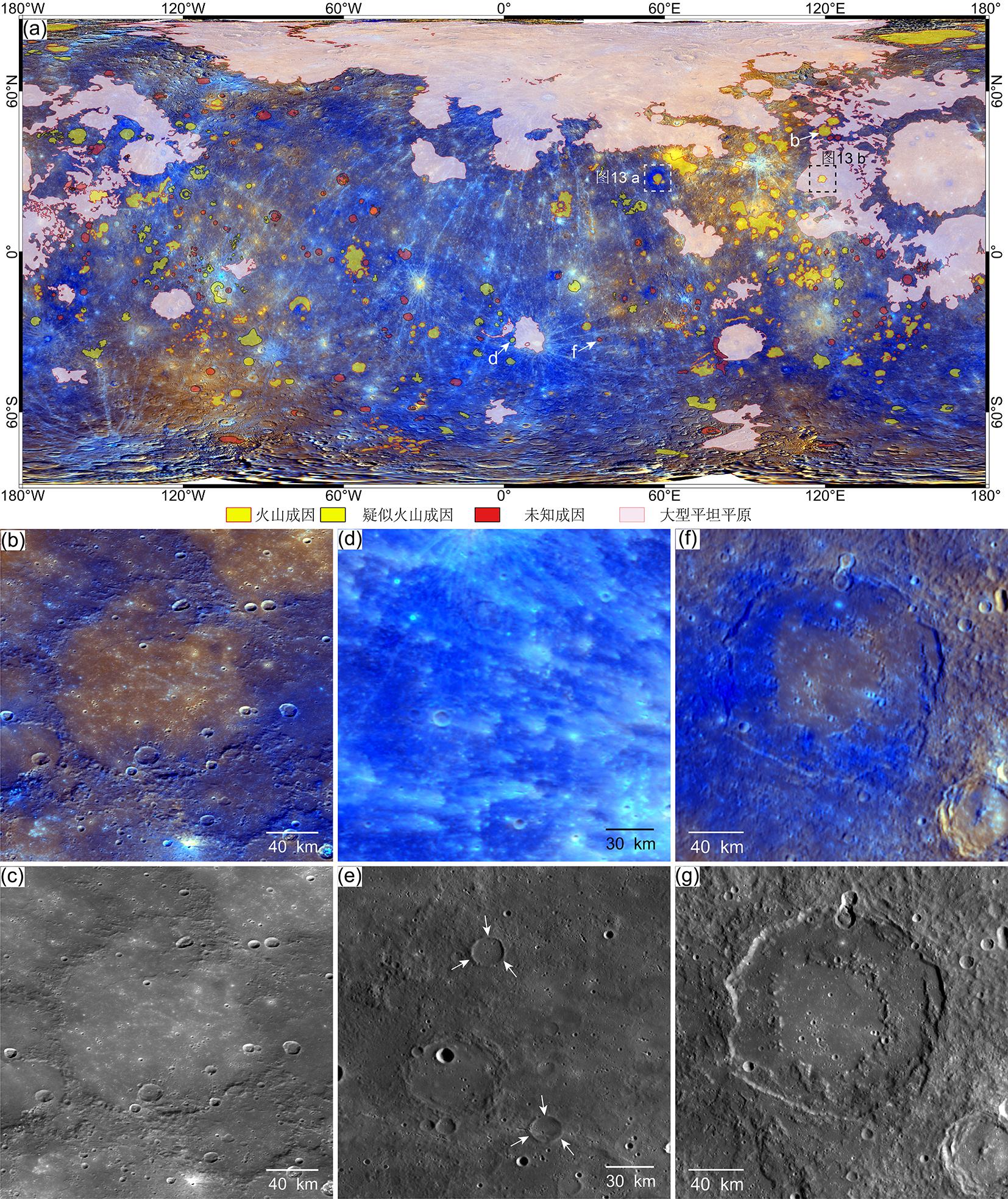
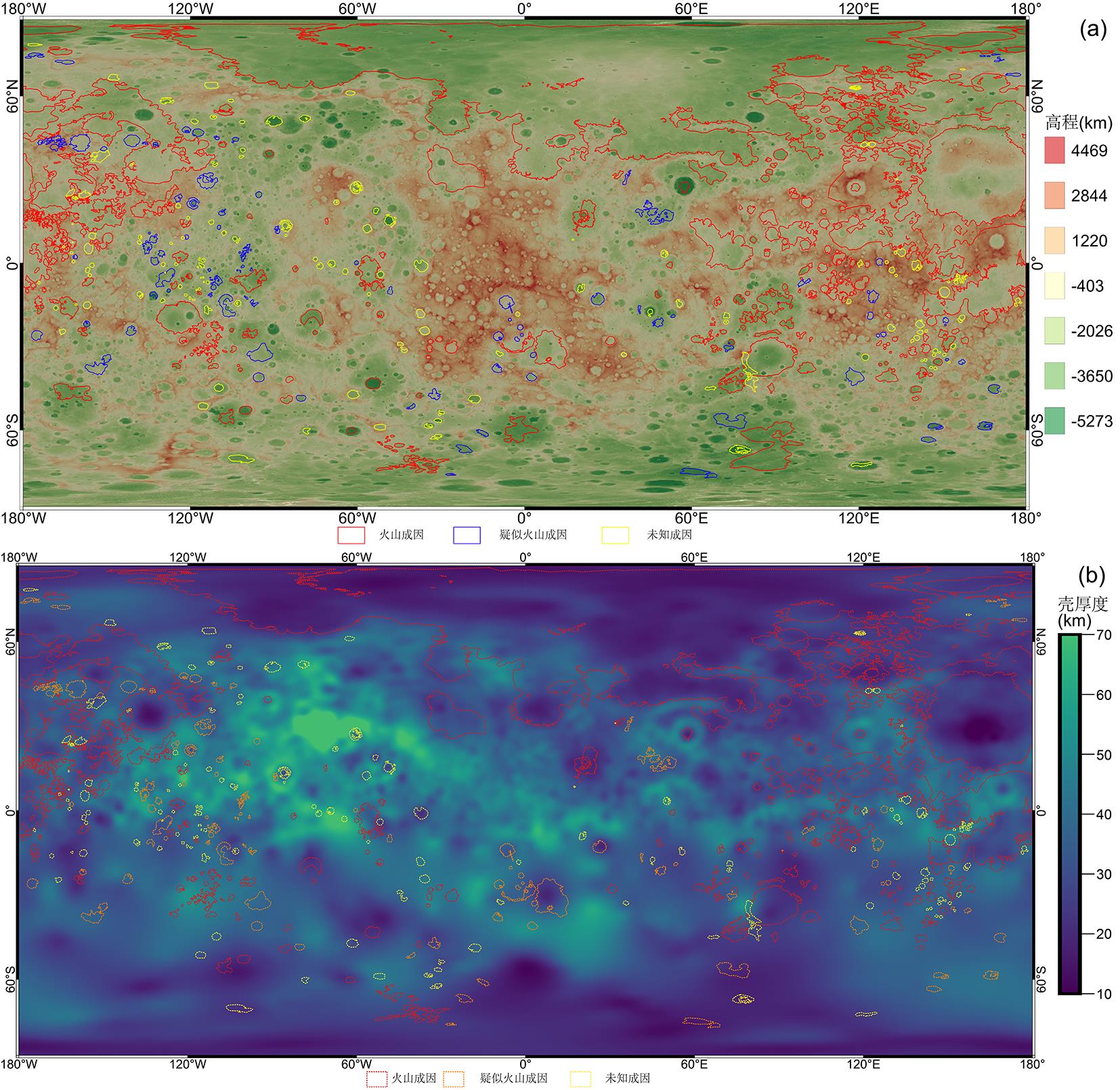
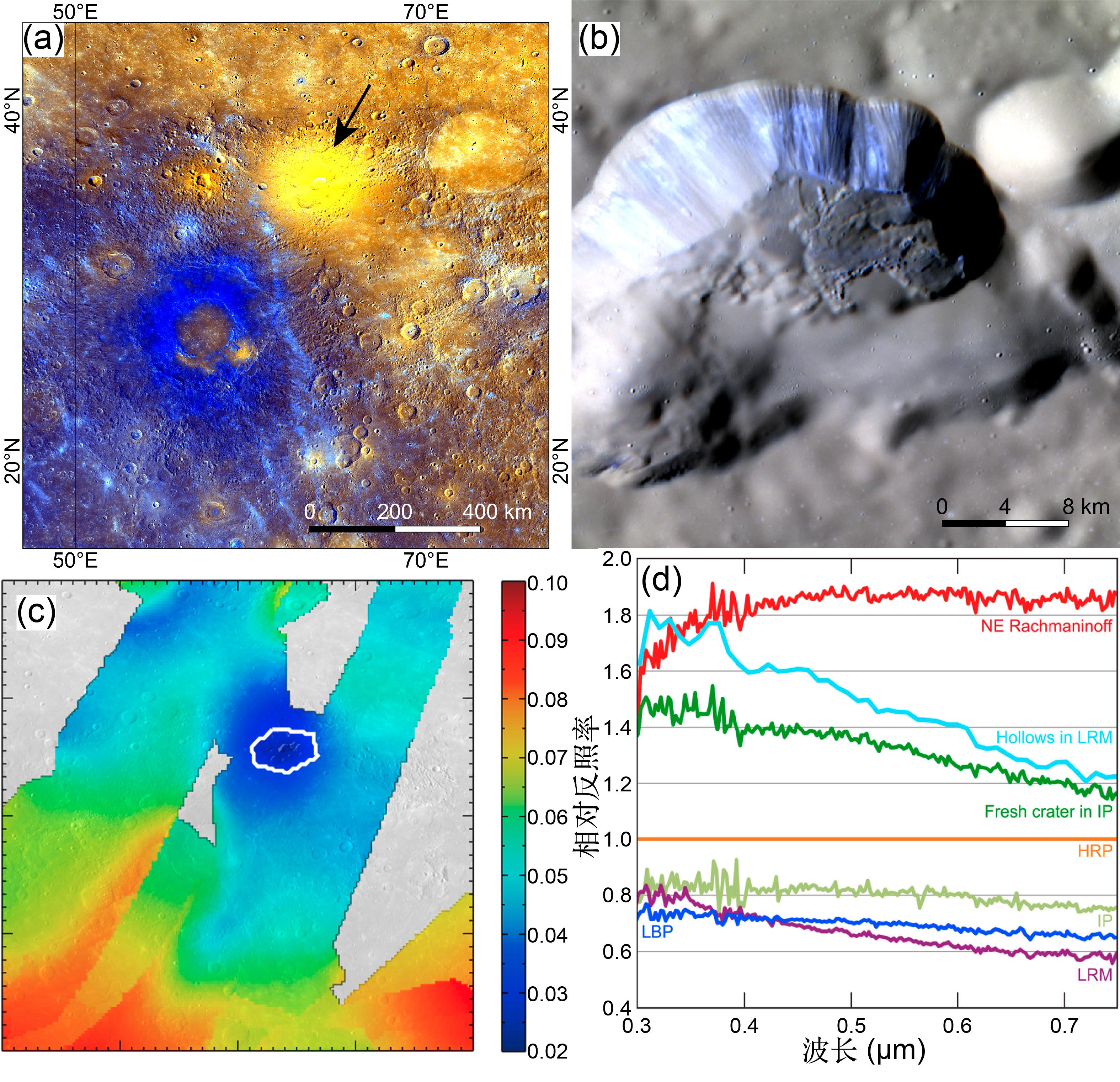
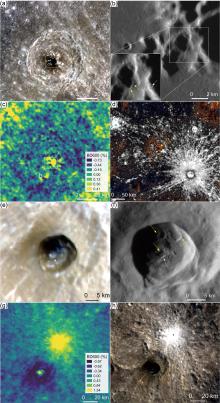
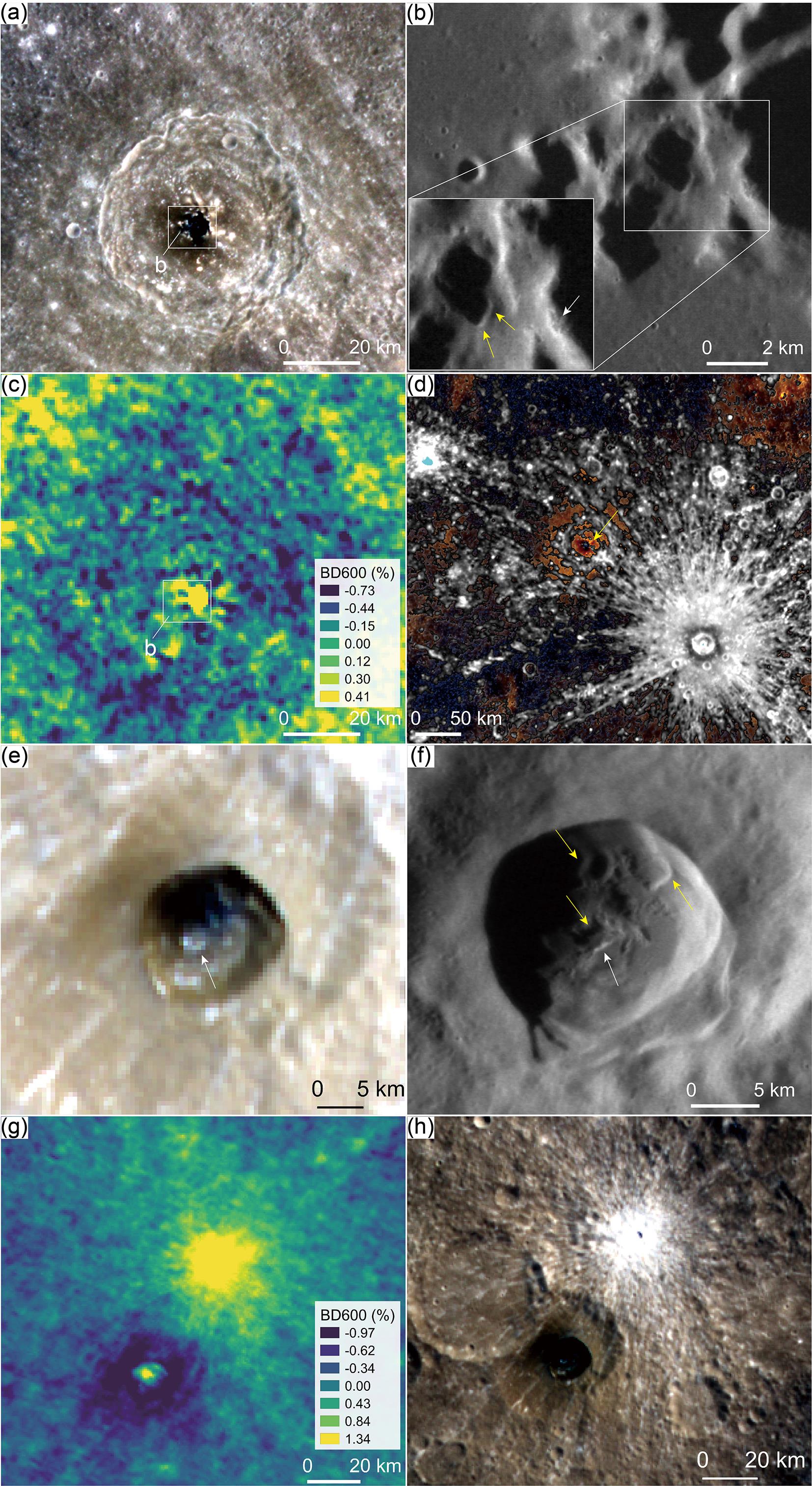
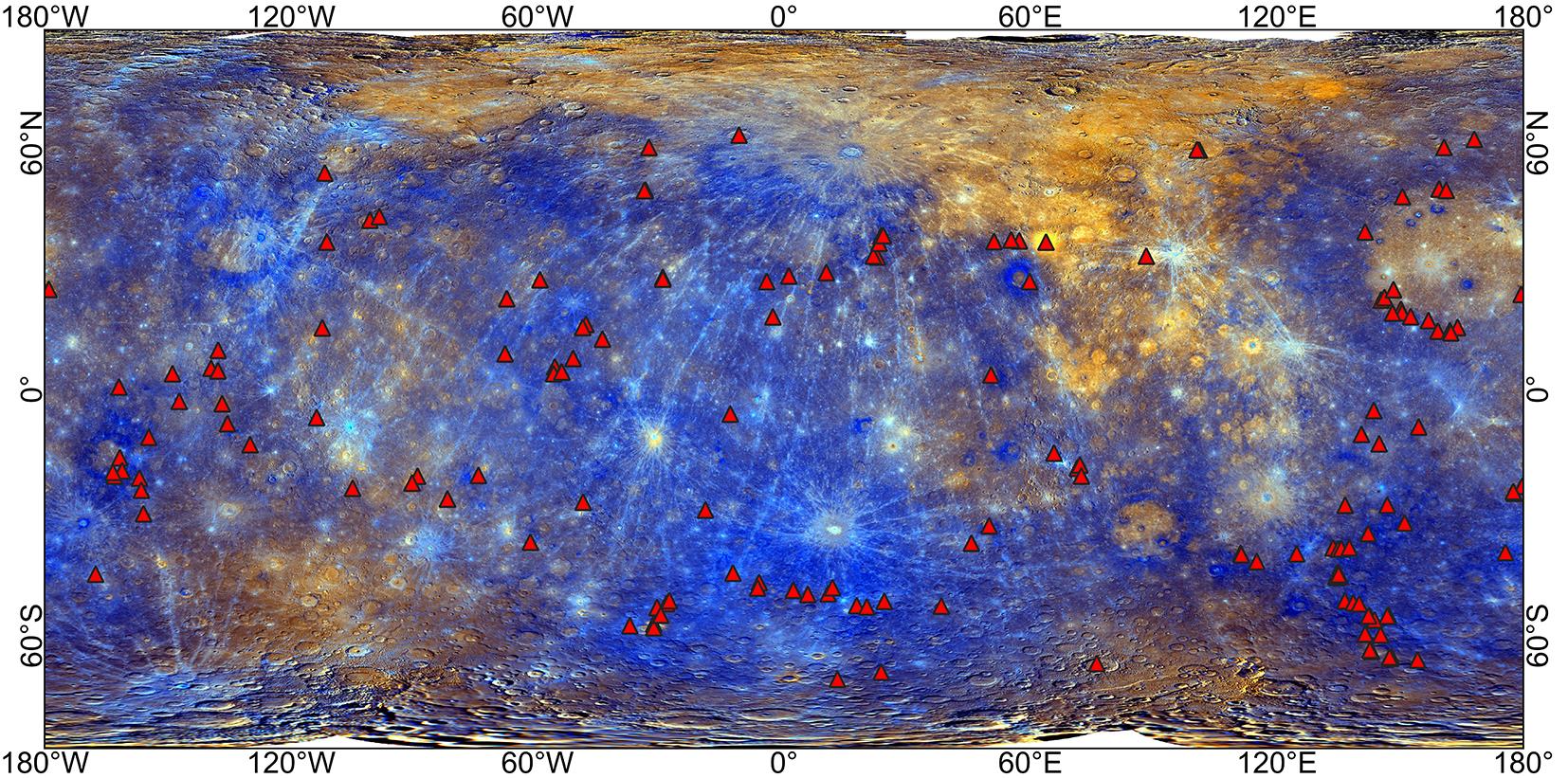
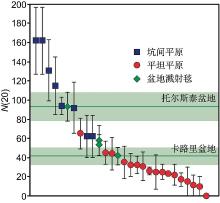
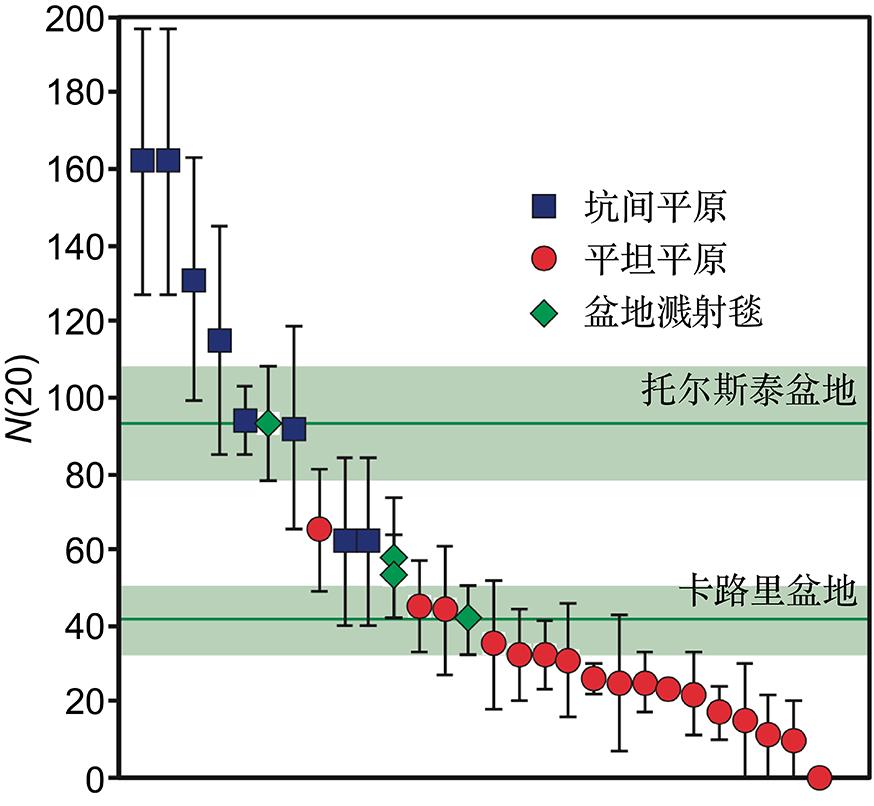
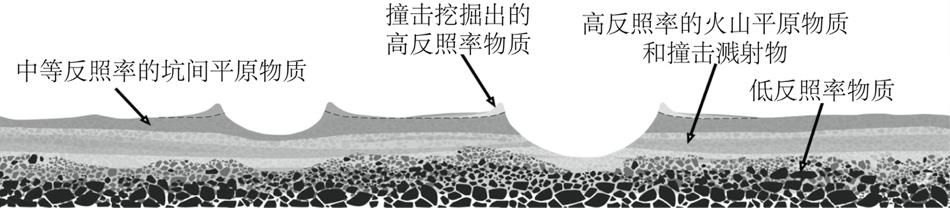
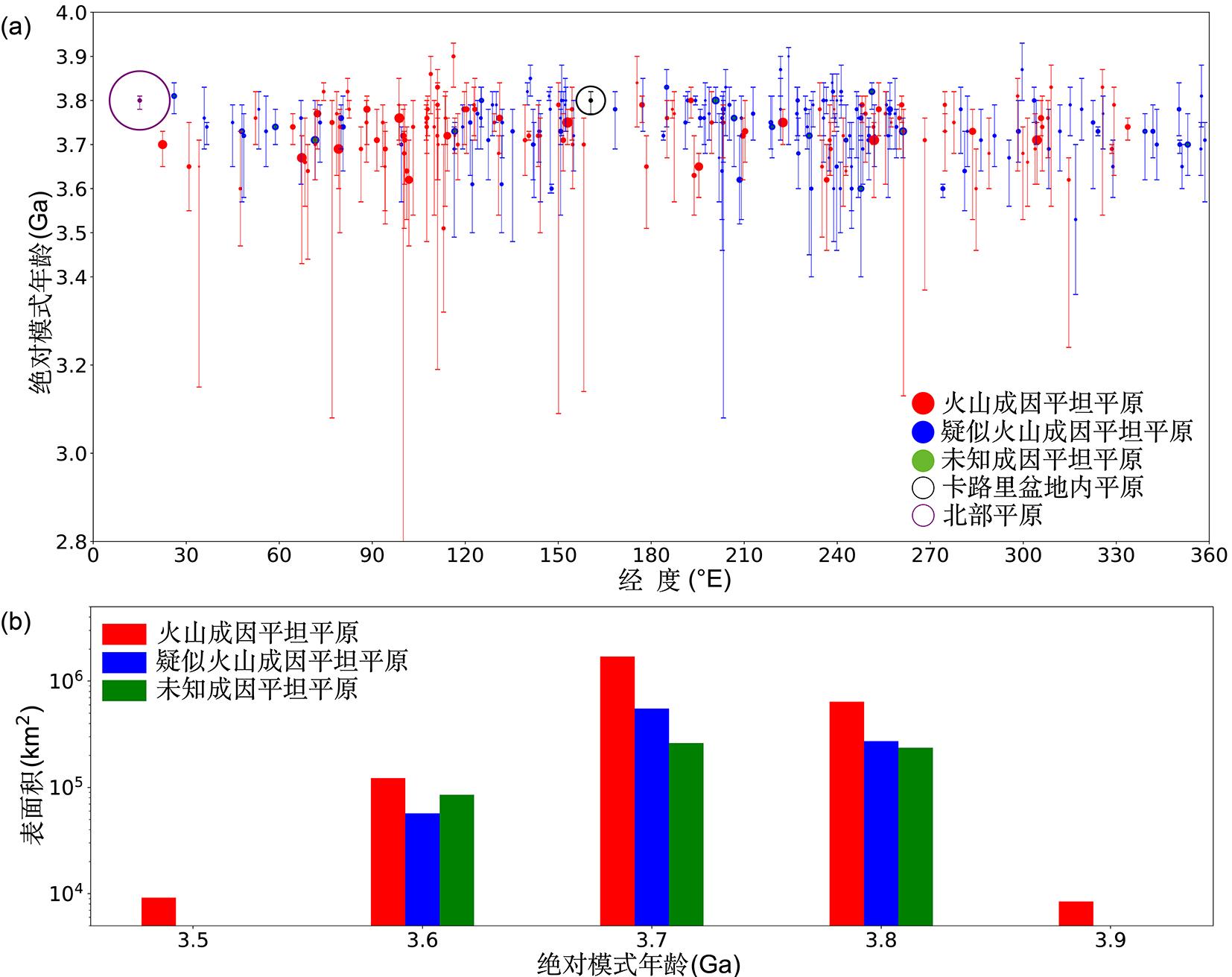
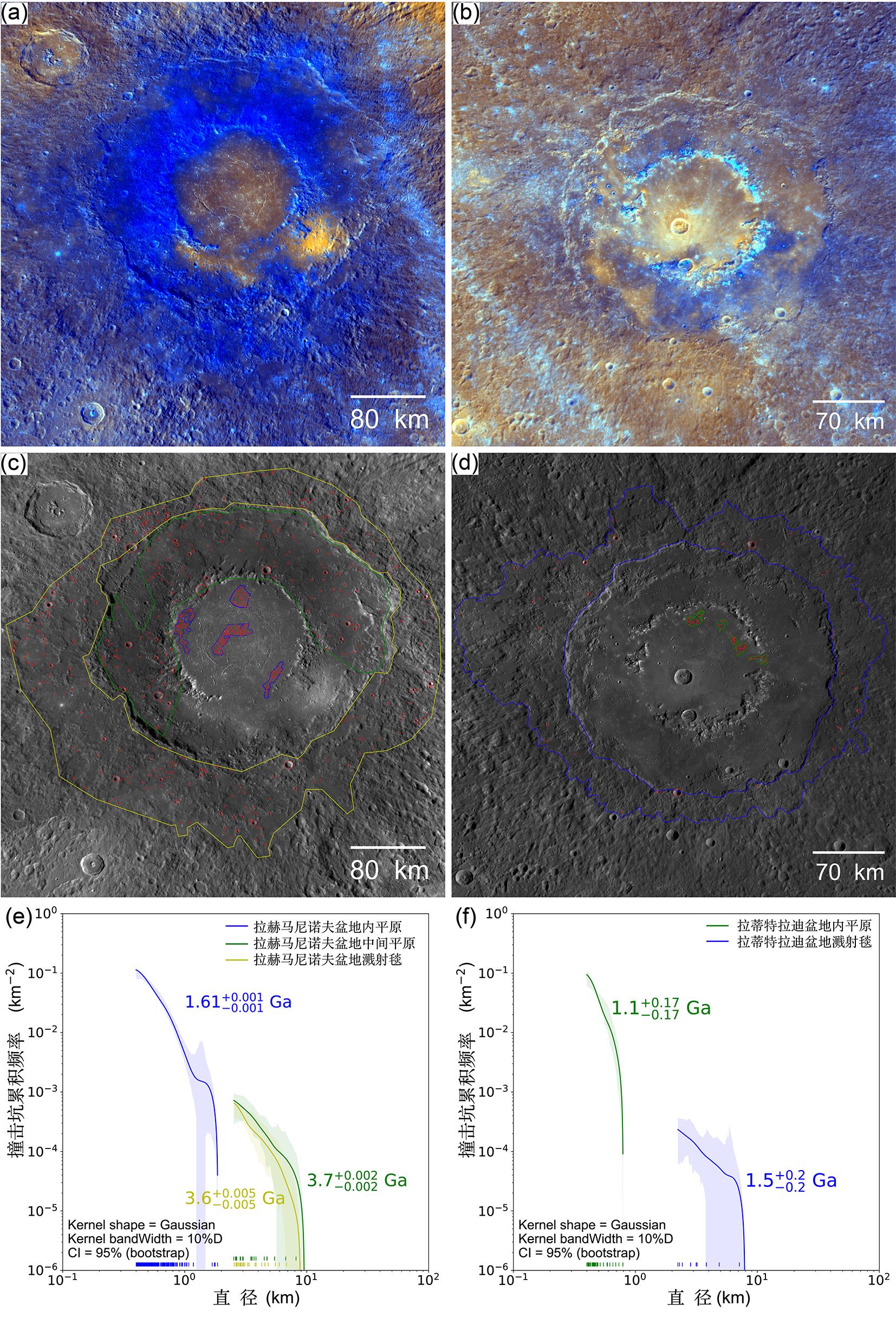
火山活动是天体内部热活动的表现,火山活动的形式和持续时间是探索行星环境和宜居性演化的重要方面.与内太阳系的其他天体一样,水星表面经历了大规模和长时期的火山活动,但是水星上的火山地貌、喷发机制、持续时间,以及火成岩的物质组成等特点和其他类地天体明显不同.水星上的火山活动主要发生在太阳系形成之初的10亿年内,溢流性火山活动形成的坑间平原和平坦平原在全球分布,是水星表面分布面积最大的火山物质.随着内部逐渐冷却,水星自约38亿年前后进入了全球收缩的热状态,岩石圈内的压应力阻碍岩浆上涌,大规模溢流性火山活动快速停止.距今约35亿年以来,水星表面的火山活动主要是挥发分驱动岩浆沿岩石圈内的薄弱带快速上升引起的爆发性火山活动,在全球形成了百余处火成碎屑沉积物.一些爆发性火山活动持续到水星地质历史的近期.水星火山活动的历史反映了独特的幔部动力过程,揭示了天体撞击作用对内部热扰动的影响,对水星的起源和演化具有重要的指示意义.
中图分类号:
- P691
| 1 | Strom R G,Trask N J,Guest J E. Tectonism and volcanism on Mercury. Journal of Geophysical Research,1975,80:2478-2507. |
| 2 | Trask N J,Guest J E. Preliminary geologic terrain map of Mercury. Journal of Geophysical Research,1975,80:2461-2477. |
| 3 | Denevi B T,Ernst C M,Prockter L M,et al. The geologic history of Mercury∥Mercury:The view after MESSENGER. Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2018:144-175. |
| 4 | Taylor S R,McLennan S M. Planetary crusts:Their composition,origin and evolution. Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2010. |
| 5 | Whitten J L,Head J W,Denevi B W,et al. Intercrater plains on Mercury:Insights into unit definition,characterization,origin from MESSENGER datasets. Icarus,2015,241:97-113. |
| 6 | Denevi B W,Ernst C M,Meyer H M,et al. The distribution and origin of smooth plains on Mercury. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2013,118:91-907. |
| 7 | Byrne P K,Ostrach L R,Fassett C I,et al. Widespread effusive volcanism on Mercury likely ended by about3.5 Ga. Geophysical Research Letter,2016,43:7408-7416. |
| 8 | Wang Y,Xiao Z. A comparison of global volcanism on the Moon and Mercury∥National Planetary Science Conference,Suzhou,China,2021:202. |
| 9 | Thomas R J,Rothery D A,Conway S J,et al. Long?lived explosive volcanism on Mercury. Geophysical Research Letters,2014,41:6084-6092. |
| 10 | Xiao Z,Xu R,Wang Y,et al. Recent dark pyroclastic on Mercury. Geophysical Research Letters,2021:2021GL092532. |
| 11 | Nittler L R,Starr R D,Weider S Z,et al. The major–element composition of Mercury's surface from MESSENGER X–ray spectrometry. Science,2011,333:1847-1850. |
| 12 | Peplowski P N,Evans L G,Hauck S A,et al. Radioactive elements on Mercury's surface from MESSENGER:Implcations for the planet's formation and evolution. Science,2011,333:1850-1852. |
| 13 | Peplowski P N,Klima R L,Lawrence D J,et al. Remote sensing evidence for an ancient carbon–bearing crust on Mercury. Nature Geoscience,2016,9:273-276. |
| 14 | Evans L G,Peplowski P N,Rhodes E A,et al. Major–element abundances on the surface of Mercury:Results from the MESSENGER Gamma–Ray spectrometer. Journal of Geophysical Research,2012,117:E00L07. |
| 15 | Evans L G,Peplowski P N,McCubbin F M,et al. Chlorine on the surface of Mercury:MESSENGER gamma?ray measurements and implications for the planet's formation and evolution. Icarus,2015,257:417-427. |
| 16 | Weider S Z,Nittler L R,Starr R D,et al. Chemical heterogeneity on Mercury's surface revealed by the MESSENGER X?Ray Spectrometer. Journal of Geophysical Research,2012,117:E00L05. |
| 17 | Weider S Z,Nittler L R,Murchie S L,et al. Evidence from MESSENGER for sulfur– and carbon?driven explosive volcanism on Mercury. Geophysical Research Letters,2016,43:3653-3661. |
| 18 | Vander Kaaden K E,McCubbin F M,Nittler L R,et al. Geochemistry,mineralogy,and petrology of boninitic and komatiitic rocks on the mercurian surface:Insights into the mercurian mantle. Icarus,2017,285:155-168. |
| 19 | McCoy T J,Peplowski P N,McCubbin F M,et al. The geochemical and mineralogical diversity of Mercury∥Mercury:The iew after MESSENGER. Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2018:176-190. |
| 20 | Weider S Z,Nittler L R,Starr R D,et al. Evidence for geochemical terranes on Mercury:The first global mapping of major elements on the surface of the innermost planet. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2015,416:109-120. |
| 21 | Peplowski P N,Stockstill?Cahill K. Analytical identification and characterization of the major geochemical terranes of Mercury's northern hemisphere. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2019,124:2019JE005997. |
| 22 | Zolotov M Y,Sprague A L,Hauck S A,et al. The redox state,FeO content,and origin of sulfur–rich magmas on Mercury. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2013,118:38-146. |
| 23 | Le Bas M J. IUGS reclassification of the high–Mg and picritic volcanic rocks. Journal of Petrology,2000,41:1467-1470. |
| 24 | Stockstill–Cahill K R,McCoy T J,Nittler L R,et al. Magnesium–rich crustal compositions on Mercury:Implications for magmatism from petrologic modeling. Journal of Geophysical Research,2012,117:E00L15. |
| 25 | Charlier B,Grove T L,Zuber M T. Phase equilibria of ultramafic compositions on Mercury and the origin of the compositional dichotomy. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2013,363:50-60. |
| 26 | Namur O,Collinet M,Charlier B,et al. Melting processes and mantle sources of surface lavas on Mercury. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2016,439:117-128. |
| 27 | Vander Kaaden K E,McCubbin F M. The origin of boninites on Mercury:An experiment study of the northern volcanic plains lava. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2016,173:246-263. |
| 28 | Byrne P K,Whitten J L,Klimczak C,et al. The volcanic character of Mercury∥Mercury:The View after MESSENGER. Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2018:287-323. |
| 29 | Weider S Z,Nittler L R. The surface composition of Mercury as seen from MESSENGER. Element,2013,9(2):90-91. |
| 30 | Murchie S L,Klima R L,Denevi B W,et al. Orbital multispectral mapping of Mercury with the MESSENGER Mercury Dual Imaging System:Evidence for the origins of plains units and low–reflectance materials. Icarus,2015,254:87-305. |
| 31 | Vander Kaaden K E,McCubbin F M. The origin of boninites on Mercury:An experimental study of the northern volcanic plains lava. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2015,173:246-263. |
| 32 | Blewett D T,Stadermann A C,Susorney A C,et al. Analysis of MESSENGER high–resolution images of Mercury's hollows and implications for hollow formation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2016,121:1798-1813. |
| 33 | Wang Y,Xiao Z,Chang Y,et al. Lost volatiles during the formation of hollows on Mercury. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2020,125:e2020JE006559. |
| 34 | Blewett D T,Vaughan W M,Xiao Z,et al. Mercury's hollows:Constraints on formation and composition from analysis of geological setting and spectral reflectance. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2013,118:1013-1032. |
| 35 | Sehlke A,Whittington A G. Rheology of lava flows on Mercury:An analog experiment study. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2015,120:1924-1955. |
| 36 | Spudis P D,Guest J E. Stratigraphy?nd geologic history of Mercury∥Mercury. Tucson:University of Arizona Press,1988:118-164. |
| 37 | Fassett C I,Kadish S J,Head J W,et al. The global population of large craters on Mercury and comparison with the Moon. Geophysical Research Letters,2011,38:L10202. |
| 38 | Fa W,Cai Y,Xiao Z,et al. Topographic roughness of the northern high latitudes of Mercury from MESSENGER laser altimeter data. Geophysical Research Letters,2016,43:3078-3087. |
| 39 | Prockter L M,Kinczyk M J,Byrne P K,et al. The first global geological map of Mercury∥The 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference,The Woodlands,TX,USA,2016:1245. |
| 40 | Denevi B W,Robinson M S,Solomon S C,et al. The evolution of Mercury's crust:A global perspective from MESSENGER. Science,2009,324:613-618. |
| 41 | Murchie S L,Klima R L,Izenberg N R,et al. Spectral reflectance constraints on the composition and evolution of Mercury's surface. In mMercury:The view after MESSENGER. Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2018:191-261. |
| 42 | Nittler L R,Chabot N L,Grove T L,et al. The chemical composition of Mercury. In mercury:The view after MESSENGER. Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2018:30-51. |
| 43 | Wilhelms D E. Mercurian volcanism questioned. Icarus,1976,28:551-558. |
| 44 | Strom R G. Origin and relative age of lunar and mercurian intercrater plains. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,1977,15:156-172. |
| 45 | Strom R G,Banks M E,Chapman C R,et al. Mercury crater statistics from MESSENGER flybys:Implications for stratigraphy and resurfacing history. Planetary and Space Science,2011,59:1960-1967. |
| 46 | Howard K A,Wilhelms D E,Scott D H. Lunar basin formation and highland stratigraphy. Reviews of Geophysics,1974,12:309-327. |
| 47 | Oberbeck V R,Horz F,Morrison R H,et al. On the origin of the lunar smooth plains. Moon,1975,12:19-54. |
| 48 | Trask N J,McCauley J F. Differentiation and volcanism in the lunar highlands:Photogeologic evidence and Apollo 16 implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1972,14(2):201-206. |
| 49 | Eggleton R E,Schaber G G. Cayley formation interpreted as basin ejecta.Apollo 16 Preliminary Science Report. Washington D.C.,USA,National Aeronautics and Space Administration,1972,29?7?29?16. |
| 50 | Le Feuvre M,Wieczorek M A. Nonuniform cratering of the terrestrial planets. Icarus,2008,197:291-306. |
| 51 | Gault D E,Guest J E,Murray J B,et al. Some comparisons of impact craters on Mercury and the Moon. Journal of Geophysical Research,1975,80:2444-2460. |
| 52 | Murray B C,Strom R G,Trask N J,et al. Surface history of Mercury:Implications for terrestrial planets. Journal of Geophysical Research,1975,80:2508-2514. |
| 53 | Malin M C. Observations of intercrater plains on Mercury. Geophysical Research Letters,1976,3:581-584. |
| 54 | Fassett C I,Head J W,Baker D M,et al. Large impact basins on Mercury:Global distribution,characteristics,and modification history from MESSENGER orbital data. Journal of Geophysical Research,2012,117:E00L08. |
| 55 | Brown S M,Elkims–Tanton L T. Compositions of Mercury's earliest crust from magma ocean models. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,285:272-282. |
| 56 | Ernst C M,Murchie S L,Barnouin O S,et al. Exposure of spectrally distinct material by impact craters on Mercury:Implications for global stratigraphy. Icarus,2010,209:210-223. |
| 57 | Robinson M S,Lucey P G. Recalibrated Mariner 10 color mosaics:Implications for mercurian volcanism. Science,1997,275:197-200. |
| 58 | Head J W,Murchie S L,Prockter L M,et al. Volcanism on Mercury:Evidence from the first MESSENGER flyby. Science,2008,321:69-72. |
| 59 | Head J W,Murchie S L,Prockter L M,et al. Volcanism on Mercury:Evidence from the first MESSENGER flyby for extrusive and explosive activity and the volcanic origin of plains. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,a285:227-242. |
| 60 | Head J W,Chapman C R,Strom R G,et al. Flood volcanism in the northern high latitudes of Mercury revealed by MESSENGER. Science,2011,333:1853-1856. |
| 61 | Ostrach L R,Robinson M S,Whitten J L,et al. Extent,age,and resurfacing history of the northern smooth plains on Mercury from MESSENGER observations. Icarus,2015,250:602-622. |
| 62 | Du J,Wieczorek M A,Fa W,et al. Thickness of lava flows within the northern smooth plains on Mercury as estimated by partially buried craters. Geophysical Research Letters,2020,47:e2020GL090578. |
| 63 | Byrne P K,Klimczak C,Williams D A,et al. An assemblage of lave flow features on Mercury. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2013,118:1303-1322. |
| 64 | Hurwitz D M,Head J W,Byrne P K,et al. Investigating the origin of candidate lava channels on Mercury with MESSENGER data:Theory and observations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2013,118:471-486. |
| 65 | Beuthe M,Charlier B,Namur O,et al. Mercury's crsutal thickness correlates with lateral variations in mantle melt production. Geophysical Research Letters,2020,47:e2020GL087261. |
| 66 | Jerram D A,Widdowson M. The anatomy of continental flood basalt provinces:Geological constraints on the processes and products of flood volcanism. Lithos,2005,79:385-405. |
| 67 | Strom R G,Chapman C R,Merline W J,et al. Mercury cratering record viewed from MESSENGER's first flyby. Science,2008,321:79-81. |
| 68 | Murchie S L,Watters T R,Robinson M S,et al. Geology of the Caloris basin,Mercury:A new view from MESSENGER. Science,2008,321:73-76. |
| 69 | Mancinelli P,Minelli F,Pauselli C,et al. Geology of the Raditladi quadrangle,Mercury (H04). Journal of Maps,2016,12:190-202. |
| 70 | Padovan S,Tosi N,Plesa A. Impact–induced changes in source depth and volume of magmatism on Mercury and their observational sighnatures. Nature Communications,2017,8:1945. |
| 71 | Roberts J H,Barnouin O S. The effect of the Caloris impact on the mantle dynamics and volcanism of Mercury,Journal of Geophysical Research,2012,117:E02007. |
| 72 | Spudis P D,McGovern P J,Kiefer W S. Large shield volcanoes on the Moon. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2013,118:1063-1081. |
| 73 | Whitten J L,Head J W. Rembrandt impact basin:Distinguishing between volcanic and impact–produced plains on Mercury. Icarus,2015,258:350-365. |
| 74 | Meyer H M,Denevi B W,Boyd A K,et al. The distribution and origin of lunar light plasin around Orientale basin. Icarus,2016,273:135-145. |
| 75 | Robinson M S,Murchie S L,Blewett D T,et al. Reflectance and color variations on Mercury:Regolith processes and compositional heterogeneity. Science,2008,321:66-69. |
| 76 | Kerber L,Head J W,Solomon S C,et al. Explosive volcanic eruptions on Mercury:Eruption conditions,magma volatile content,and implications for interior volatile abundances. Earth Planetary Science Letters,2009,285:263-271. |
| 77 | Kerber L,Head J W,Blewett D T,et al. The global distribution of pyroclastic deposits on Mercury:The view from MESSENGER flybys 1-3. Planetary and Space Science,2011,59:1895-1909. |
| 78 | Goudge T A,Head J W,Kerber L,et al. Global inventory and characterization of pyroclastic deposits on Mercury:New insights into pyroclastic activity from MESSENGER orbital data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2014,119:635-658. |
| 79 | Thomas R J,Rothery D A,Conway S J,et al. Mechanisms of explosive volcanism on Mercury:Implications from its globaldistribution and morphology. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets,2014,b119:2239-2254. |
| 80 | Jozwiak L M,Head J W,Wilson L. Explosive volcanism on Mercury:Analysis of vent and deposit mophology and modes of eruption. Icarus,2018,302:191-212. |
| 81 | Rothery D A,Thomas R J,Kerber L. Prolonged eruptive history of a compound volcano on Mercury:Volcanic and tectonic implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2014,385:59-67. |
| 82 | Besse S,Doressoundiram A,Barraud O,et al. Spectral properties and physical extent of pyroclastic deposits on Mercury:Variability within selected deposits and implications for explosive volcanism. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2020,125,2018JE005879. |
| 83 | Thomas R J,Rothery D A,Conway S J,et al. Explosive volcanism in complex impact craters on Mercury and the Moon:Influence of tectonic regime on depth of magmatic intrusion. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2015,431:164-172. |
| 84 | Blewett D T,Levy C L,Chabot N L,et al. Phase–ratio images of the surface of Mercury:Evidence for differences in sub–resolution texture. Icarus,2014,242:142-148. |
| 85 | Izenberg N R,Klima R L,Murchie S L,et al. The low–iron,reduced surface of Mercury as seen in spectral reflectance by MESSENGER. Icarus,2014,228:364-374. |
| 86 | Besse S,Doressoundiram A,Benkhoff J. Spectroscopic properties of explosive volcanism within the Caloris basin with MESSENGER observations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planet,2015,120:2015JE004819. |
| 87 | Banks M E,Xiao Z,Barden S E,et al. Revised age constraints for Mercury's Kuiperian and Mansurain systems∥The 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference,The Woodlands,TX,USA,2016:2943. |
| 88 | Ernst C I,Denevi B W,Ostrach L R. Updated absolute age estimates for the Tolstoj and Caloris basins,Mercury. Lunar Planetary Science,2017,48:2934. |
| 89 | Marchi S,Chapman C R,Fassett C I,et al. Global resurfacing of Mercury4.0~4.1 billion years ago by heavy bombardment and volcanism. Nature,2013,499:59-61. |
| 90 | Melosh H J. Impact Cratering:A geologic process. London,UK:Oxford University Press,1989,1-253. |
| 91 | Ernst C M,Murchie S L,Barnouin O S,et al. Exposure of spectrally distinct material by impact craters on Mercury:Implications for global stratigraphy. Icarus,2010,209:210-223. |
| 92 | Deng Q,Li F,Yan J,et al. The thermal evolution of Mercury over the past ~4.2 Ga as revealed by relaxation states of mantle plugs beneath impact basins. Geophysical Research Letters,2020,47:e2020GL089051. |
| 93 | Solomon S,Head J W. Mechanisms for lithospheric heat transport on Venus:Implications for rectonic style and volcanism. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,1982,87:9236-9246. |
| 94 | Byrne P K. A comparison of inner Solar System volcanism. Nature Astronomy,2019(4):321-327. |
| 95 | Crisp J A. Rates of magma emplacemnt and volcanic output. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,1984,20:177-211. |
| 96 | Black B A,Manga M. The eruptibility of magmas at Tharsis and Syrtis Major on Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2016,121:944-964. |
| 97 | Head J W,Wilsom L. Lunar graben formation due to near–surface deformation accompanying dike emplacement. Planetary and Space Science,1993,41(10):719-727 |
| 98 | Shirey S B,Hanson G N. Mantle–derived Archaean monzodiorites and trachyandesites. Nature,1984,310:222-224. |
| 99 | Schultz P H. Floor–fractured lunar craters. Moon,1976,15:241-273. |
| 100 | Head J W,Murchie S L,Prockter L M,et al. Evidence for intrusive activity on Mercury from the first MESSENGER flyby. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,b285:251-262. |
| 101 | Rothery D A,Massironi M,Alemanno G,et al. Rationale for BepiColombo studies of Mercury's surface and composition.Space Science Reviews,2020,216:66. |
| [1] | 王大勇 1 ** , 陆现彩 2 , 徐士进 2 , 胡文瑄 2 , 齐 天 1 . 沉积盆地内侵入岩席对富含有机质围岩热影响的热传输模型研究 * [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(1): 45-50. |
|
||