南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (2): 264–274.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.02.010
• • 上一篇
基于欧式空间⁃加权逻辑回归迁移学习的运动想象EEG信号解码
- 1.昆明理工大学信息工程与自动化学院,昆明,650500
2.昆明理工大学脑认知与脑机智能融合创新团队,昆明,650500
3.武警工程大学信息工程学院,西安,710000
EEG signal decoding of motor imagination based on euclidean space⁃weighted logistic regression transfer learning
Li Chen1,2, Anmin Gong3, Peng Ding1,2, Yunfa Fu1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Information Engineering and Automation,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming,650500,China
2.Brain Cognition and Brain?Computer Intelligence Integration Group,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming,650500,China
3.College of Information Engineering,Engineering University of PAP,Xi'an,710000,China
摘要:
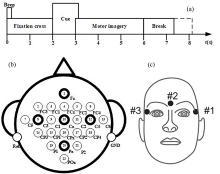
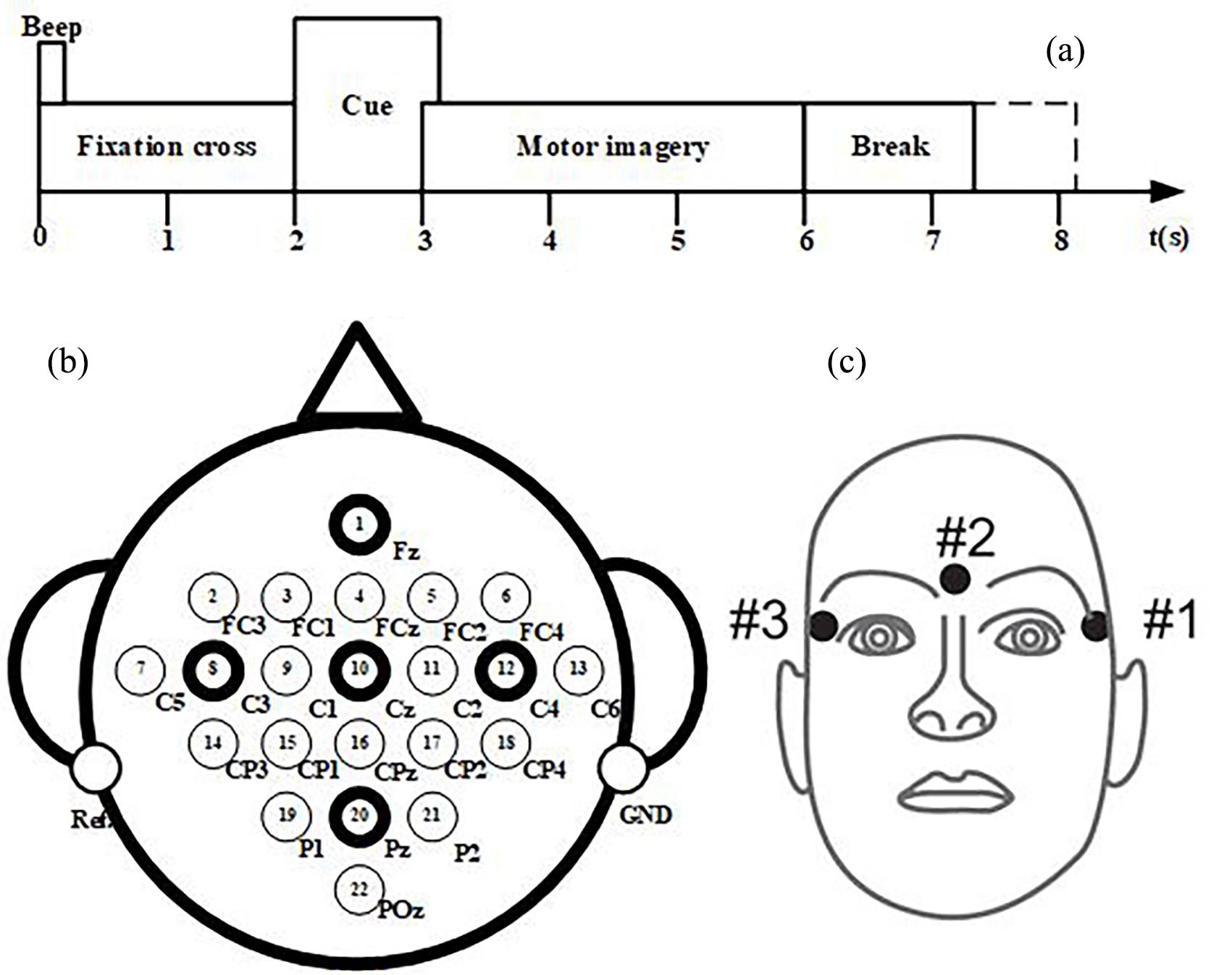
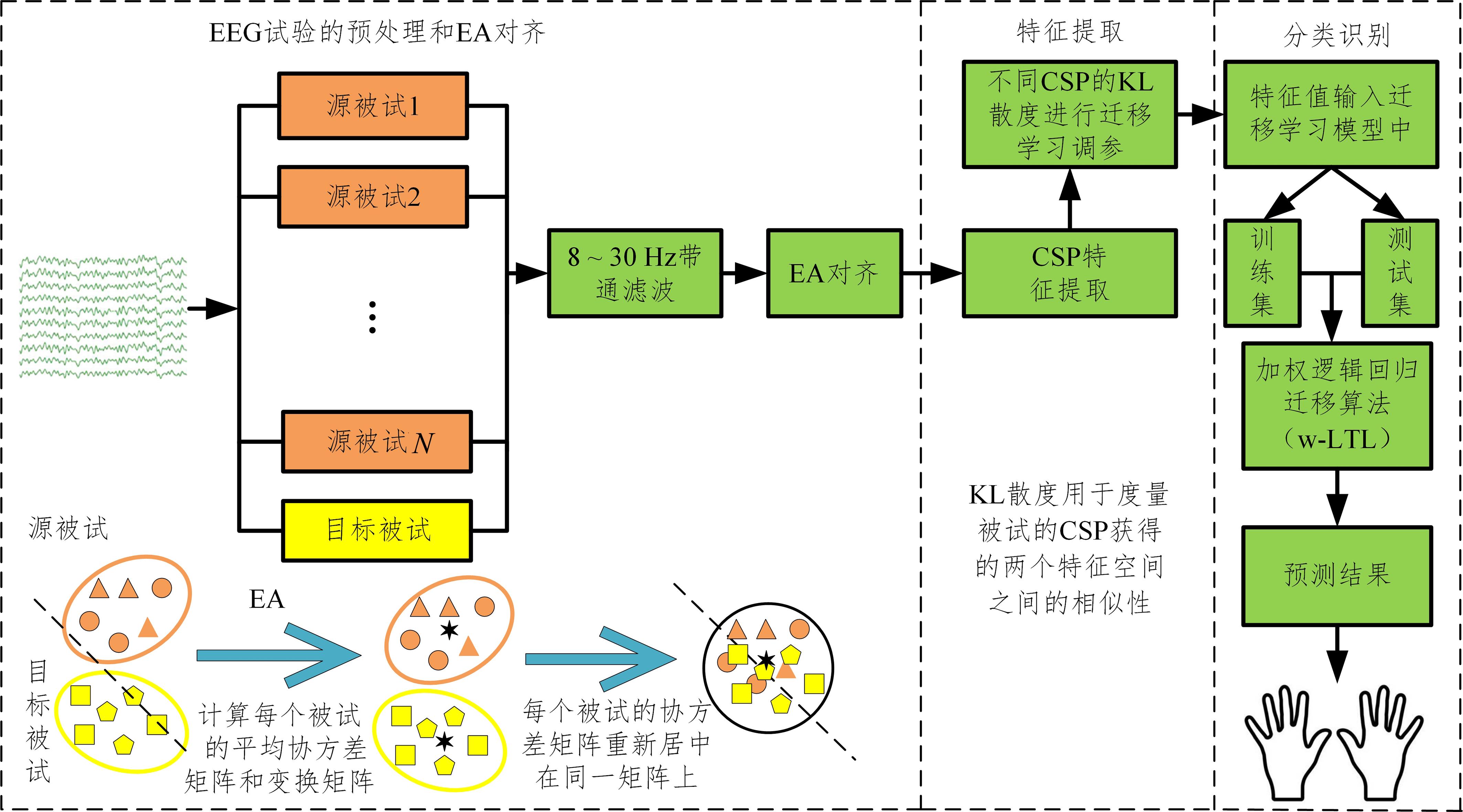
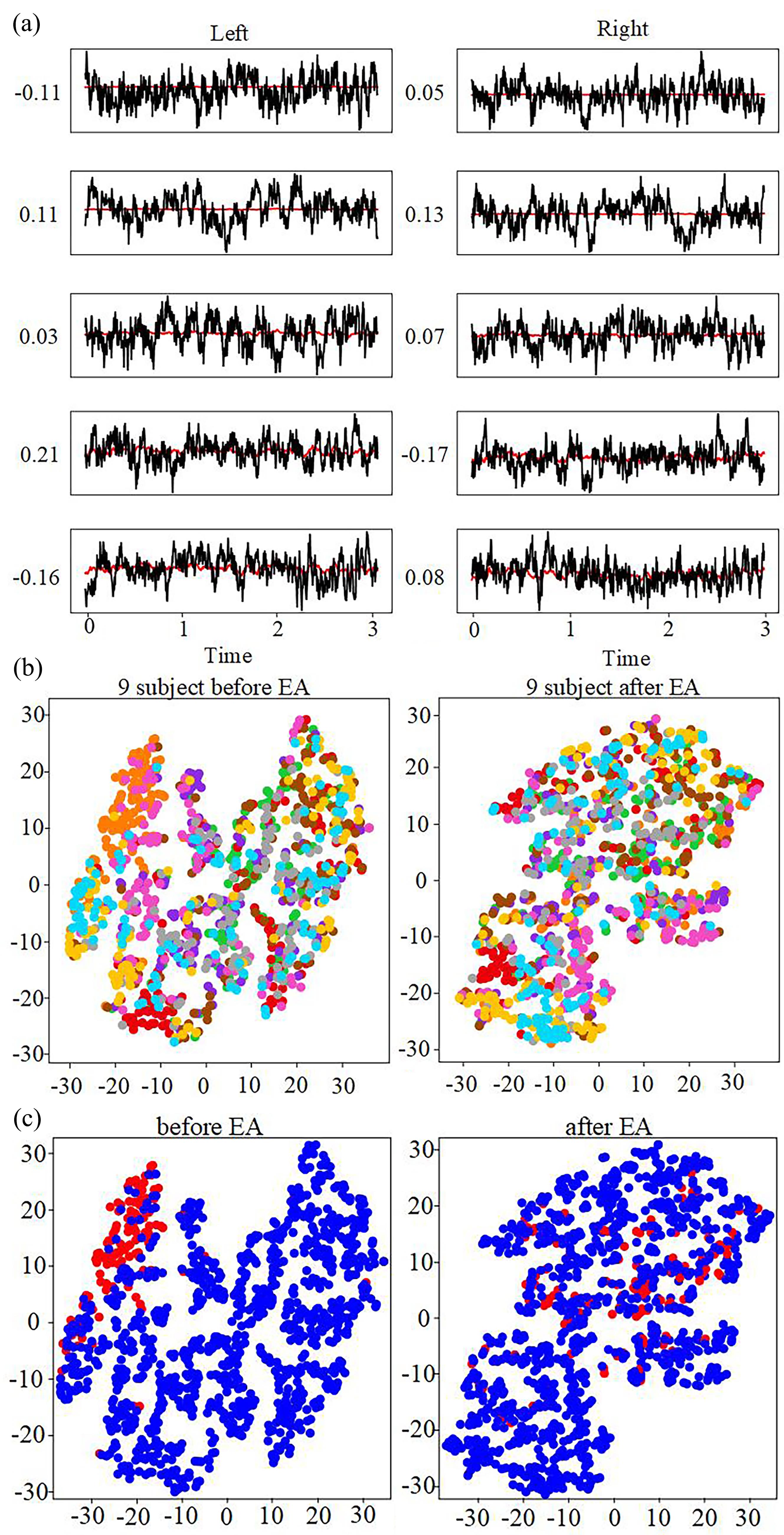
基于脑电图(Electroencephalography,EEG)信号的运动想象(Motor Imagery,MI)意图识别是脑机接口(Brain?Computer Interface,BCI)研究中的重要问题.然而,EEG信号存在严重的个体性差异,不同被试之间的EEG信号特征空间分布差异很大,不同被试之间的分类模型不能通用.针对这一问题,提出一种基于欧式空间的加权逻辑回归迁移学习方法,算法首先将不同被试的EEG数据进行欧几里得空间对齐,使各信号更加相似,减少差异性,然后计算特定被试共空间模式(Common Spatial Pattern,CSP)获得不同的特征值,并计算这些特征值的KL(Kullback?Leibler)散度,进而利用KL散度调整迁移学习的加权逻辑回归算法,得到分类模型.实验结果表明:对于BCI竞赛IV中的数据集2a,提出的方法可以极大地提升BCI的学习性能,算法分类准确率比基线算法(线性判别分析)高出15%.在数据样本增多的情况下,被试的分类准确性也得到了明显的提升,和同类算法相比,分类准确率提升4%,说明提出的算法能进一步提高BCI的学习性能,改善分类模型的通用性问题.
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Lance B J, Kerick S E, Ries A J,et al. Brain–computer interface technologies in the coming decades. Proceedings of the IEEE,2012(100,Special Centennial Issue):1585- 1599. |
| 2 | Wolpaw J R, Birbaumer N, McFarland D J,et al. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clinical Neurophysiology,2002,113(6):767-791. |
| 3 | Stam C J, Nolte G, Daffertshofer A. Phase lag index:Assessment of functional connectivity from multi channel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Human Brain Mapping,2007,28(11):1178-1193. |
| 4 | Li M A, Luo X Y, Yang J F,et al. Applying a locally linear embedding algorithm for feature extraction and visualization of MI?EEG. Journal of Sensors,2016:7481946. |
| 5 | Chikara R K, Ko L W. Classification of EEG?P300 signals using phase locking value and pattern recognition classifiers∥2015 Conference on Technologies and Applications of Artificial Intelligence. Tainan,China:IEEE,2015:367-372. |
| 6 | Oehler M, Neumann P, Becker M,et al. Extraction of SSVEP signals of a capacitive EEG helmet for human machine interface∥2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Vancouver,Canada:IEEE,2008:4495-4498. |
| 7 | Saha S, Ahmed K I U, Mostafa R,et al. Evidence of variabilities in EEG dynamics during motor imagery?based multiclass brain–computer interface. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2018,26(2):371-382. |
| 8 | Tu W T, Sun S L. A subject transfer framework for EEG classification. Neurocomputing,2012(82):109-116. |
| 9 | Lotte F. Signal processing approaches to minimize or suppress calibration time in oscillatory activity?based brain–computer interfaces. Proceedings of the IEEE,2015,103(6):871-890. |
| 10 | Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2010,22(10):1345-1359. |
| 11 | Wu D R, Lawhern V J, Gordon S,et al. Driver drowsiness estimation from EEG signals using online weighted adaptation regularization for regression (OwARR). IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,2017,25(6):1522-1535. |
| 12 | Wu D R, Lawhern V J, Hairston W D,et al. Switching EEG headsets made easy:Reducing offline calibration effort using active weighted adaptation regularization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2016,24(11):1125-1137. |
| 13 | Hossain I, Khosravi A, Hettiarachchi I,et al. Multiclass informative instance transfer learning framework for motor imagery?based brain?computer interface. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience,2018:6323414,doi:10.1155/2018/6323414 . |
| 14 | Li Y, Kambara H, Koike Y,et al. Application of covariate shift adaptation techniques in brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2010,57(6):1318-1324. |
| 15 | Samek W, Meinecke F C, Müller K R. Transferring subspaces between subjects in brain?computer interfacing. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2013,60(8):2289-2298. |
| 16 | He H, Wu D R. Transfer learning enhanced common spatial pattern filtering for brain computer interfaces (BCIs):Overview and a new approach∥International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2017:811-821. |
| 17 | Lotte F, Guan C T. Learning from other subjects helps reducing brain?computer interface calibration time∥2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing. Dallas,TX,USA:IEEE,2010:614-617. |
| 18 | Wu D R, Jiang X, Peng R M,et al. Transfer learning for motor imagery based brain?computer interfaces:A complete pipeline. 2020,arXiv:. |
| 19 | Wu D R, Xu Y F, Lu B L. Transfer learning for EEG?based brain?computer interfaces:A review of progress made since 2016. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems,2020,doi:10.1109/TCDS.2020.3007453 . |
| 20 | Tariq M, Uhlenberg L, Trivailo P,et al. Mu?beta rhythm ERD/ERS quantification for foot motor execution and imagery tasks in BCI applications∥2017 8th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications. Debrecen,Hungary:IEEE,2017:91-96. |
| 21 | Yger F, Berar M, Lotte F. Riemannian approaches in brain?computer interfaces:A review. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2017,25(10):1753-1762. |
| 22 | He H, Wu D R. Transfer learning for brain–computer interfaces:A Euclidean space data alignment approach. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2020,67(2):399-410. |
| 23 | Nasrabadi N M. Pattern recognition and machine learning. Journal of Electronic Imaging,2007,16(4):049901. |
| 24 | Shalev?Shwartz S, Tewari A. Stochastic methods for l1?regularized loss minimization. The Journal of Machine Learning Research,2011(12):1865-1892. |
| 25 | Iturrate I, Montesano L, Minguez J. Task?dependent signal variations in EEG error?related potentials for brain–computer interfaces. Journal of Neural Engineering,2013,10(2):026024. |
| 26 | Samek W, Kawanabe M, Müller K R. Divergence?based framework for common spatial patterns algorithms. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering,2013(7):50-72. |
| 27 | Van Der Maaten L, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t?SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2008(9):1-48. |
| 28 | Lotte F, Guan C T. Regularizing common spatial patterns to improve BCI designs:Unified theory and new algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2011,58(2):355-362. |
| 29 | Fiebig K H, Jayaram V, Peters J,et al. Multi?task logistic regression in brain?computer interfaces∥2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics. Budapest,Hungary:IEEE,2016:2307-2312. |
| 30 | Azab A M, Mihaylova L, Ang K K,et al. Weighted transfer learning for improving motor imagery?based brain–computer interface. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2019,27(7):1352-1359. |
| 31 | Shimodaira H. Improving predictive inference under covariate shift by weighting the log?likelihood function. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference,2000,90(2):227-244. |
| 32 | Utgoff P E. Shift of bias for inductive concept learning∥Michalski R S,Carbonell J G,Mitchell T M. Machine Learning:An Artificial Intelligence Approach. Los Alton,CA,USA:Morgan Kaufmann,1986,2:107-148. |
| 33 | Dai D Q, Yuen P C. Regularized discriminant analysis and its application to face recognition. Pattern Recognition,2003,36(3):845-847. |
| [1] | 张玮, 赵永虹, 邱桃荣. 基于注意力机制和深度学习的运动想象脑电信号分类方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(1): 29-37. |
| [2] | 樊炎, 匡绍龙, 许重宝, 孙立宁, 张虹淼. 一种同步提取运动想象信号时⁃频⁃空特征的卷积神经网络算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(6): 1064-1074. |
| [3] | 王丽娟,丁世飞,丁玲. 基于迁移学习的软子空间聚类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 515-523. |
| [4] | 钟琪,冯亚琴,王蔚. 跨语言语料库的语音情感识别对比研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(5): 765-773. |
| [5] | 孟佳娜*, 赵丹丹, 于玉海, 孙世昶. 归纳式迁移学习在跨领域情感倾向性分析中的应用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(1): 175-183. |
| [6] | 李文石,钱重阳,李雷,魏锋 . 让耳朵说话:基于单通道耳穴近红外谱的脑机接口[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(5): 655-660. |
|
||