南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (2): 276–286.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2024.02.009
• • 上一篇
数值天气预报模式的行星边界层方案热力预报变量选择
- 中尺度灾害性天气教育部重点实验室,南京大学大气科学学院,南京,210023
On the choice of prognostic thermal variable in planetary boundary layer schemes for numerical weather prediction models
- Key Laboratory for Mesoscale Severe Weather,Ministry of Education,and School of Atmospheric Sciences,Nanjing University,Nanjing,210023,China
摘要:
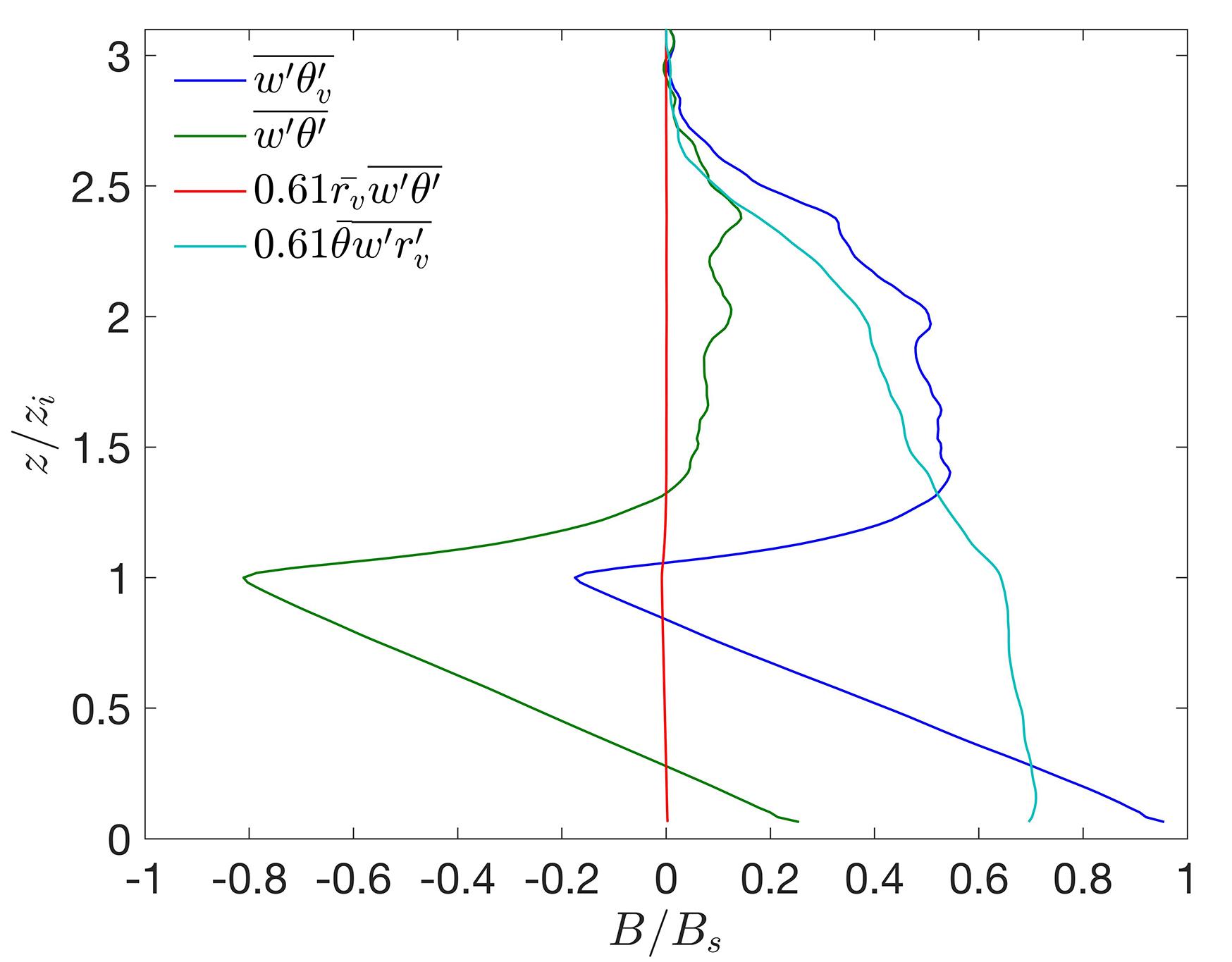
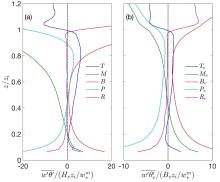
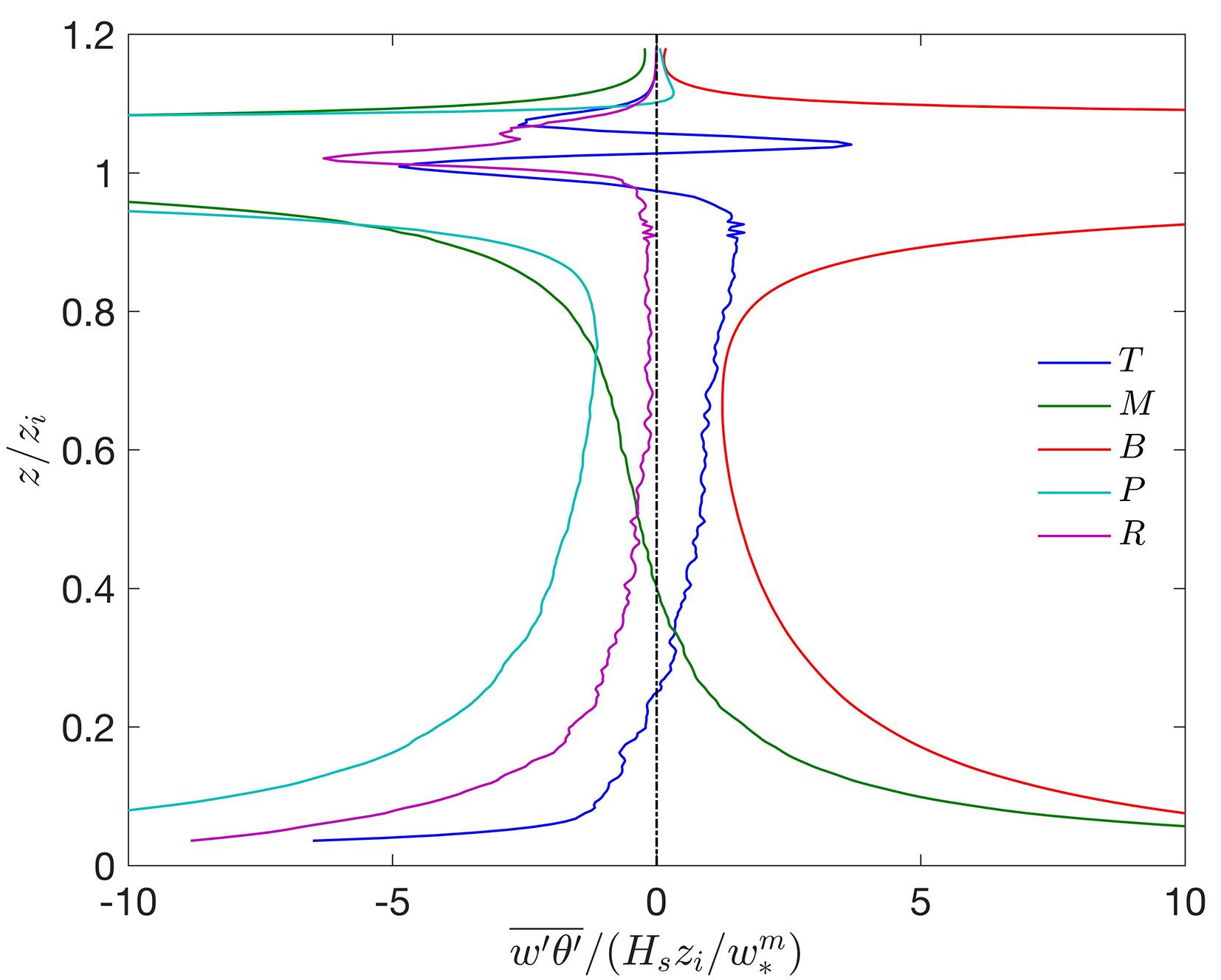
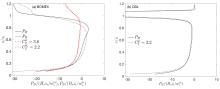
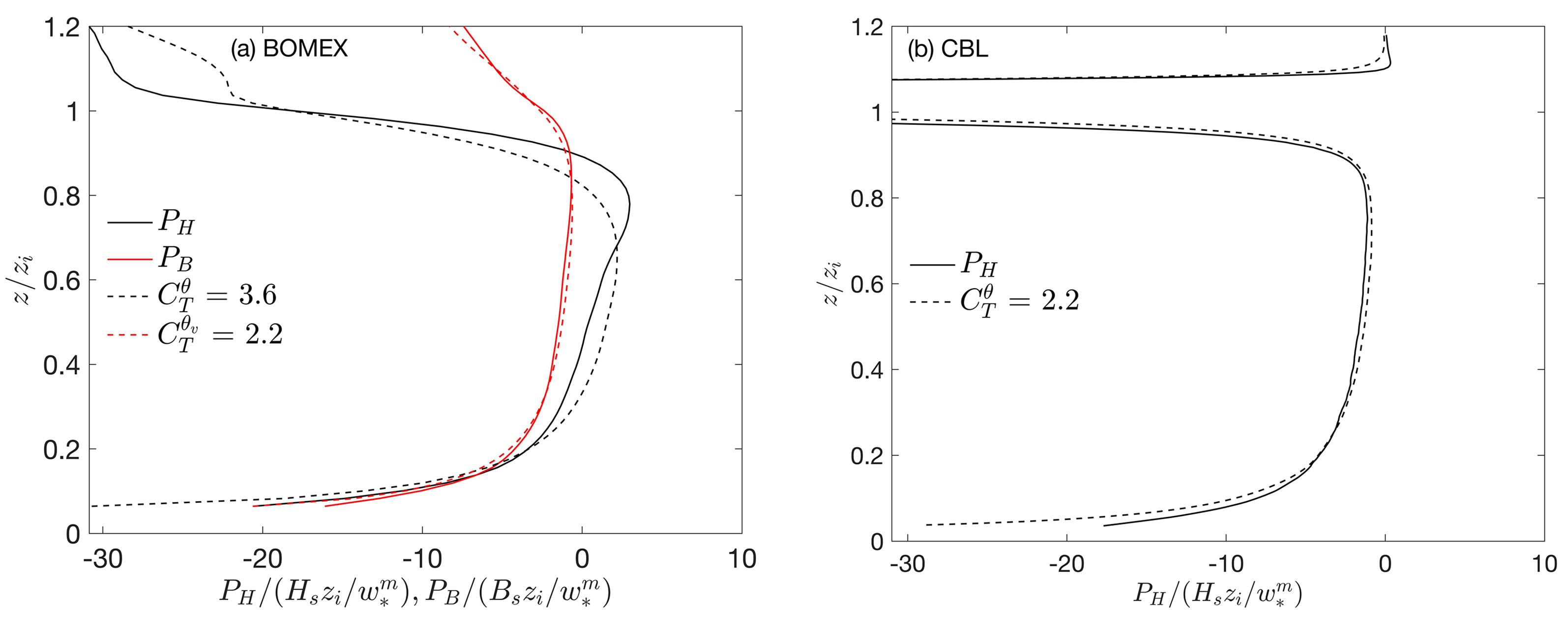
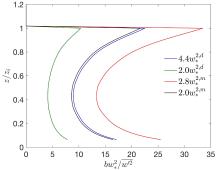
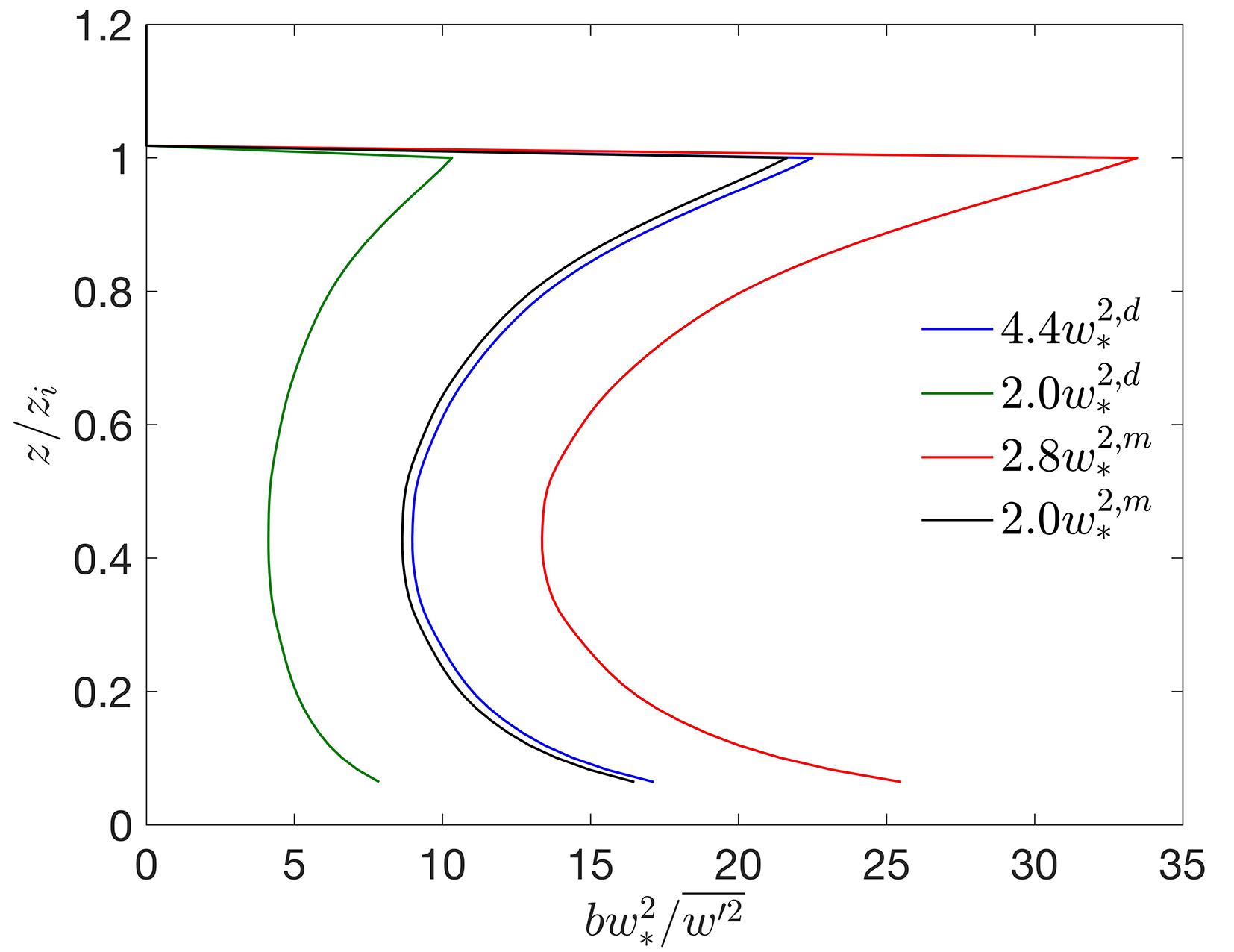
在数值天气预报模式中,大气边界层湍流混合由行星边界层方案承担.传统的边界层方案多采用位温作为热力学预报变量,计算感热通量并获得位温的湍流倾向,多数边界层方案设计之初,也往往只考虑干边界层中的位温湍流混合.事实上,驱动边界层热对流的是浮力而非热力,前者还包含了水汽的作用,由虚位温表征.基于湍流可分辨的大涡模拟来评估传统边界层方案所参数化的感热通量在湿边界层中的适用性,重点关注方案中涉及逆梯度修正项的关键系数,同时也考察浮力通量的参数化评估结果显示浮力通量在干湿边界层中具备一致性,其模式系数不随水汽条件变化,因此,推荐以虚位温替代位温作为行星边界层方案热力预报变量.
中图分类号:
- P445
| 1 | Stull R B. An introduction to boundary layer meteorology. Boston:Kluwer Academic Publishers,1988. |
| 2 | Hunt J C R, Kaimal J C, Gaynor J E. Eddy structure in the convective boundary layer?new measurements and new concepts. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society,1988,114(482):827-858. |
| 3 | Salesky S T, Chamecki M, Bou?Zeid E. On the nature of the transition between roll and cellular organization in the convective boundary layer. Boundary?Layer Meteorology,2017,163(1):41-68. |
| 4 | Young G S. Turbulence structure of the convective boundary layer. Part Ⅱ. Phonenix 78 aircraft observations of thermals and their environment. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,1988,45(4):727-735. |
| 5 | Warner J, Telford J W. Convection below cloud base. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,1967,24(4):374-382. |
| 6 | Lenschow D H, Stephens P L. The role of thermals in the convective boundary layer. Boundary?Layer Meteorology,1980,19(4):509-532. |
| 7 | Townsend A A. The structure of turbulent shear flow. New York:Cambridge University Press,1976,429. |
| 8 | Deardorff J W. Theoretical expression for the countergradient vertical heat flux. Journal of Geophysical Research,1972,77(30):5900-5904. |
| 9 | Hu X M, Xue M, Li X L. The use of high?resolution sounding data to evaluate and optimize nonlocal PBL schemes for simulating the slightly stable upper convective boundary layer. Monthly Weather Review,2019,147(10):3825-3841. |
| 10 | Zhou B W, Sun S W, Yao K,et al. Reexamining the gradient and countergradient representation of the local and nonlocal heat fluxes in the convective boundary layer. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2018,75(7):2317-2336. |
| 11 | 赵昭,周博闻. 日间对流边界层中的非局地动量混合. 气象科学,2021,41(5):631-643. |
| Zhao Z, Zhou B W. Non?local mixing of momentum in the daytime convective boundary layer. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences,2021,41(5):631-643. | |
| 12 | Davies?Jones R. An expression for effective buoyancy in surroundings with horizontal density gradients. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2003,60(23):2922-2925. |
| 13 | Wang Y H, Cheng X P, Fei J F,et al. Modeling the shallow cumulus?topped boundary layer at gray zone resolutions. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2022,79(9):2435-2451. |
| 14 | Wyngaard J C. Turbulence in the atmosphere. New York:Cambridge University Press,2010,393. |
| 15 | LeMone M A, Pennell W T. The relationship of trade wind cumulus distribution to subcloud layer fluxes and structure. Monthly Weather Review,1976,104(5):524-539. |
| 16 | LeMone M A, Angevine W M, Bretherton C S,et al. 100 years of progress in boundary layer meteorology. Meteorological Monographs,2019,59(1):9.1-9.85. |
| 17 | Conzemius R J, Fedorovich E. Dynamics of sheared convective boundary layer entrainment. Part I:Methodological background and large?eddy simu?lations. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2006,63(4):1151-1178. |
| 18 | Liu P, Sun J N, Shen L D. Parameterization of sheared entrainment in a well?developed CBL. Part I:Evaluation of the scheme through large?eddy simu?lations. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2016,33(10):1171-1184. |
| 19 | De Roode S R, Duynkerke P G, Jonker H J J. Large?eddy simulation:how large is large enough? Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2004,61(4):403-421. |
| 20 | Willis G E, Deardorff J W. A laboratory model of diffusion into the convective planetary boundary layer. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society,1976,102(432):427-445. |
| 21 | Deardorff J W. Three?dimensional numerical study of the height and mean structure of a heated planetary boundary layer. Boundary?Layer Meteorology,1974,7(1):81-106. |
| 22 | Ertel H. Der vertikale turbulenz?w?rmestrom in der atmosph?re. Meteorologische Zeitschrift,1942,59:250-253. |
| 23 | Priestley C H B, Swinbank W C. Vertical transport of heat by turbulence in the atmosphere. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences,1947,189(1019):543-561. |
| 24 | Deardorff J W. The counter?gradient heat flux in the lower atmosphere and in the laboratory. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,1966,23(5):503-506. |
| 25 | Therry G, Lacarrère P. Improving the eddy kinetic energy model for planetary boundary layer description. Boundary?Layer Meteorology,1983,25(1):63-88. |
| 26 | Troen I B, Mahrt L. A simple model of the atmospheric boundary layer; sensitivity to surface evaporation. Boundary?Layer Meteorology,1986,37(1-2):129-148. |
| 27 | Holtslag A A M, Moeng C H. Eddy diffusivity and countergradient transport in the convective atmospheric boundary layer. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,1991,48(14):1690-1698. |
| 28 | Moeng C H, Wyngaard J C. An analysis of closures for pressure?scalar covariances in the convective boundary layer. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,1986,43(21):2499-2513. |
| 29 | Rotta J. Statistische theorie nichthomogener turbulenz. Zeitschrift für Physik,1951,129(6):547-572. |
| 30 | Holland J Z, Rasmusson E M. Measurements of the atmospheric mass,energy,and momentum budgets over a 500?kilometer square of tropical ocean. Monthly Weather Review,1973,101(1):44-55. |
| 31 | Pier Siebesma A, Bretherton C S, Brown A,et al. A large eddy simulation intercomparison study of shallow cumulus convection. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2003,60(10):1201-1219. |
| 32 | Shin H H, Hong S Y. Analysis of resolved and parameterized vertical transports in convective boundary layers at gray?zone resolutions. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2013,70(10):3248-3261. |
| 33 | Heinze R, Mironov D, Raasch S. Second?moment budgets in cloud topped boundary layers:A large?eddy simulation study. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems,2015,7(2):510-536. |
| [1] | 殷雷1,2,孙鉴泞1**,刘罡 . 地表非均匀加热影响对流边界层湍流特征的大涡模拟研究* [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(6): 643-656. |
| [2] | 林 恒 1 , 孙鉴泞 1 ** , 卢 伟 2 . 有切变对流边界层夹卷厚度参数化的大涡模拟研究 * [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 46(6): 616-624. |
|
||