南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (6): 1003–1012.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2023.06.010
• •
改进边界分类的Borderline‑SMOTE过采样方法
- 1.江苏师范大学计算机科学与技术学院,徐州,221116
2.江苏师范大学管理科学与工程研究中心,徐州,221116
Improved Borderline⁃SMOTE oversampling method for boundary classification
He Ma1, Mei Song1,2( ), Yi Zhu1
), Yi Zhu1
- 1.School of Computer Science and Technology, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou, 221116, China
2.Management Science and Technology Center, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou, 221116, China
摘要:
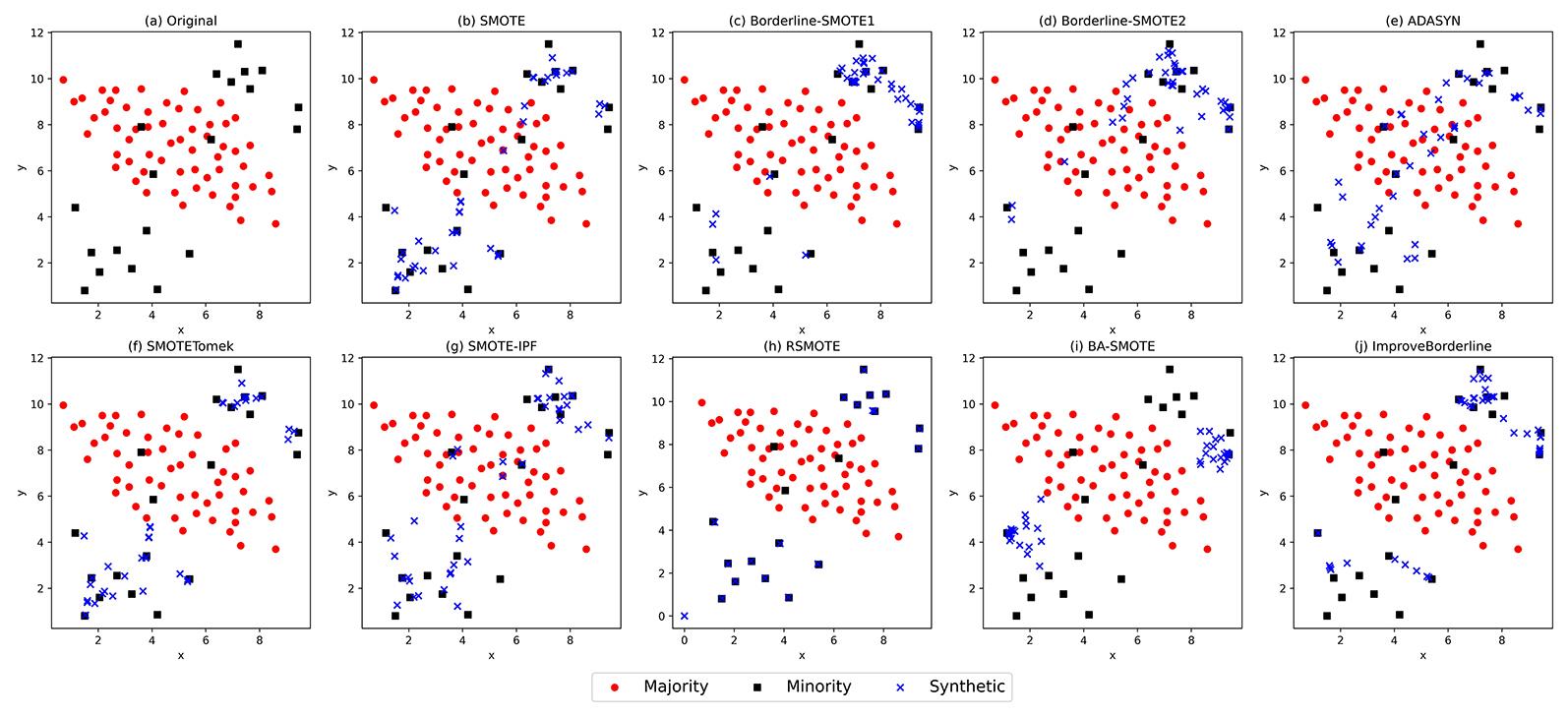
针对不平衡数据中类重叠区域易造成分类错误的问题,提出一种引入合成因子改进边界分类的Borderline?SMOTE过采样方法(IBSM).首先根据少数类样本近邻分布情况找出处于边界的少数类样本,然后计算边界样本对应的合成因子,并根据其取值更新该样本需生成的样本数,最后在近邻中根据合成因子挑选距离最近的top?Z少数类样本进行新样本生成.将提出的方法与八种采样方法在KNN和SVM两种分类器、10个KEEL不平衡数据集上进行对比实验,结果表明,提出的方法在大部分数据集上的F1,G?mean,AUC (Area under Curve)均获得最优值,且F1与AUC的Friedman排名最优,证明所提方法和其余采样方法相比,在处理不平衡数据中的边界样本分类问题时有更好的表现,通过合成因子设定一定的约束条件与分配策略,可以为同类研究提供思路.
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | Chao X R, Kou G, Peng Y,et al. An efficiency curve for evaluating imbalanced classifiers considering intrinsic data characteristics:Experimental analysis. Information Sciences,2022(608):1131-1156. |
| 2 | Chen L, Jia N, Zhao H K,et al. Refined analysis and a hierarchical multi?task learning approach for loan fraud detection. Journal of Management Science and Engineering,2022,7(4):589-607. |
| 3 | Gao Y X, Zhu Y, Zhao Y. Dealing with imbalanced data for interpretable defect prediction. Information and Software Technology,2022(151):107016. |
| 4 | Al S, Dener M. STL?HDL:A new hybrid network intrusion detection system for imbalanced dataset on big data environment. Computers & Security,2021(110):102435. |
| 5 | Milosevic M S, Ciric V M. Extreme minority class detection in imbalanced data for network intrusion. Computers & Security,2022(123):102940. |
| 6 | Rai H M, Chatterjee K. Hybrid CNN?LSTM deep learning model and ensemble technique for automatic detection of myocardial infarction using big ECG data. Applied Intelligence,2022,52(5):5366-5384. |
| 7 | Chawla N V, Bowyer K W, Hall L O,et al. SMOTE:Synthetic minority over?sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,2002(16):321-357. |
| 8 | 周玉,孙红玉,房倩,等. 不平衡数据集分类方法研究综述. 计算机应用研究,2022,39(6):1615-1621. |
| Zhou Y, Sun H Y, Fang Q,et al. Review of imba?lanced data classification methods. Application Research of Computers,2022,39(6):1615-1621. | |
| 9 | Han H, Wang W Y, Mao B H. Borderline?SMOTE:A new over?sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning∥Proceeding of 2005 International Conference on Advances in Intelligent Computing. Hefei,China Springer,2005:878-887. |
| 10 | He H B, Bai Y, Garcia E A,et al. ADASYN:Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning∥2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Hong Kong,China:IEEE,2008:1322-1328. |
| 11 | 陈海龙,杨畅,杜梅,等. 基于边界自适应SMOTE和Focal Loss函数改进LightGBM的信用风险预测模型. 计算机应用,2022,42(7):2256-2264. |
| Chen H L, Yang C, Du M,et al. Credit risk prediction model based on borderline adaptive SMOTE and Focal Loss improved LightGBM. Journal of Computer Applications,2022,42(7):2256-2264. | |
| 12 | 陶佳晴,贺作伟,冷强奎,等. 基于Tomek链的边界少数类样本合成过采样方法. 计算机应用研究,2023,40(2):463-469. |
| Tao J Q, He Z W, Leng Q K,et al. Synthetic oversampling method for boundary minority samples based on Tomek links. Application Research of Computers,2023,40(2):463-469. | |
| 13 | 高雷阜,张梦瑶,赵世杰. 融合簇边界移动与自适应合成的混合采样算法. 电子学报,2022,50(10):2517-2529. |
| Gao L F, Zhang M Y, Zhao S J. Mixed?sampling algorithm combining cluster boundary movement and adaptive synthesis. Acta Electronica Sinica,2022,50(10):2517-2529. | |
| 14 | Xu Z Z, Shen D R, Nie T Z,et al. A cluster?based oversampling algorithm combining SMOTE and k?means for imbalanced medical data. Information Sciences,2021(572):574-589. |
| 15 | 陈俊丰,郑中团. WKMeans与SMOTE结合的不平衡数据过采样方法. 计算机工程与应用,2021,57(23):106-112. |
| Chen J F, Zheng Z T. Over?sampling method on imbalanced data based on WKMeans and SMOTE. Computer Engineering and Applications,2021,57(23):106-112. | |
| 16 | Chen B Y, Xia S Y, Chen Z Z,et al. RSMOTE:A self?adaptive robust SMOTE for imbalanced problems with label noise. Information Sciences,2021(553):397-428. |
| 17 | Batista G E A P A, Prati R C, Monard M C. A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter,2004,6(1):20-29. |
| 18 | Sáez J A, Luengo J, Stefanowski J,et al. SMOTE?IPF:Addressing the noisy and borderline examples problem in imbalanced classification by a re?sampling method with filtering. Information Sciences,2015(291):184-203. |
| 19 | Dou J, Gao Z, Wei G,et al. Switching synthesizing?incorporated and cluster?based synthetic over?sampling for imbalanced binary classification. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,2023(123):106193. |
| 20 | Douzas G, Bacao F, Last F. Improving imbalanced learning through a heuristic oversampling method based on k?means and SMOTE. Information Sciences,2018(465):1-20. |
| 21 | Palakonda V, Kang J M, Jung H. An adaptive neighborhood based evolutionary algorithm with pivot?solution based selection for multi? and many?objective optimization. Information Sciences,2022(607):126-152. |
| 22 | Rivera W A. Noise reduction a priori synthetic over?sampling for class imbalanced data sets. Information Sciences,2017(408):146-161. |
| [1] | 吕佳, 郭铭. 基于密度峰值聚类和局部稀疏度的过采样算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(3): 483-494. |
| [2] | 程永林, 李德玉, 王素格. 基于极大相容块的邻域粗糙集模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 529-536. |
| [3] | 赵小强1,2,3*,张 露1. 基于SVM的高维不平衡数据集分类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(2): 452-. |
| [4] | 朱亚奇1,邓维斌1 ,2*. 一种基于不平衡数据的聚类抽样方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 421-429. |
| [5] | 朱亚奇1,邓维斌1,2*. 一种基于不平衡数据的聚类抽样方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(2): 421-429. |
|
||