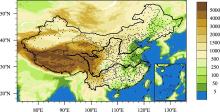
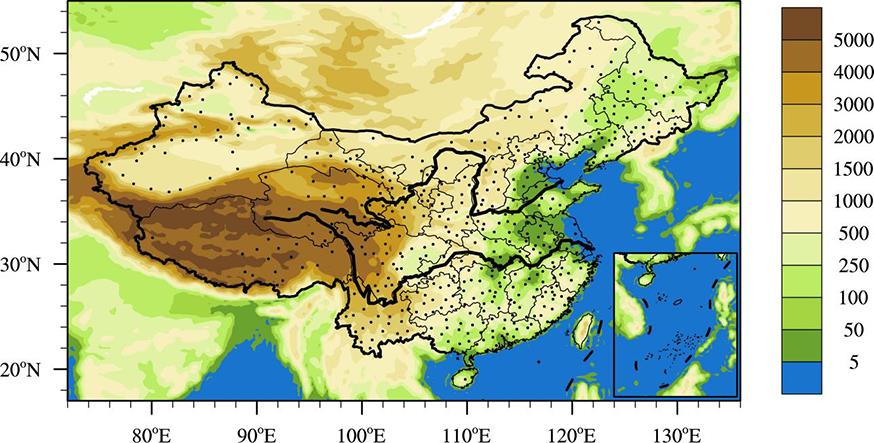
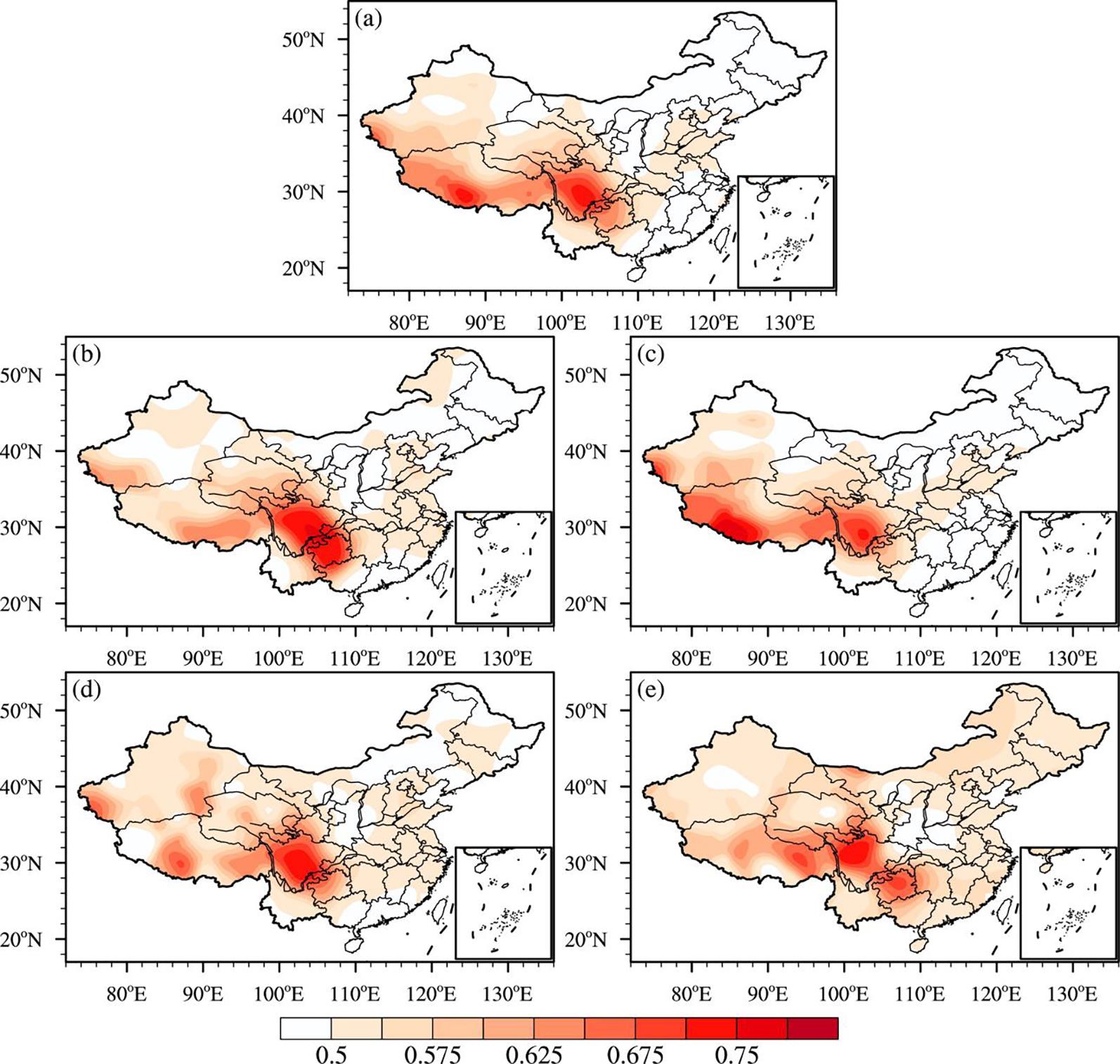
南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (5): 750–765.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.05.002
中国夜雨的时空变化特征研究
- 1.南京大学大气科学学院,南京,210023
2.南京信息工程大学大气科学学院,南京,210044
3.国家气象中心,北京,100081
Characteristics of temporal and spatial variations of nocturnal precipitation in China
Jingshi Wang1, Xi Jiang2( ), Xidi Zhang3
), Xidi Zhang3
- 1.School of Atmosphere Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023, China
2.School of Atmosphere Sciences, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China
3.National Meteorological Center, Beijing, 100081, China
摘要:
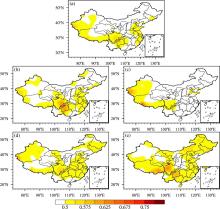
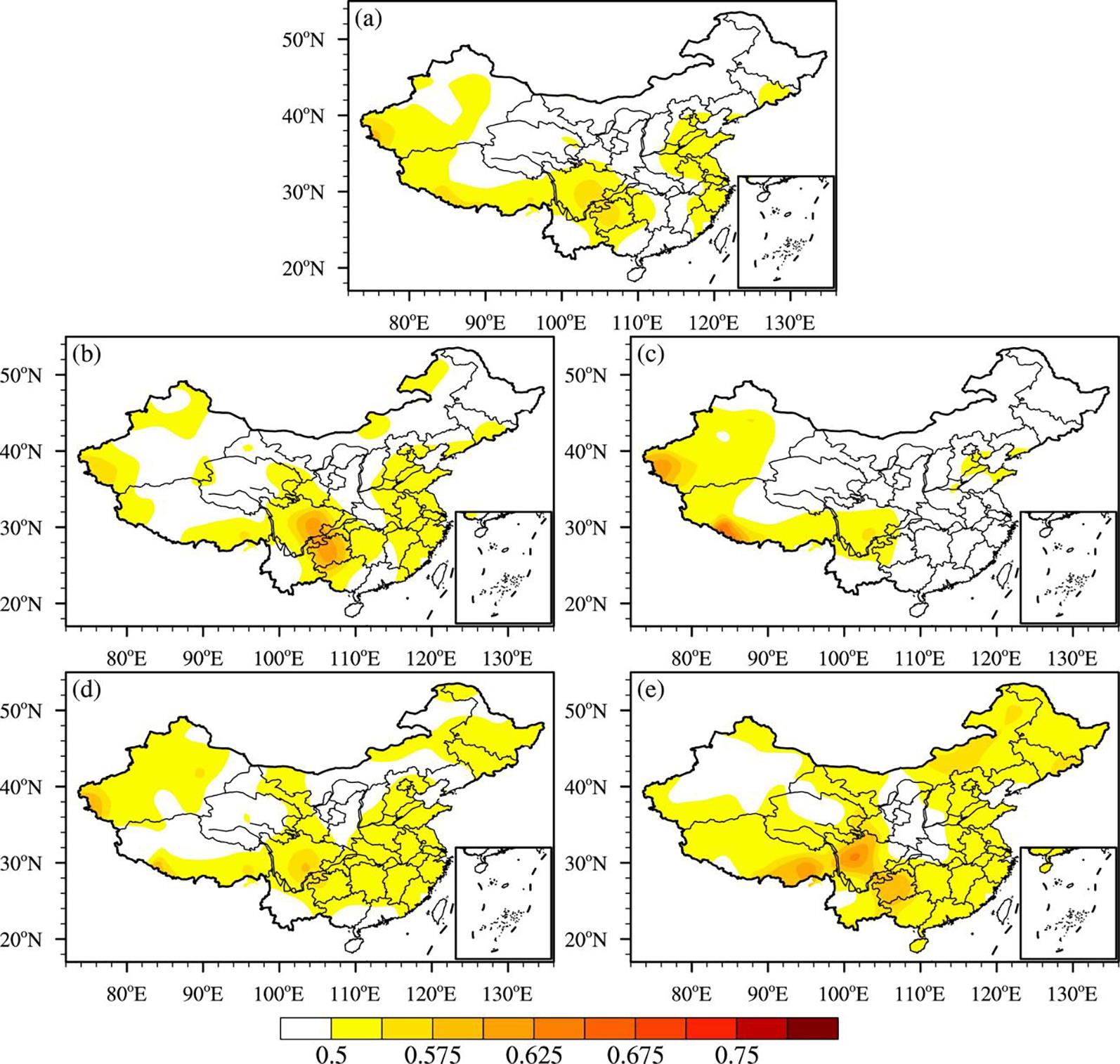
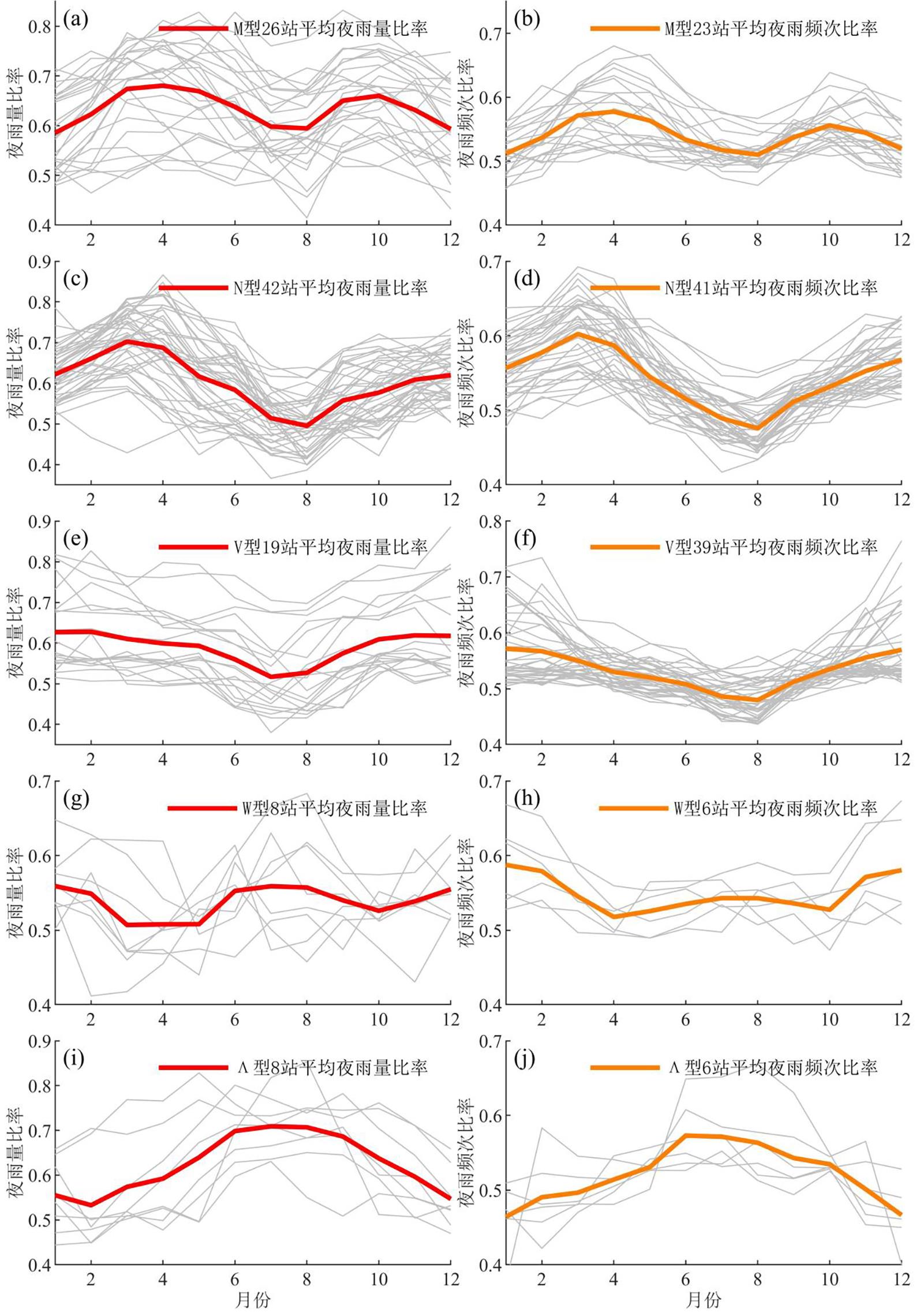
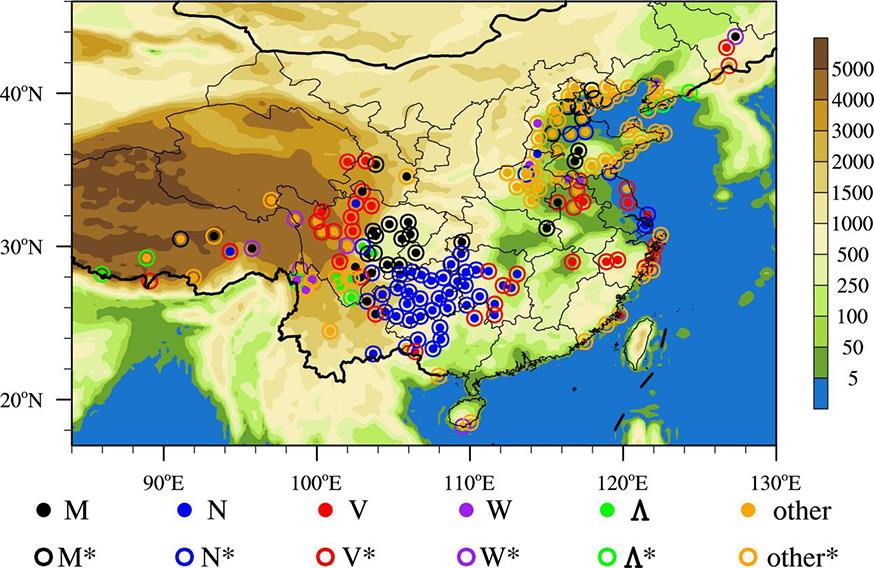
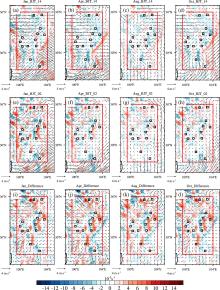
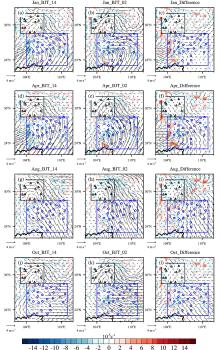
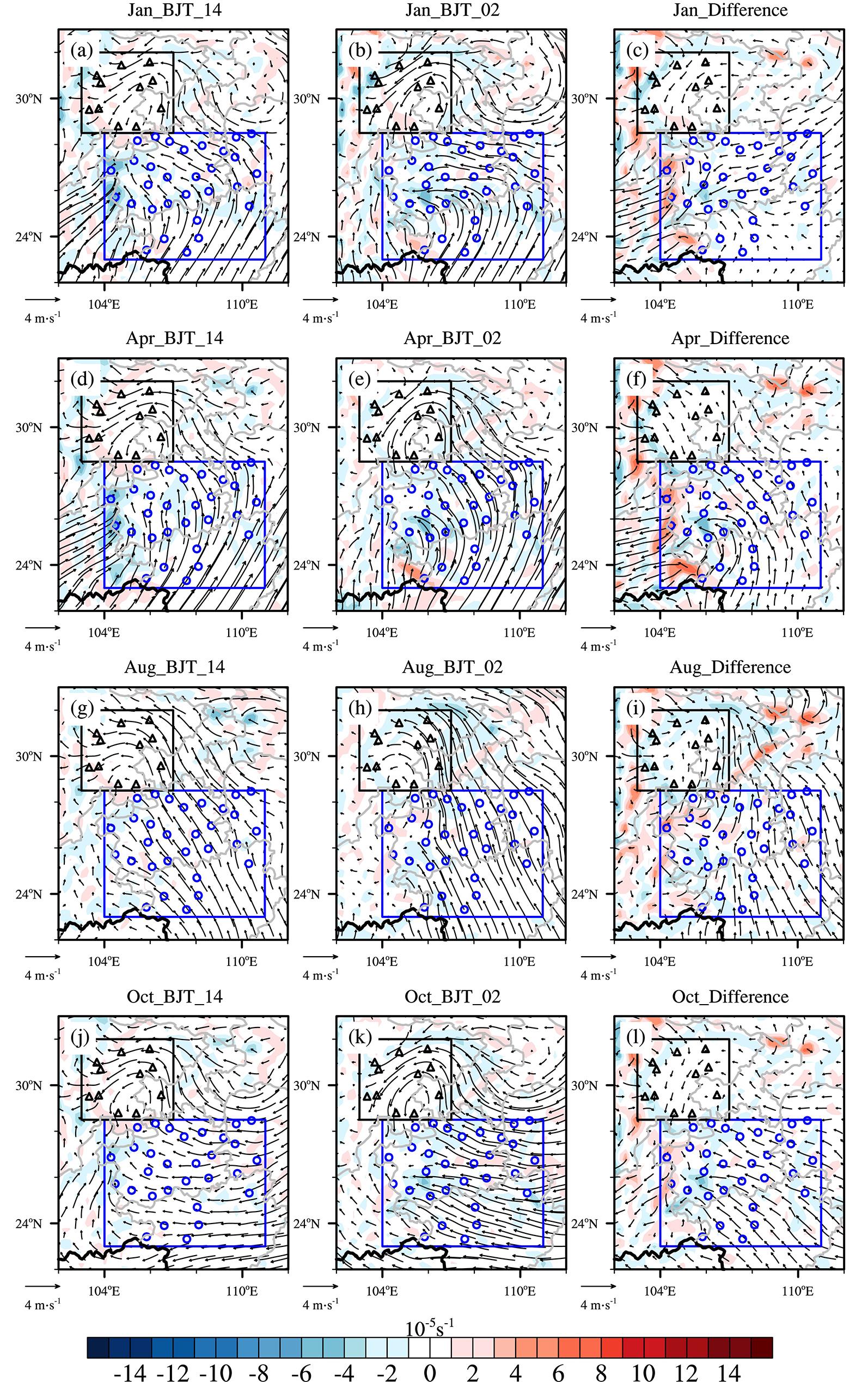
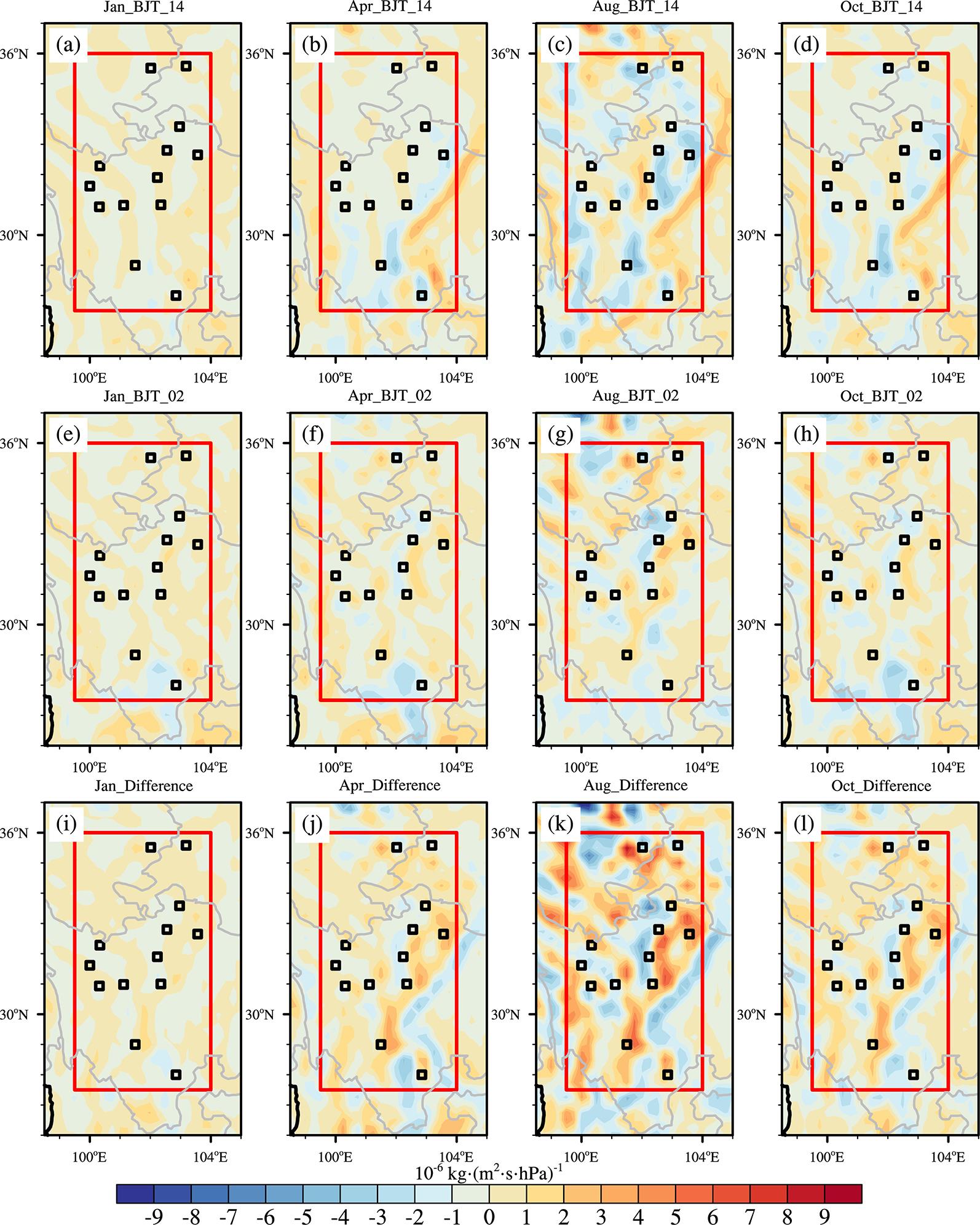
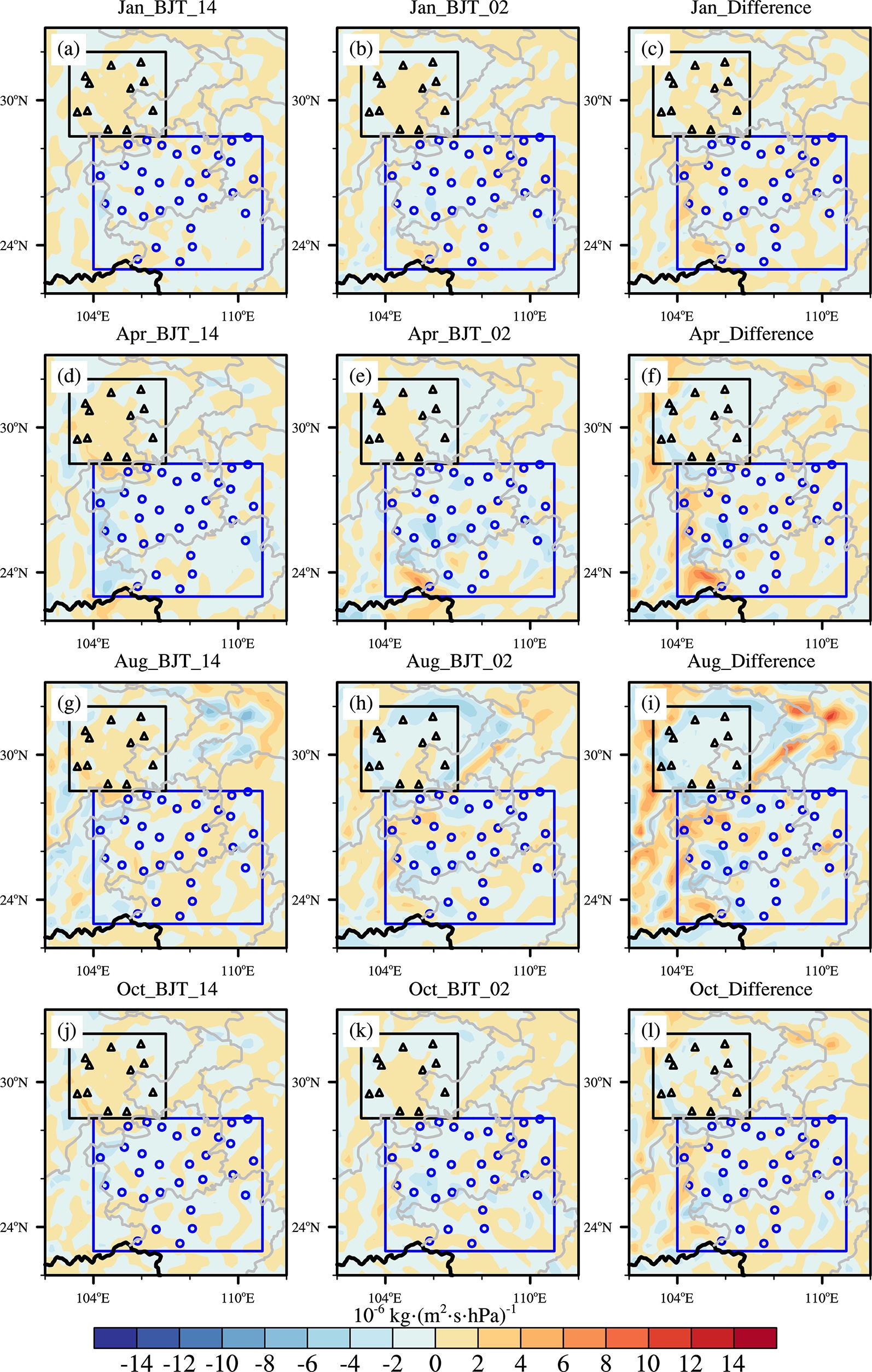
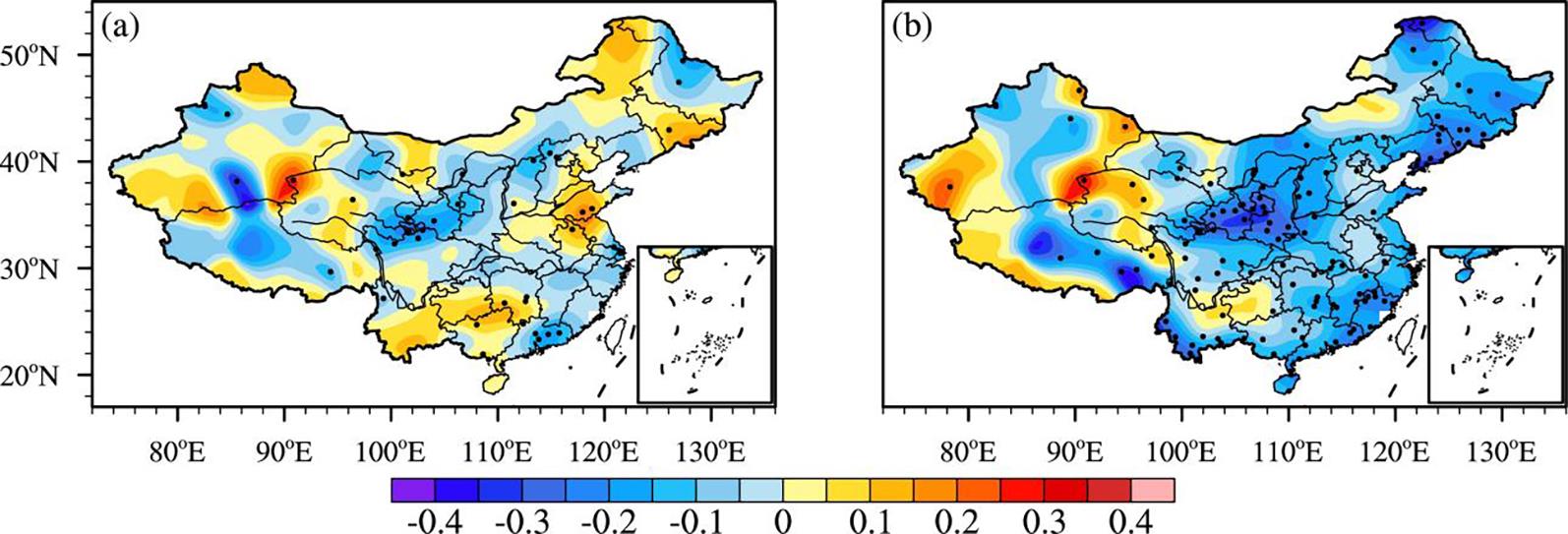
利用1967-2016年中国603个测站降水资料和ERA5的逐小时再分析资料从夜雨量和频次两个角度分析中国夜雨时空变化特征.结果表明:我国存在夜雨现象的站点主要分布在西南部、西北部、黄淮流域、华中地区、京津冀、华南西北部和东北南部,其中,四川、西藏、贵州、新疆和青海夜雨现象最为显著.根据夜雨率的月变化特征,将夜雨现象显著站点分为N型、V型、M型、W型和Λ型,N型主要分布在云贵高原,V型主要分布在青藏高原东麓,M型主要分布在四川盆地.影响N型、V型、M型站点所在区域降水的动力和水汽条件的夜昼差异月变化与对应站点的夜雨率月变化基本一致,N型区域的夜昼差异于春季达到最大,夏季最小,V型区域在夏季最小,冬季最大,M型区域在春季最大.在1967-2016年,夜雨现象显著的地区中,青海诺木洪夜雨现象愈加明显,西藏林芝等地夜雨现象逐渐减弱,这些地区夜雨量比率每十年约变化1%~3%,夜雨频次比率约变化0.4%~1.5%.
中图分类号:
- P426.6
| 1 | Rickenbach T M. Nocturnal cloud systems and the diurnal variation of clouds and rainfall in Southwestern Amazonia. American Meteorological Society,2004,132(5):1201-1219. |
| 2 | 覃卫坚,庞庭颐. 广西夜雨特征及其农业利用. 广西气象,2000,21(1):39-42. |
| Qin W J, Pang T Y. The features of night rain and its utilization in agriculture of Guangxi. Journal of Guangxi Meteorology,2000,21(1):39-42. | |
| 3 | Qian T T, Zhao P, Zhang F Q,et al. Rainy?season precipitation over the Sichuan Basin and adjacent regions in Southwestern China. Monthly Weather Review,2015,143(1):383-394. |
| 4 | 段春锋,曹雯,缪启龙,等. 中国夏季夜雨的空间分布特征. 自然资源学报,2013,28(11):1935-1944. |
| Duan C F, Cao W, Miao Q L,et al. Spatial distribution of night rainfall in summer over China. Journal of Natural Resources,2013,28(11):1935-1944. | |
| 5 | 胡迪,李跃清. 青藏高原东侧四川地区夜雨时空变化特征. 大气科学,2015,39(1):161-179. |
| Hu D, Li Y Q,Spatial and temporal variations of nocturnal precipitation in Sichuan over the Eastern Tibetan plateau. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences,2015,39(1):161-179. | |
| 6 | Yu R C, Xu Y P, Zhou T J,et al. Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophysical Research Letters,2007,34(13):n/a?n/a. |
| 7 | 唐红玉,顾建峰,俞胜宾,等. 西南地区降水日变化特征分析. 高原气象,2011,30(2):376-384. |
| Tang H Y, Gu J F, Yu S B,et al. Analysis on diurnal variation of precipitation in Southwest China,Plateau Meteorology,2011,30(2):376-384. | |
| 8 | 宇如聪,李建. 中国大陆日降水峰值时间位相的区域特征分析. 气象学报,2016,74(1):18-30. |
| Yu R C, Li J. Regional characteristics of diurnal peak phases of precipitation over contiguous China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica,2016,74(1):18-30. | |
| 9 | 潘岑,罗俊才,苏静文,等. 贵州夜间降水特征与暴雨预警发布现状分析. 中低纬山地气象,2021,45(5):109-116. |
| Pan C, Luo J C, Su J W,et al. Analysis of the nocturnal precipitation characteristics and the current situation of rainstorm warning signals release in Guizhou Province. Mid?low Latitude Mountain Meteorology,2021,45(5):109-116. | |
| 10 | 计晓龙,吴昊旻,黄安宁,等. 青藏高原夏季降水日变化特征分析. 高原气象,2017,36(5):1188-1200. |
| Ji X L, Wu H M, Huang A N,et al. Characteristics of the precipitation diurnal variation over Qinghai?Tibetan plateau in summer. Plateau Meteorology,2017,36(5):1188-1200. | |
| 11 | 王胜,谢五三,唐为安,等. 1961-2009年淮河流域昼夜降水变化特征. 生态学杂志,2011,30(12):2881-2887. |
| Wang S, Xie W S, Tang W A. Change characteristics of day and night precipitation in Huaihe river basin in 1961-2009. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2011,30(12):2881-2887. | |
| 12 | 崔彩霞,李杨,杨青. 新疆夜雨和昼雨的空间分布和长期变化. 中国沙漠,2008,28(5):903-907,1002. |
| Cui C X, Li Y, Yang Q. Spatial distribution and long?term variation of nocturnal and daytime rainfall in Xinjiang. Journal of Desert Research,2008,28(5):903-907, 1002. | |
| 13 | 戴泽军,宇如聪,陈昊明. 湖南夏季降水日变化特征. 高原气象,2009,28(6):1463-1470. |
| Dai Z J, Yu R C, Chen H M. Characteristics of summer precipitation diurnal variations in Hunan. Plateau Meteorology,2009,28(6):1463-1470. | |
| 14 | 郭军,熊明明,黄鹤. 京津冀地区暖季降水日变化特征分析. 海洋气象学报,2019,39(2):58-67. |
| Guo J, Xiong M M, Huang H. Analysis of diurnal variation characteristics of rainfall during warm season in Beijing?Tianjin?Hebei region. Journal of Marine Meteorology,2019,39(2):58-67. | |
| 15 | 范江琳,曹萍萍,冯良敏,等. 1961-2018年四川盆地夜雨特征分析. 高原山地气象研究,2019,39(4):24-30. |
| Fan J L, Cao P P, Feng L M,et al. Analysis of night precipitation characteristics in Sichuan basin in recent 58 years. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research,2019,39(4):24-30. | |
| 16 | 于俊伟,吴战平,高秋沙. 贵州的夜雨特征. 贵州气象,2010,34(2):13-14,17. |
| 17 | 张核真,唐小萍,普布卓玛.近46年西藏高原昼夜降水变化趋势. 气象科技,2010,38(2):205-208. |
| Zhang H Z, Tang X P,Pubuzhuoma. Trends of day/night precipitation in Tibet plateau in recent 46 years. Meteorological Science and Technology,2010,38(2):205-208. | |
| 18 | 贾艳青,张勃,张耀宗,等. 中国华北地区昼夜降水时空变化特征. 地理与地理信息科学,2016,32(5):103-109. |
| Jia Y Q, Zhang B, Zhang Y Z,et al. Characteristics of spatio?temporal variation of day and night precipitation in North China. Geography and Geo?information Science,2016,32(5):103-109. | |
| 19 | 余忠水. 1955-2007年拉萨市雨季夜雨率变化特征. 气象,2011,37(12):1584-1588. |
| Yu Z S. The night rain rate variations of Lhasa in rainy season during 1955-2007. Meteorological Monthly,2011,37(12):1584-1588. |
| No related articles found! |
|
||