南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 660–670.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.04.015
• • 上一篇
基于新健康因子的锂电池健康状态估计和剩余寿命预测
- 西安电子科技大学数学与统计学院,西安,710126
State of health estimation and remaining using life prediction of lithium⁃ion batteries based on new health indicators
- School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University, Xi'an 710126, China
摘要:
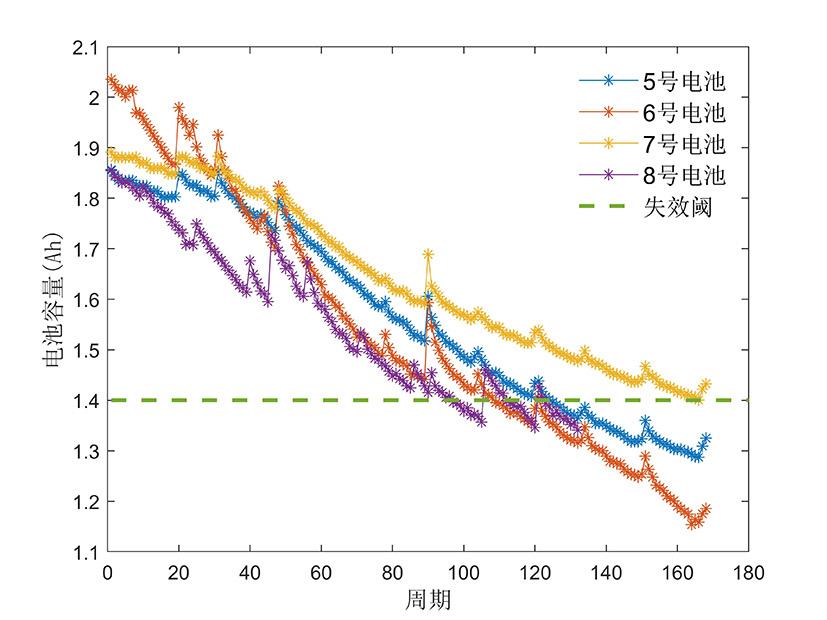
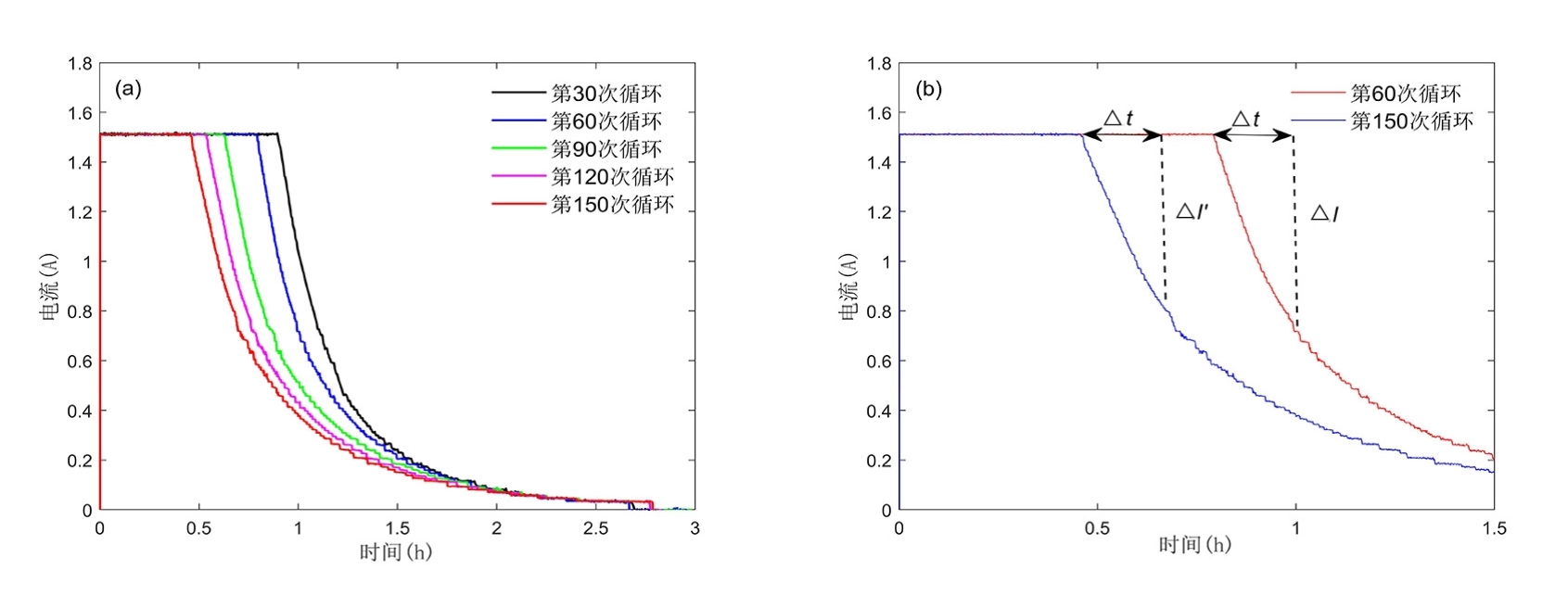
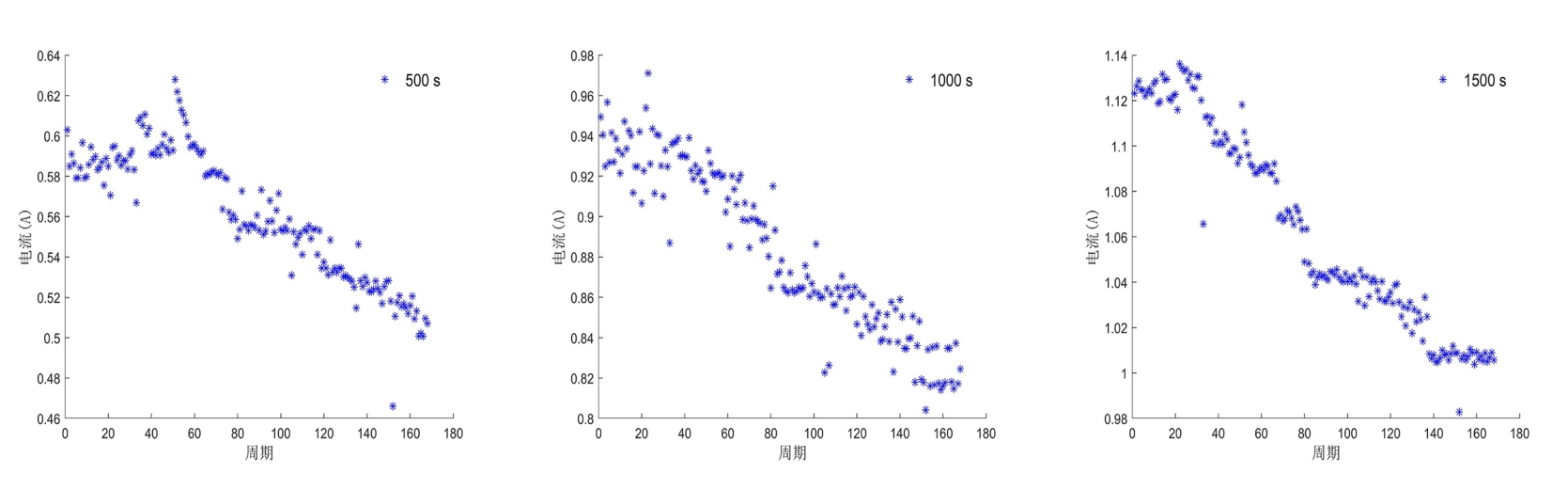
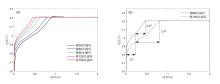
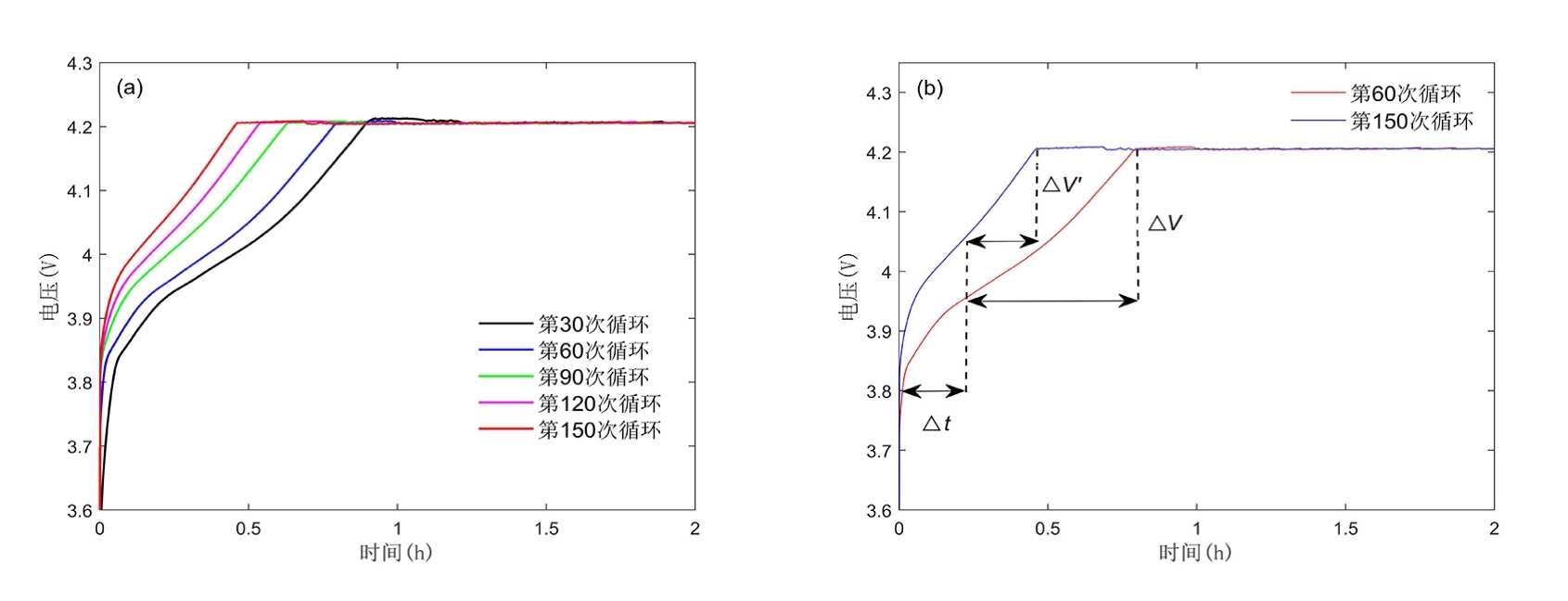
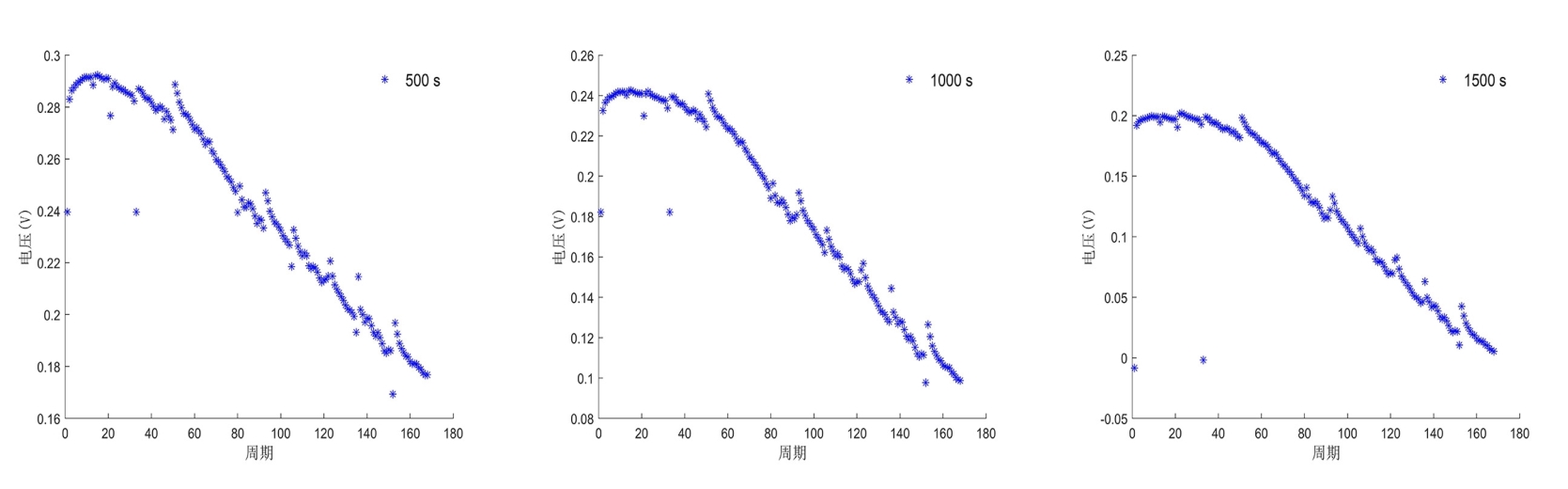
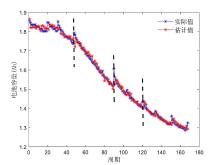
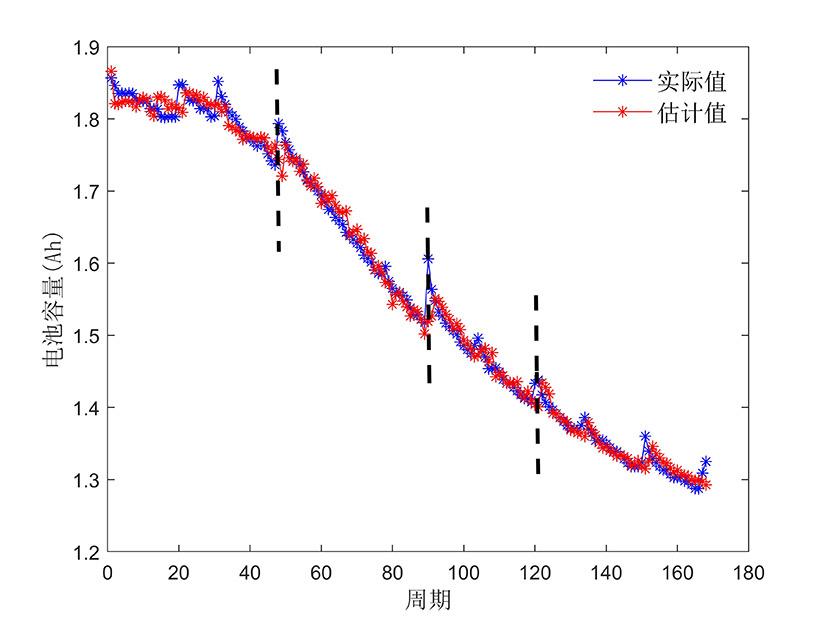
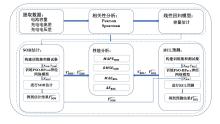
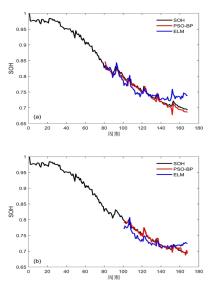
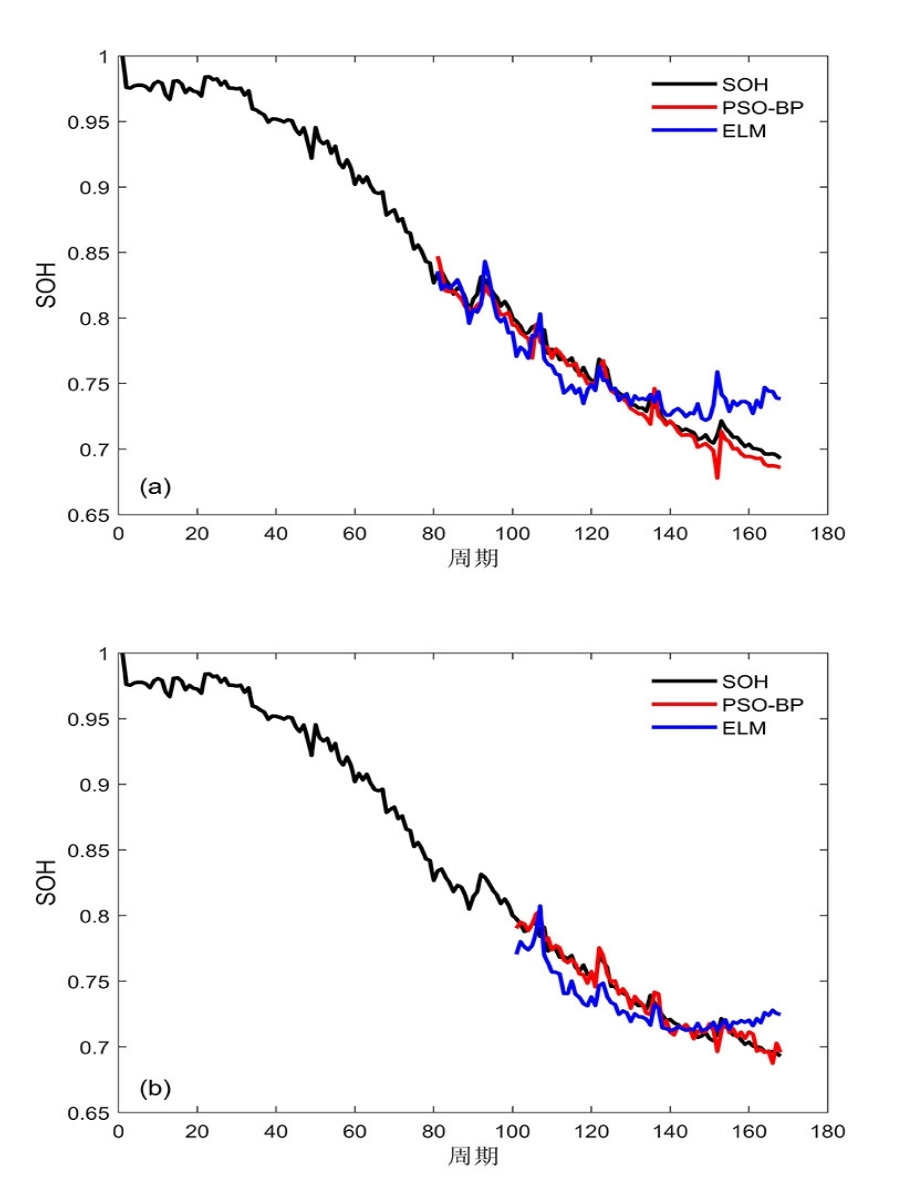
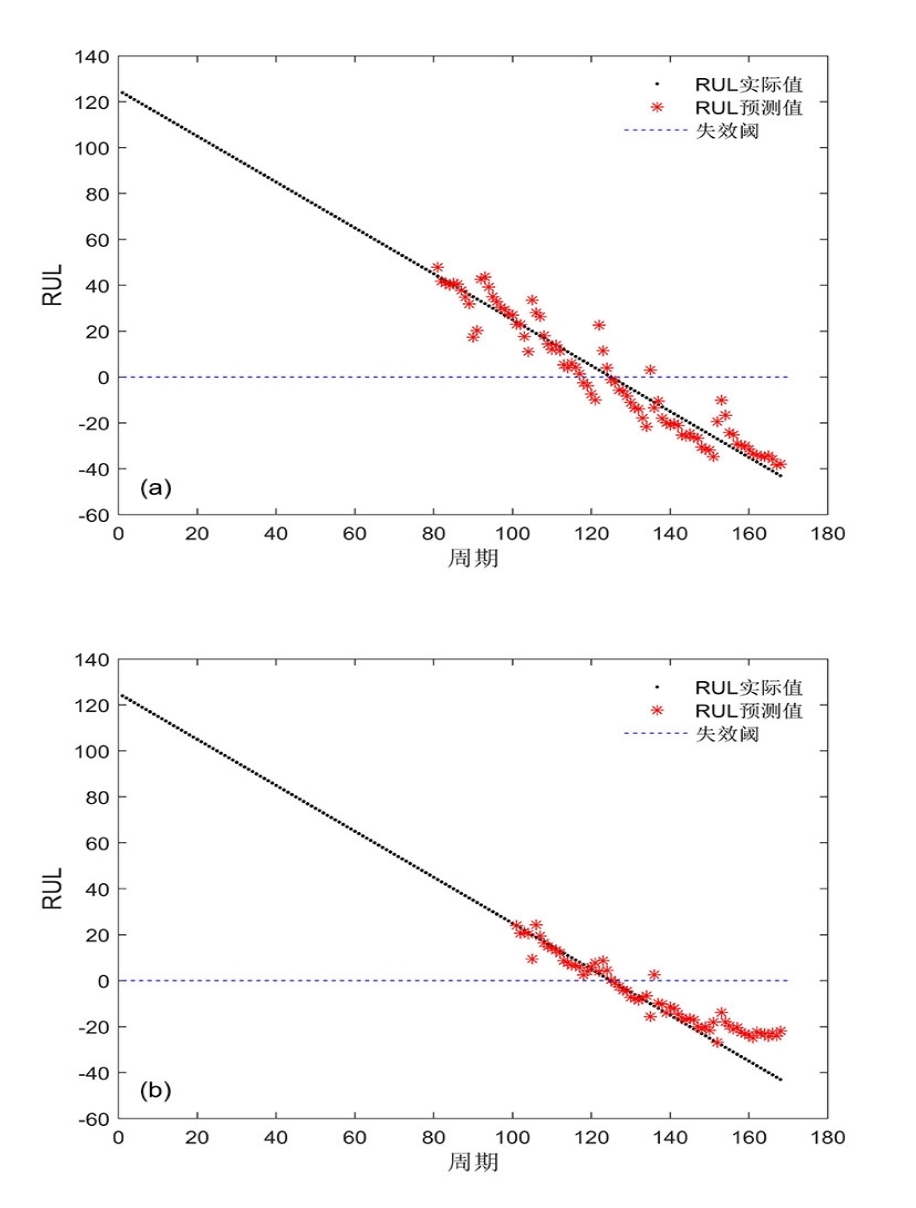
容量和内阻是评估锂离子电池健康状态和预测其剩余寿命的重要指标,然而电池容量和内阻难以直接在线测量.通过分析锂离子电池充电过程中电流和电压的变化特征后提取出两种健康因子,并且证明所提因子与电池容量高度相关,进一步建立了用于锂电池容量估计的两因子线性回归模型.在此基础上,通过结合BP (back propagation)神经网络和粒子群优化思想设计锂离子电池健康状态估计算法.考虑到锂电池的健康状态和剩余使用寿命之间存在一定的映射关系,因此再利用所提取的健康因子和其健康状态估计结果设计了锂电池的剩余使用寿命预测算法.实验结果表明,所提取的健康因子能够准确地进行电池容量估计并应用于在线评估锂离子电池的健康状态和预测其剩余使用寿命.
中图分类号:
- TM912
| 1 | Zhao Q,Qin X L,Zhao H B,et al. A novel prediction method based on the support vector regression for the remaining useful life of lithium?ion batteries. Microelectronics & Reliability,2018(85):99-108. |
| 2 | Wang Q S,Mao B B,Stoliarov S I,et al. A review of lithium ion battery failure mechanisms and fire prevention strategies. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2019(73):95-131. |
| 3 | Xing Y,Ma E W M,Tsui K L,et al. Battery Management Systems in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. Energies,2011,4(12):1840-1857. |
| 4 | 彭宇,刘大同,彭喜元.故障预测与健康管理技术综述. 电子测量与仪器学报,2010,24(1):1-9. |
| Peng Y,Liu D T,Peng X Y. A review:Prognostics and health management. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument,2010,24(1):1-9. | |
| 5 | Wei J W,Dong G Z,Chen Z H. Remaining useful life prediction and state of health diagnosis for lithium?ion batteries using particle filter and support vector regression. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2018,65(7):5634-5643. |
| 6 | Lei Y G,Li N P,Guo L,et al. Machinery health prognostics:A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2018(104):799-834. |
| 7 | Liu D T,Wang H,Peng Y,et al. Satellite lithium?ion battery remaining cycle life prediction with novel indirect health indicator extraction. Energies,2013, |
| 6(8):3654-3668. | |
| 8 | Yang L,Zhao L L,Su X H,et al. A lithium?ion battery RUL prognosis method using temperature changing rate∥2016 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management. Ottawa,Canada:IEEE Press,2016:1-7. |
| 9 | Zhou Y P,Huang M H,Chen Y P,et al. A novel health indicator for on?line lithium?ion batteries remaining useful life prediction. Journal of Power Sources,2016(321):1-10. |
| 10 | Widodo A,Shim M C,Caesarendra W. Intelligent prognostics for battery health monitoring based on sample entropy. Expert Systems with Application,2011,38(9):11763-11769. |
| 11 | 高栋,黄妙华,周亚鹏.基于充电电流数据的锂电池容量估计.电源技术,2018,42(10):1447-1450, 1580. (Gao D,Huang M H,Zhou Y P. Lithium?ion battery's capacity estimation based on charging |
| current data. Chinese Journal of Power Sources,2018,42(10):1447-1450, 1580. | |
| 12 | Kan M S,Tan A C C,Mathew J. A review on prognostic techniques for non?stationary and |
| non?linear rotating systems. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing,2015(62-63):1-20. | |
| 13 | Jin X,Vora A,Hoshing V,et al. Physically?based reduced?order capacity loss model for graphite anodes in Li?ion battery cells. Journal of Power Sources,2017(342):750-761. |
| 14 | Guo Y F,Zhao Z S,Huang L M. SoC Estimation of lithium battery based on improved BP neural network. Energy Procedia,2017(105):4153-4158. |
| 15 | Geng P,Wang J Z,Xu X Y,et al. SOC Prediction of power lithium battery using BP neural network theory based on keras. International Core Journal of Engineering,2020,6(1):171-181. |
| 16 | Yang D,Zhang X,Pan R,et al. A novel Gaussian process regression model for state?of?health estimation of lithium?ion battery using charging curve. Journal of Power Sources,2018(384):387-395. |
| 17 | Jia J F,Liang J Y,Shi Y H,et al. SOH and RUL prediction of lithium?ion batteries based on Gaussian process regression with indirect health indicators. Energies,2020,13(2):387-395. |
| 18 | Ebrahimzade H,Khayati G R,Schaffie M. PSO–ANN?based prediction of cobalt leaching rate from waste lithium?ion batteries. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2020,22(1):228-239. |
| 19 | Saha B,Goebel K,Poll S,et al. Prognostics methods for battery health monitoring using a Bayesian framework. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2009,58(2):291-296. |
| 20 | Sun Y Q,Hao X L,Pecht M,et al. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium?ion batteries based on an integrated health indicator. Microelectronics & Reliability,2018(88-90):1189-1194. |
| 21 | Yu J B. State of health prediction of lithium?ion batteries:Multiscale logic regression and Gaussian process regression ensemble. Reliability Engineering & System Safety,2018(174):82-95. |
| 22 | Wu J,Wang Y J,Zhang X,et al. A novel state of health estimation method of Li?ion battery using group method of data handling. Journal of Power Sources,2016(327):457-464. |
| 23 | Huang G B,Zhu Q Y,Siew C K. Extreme learning machine:Theory and applications. Neurocomputing,2006,70(1-3):489-501. |
| [1] | 章福平1,Hasuck Kim2 , Byungwoo Park3. 掺杂稀土元素的锉离子电池正极材料 LiCo1 _y Rey O2电化学性能[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(3): 343-350. |
|
||