海洋性大陆地形对夏季季节内振荡的影响:基于2020年9月个例的数值模拟分析
|
|
孔钰博, 周逸豪, 汪曙光
|
The influence of topography of Maritime Continent on the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation: Numerical simulation analysis based on a case in September 2020
|
|
Yubo Kong, Yihao Zhou, Shuguang Wang
|
|
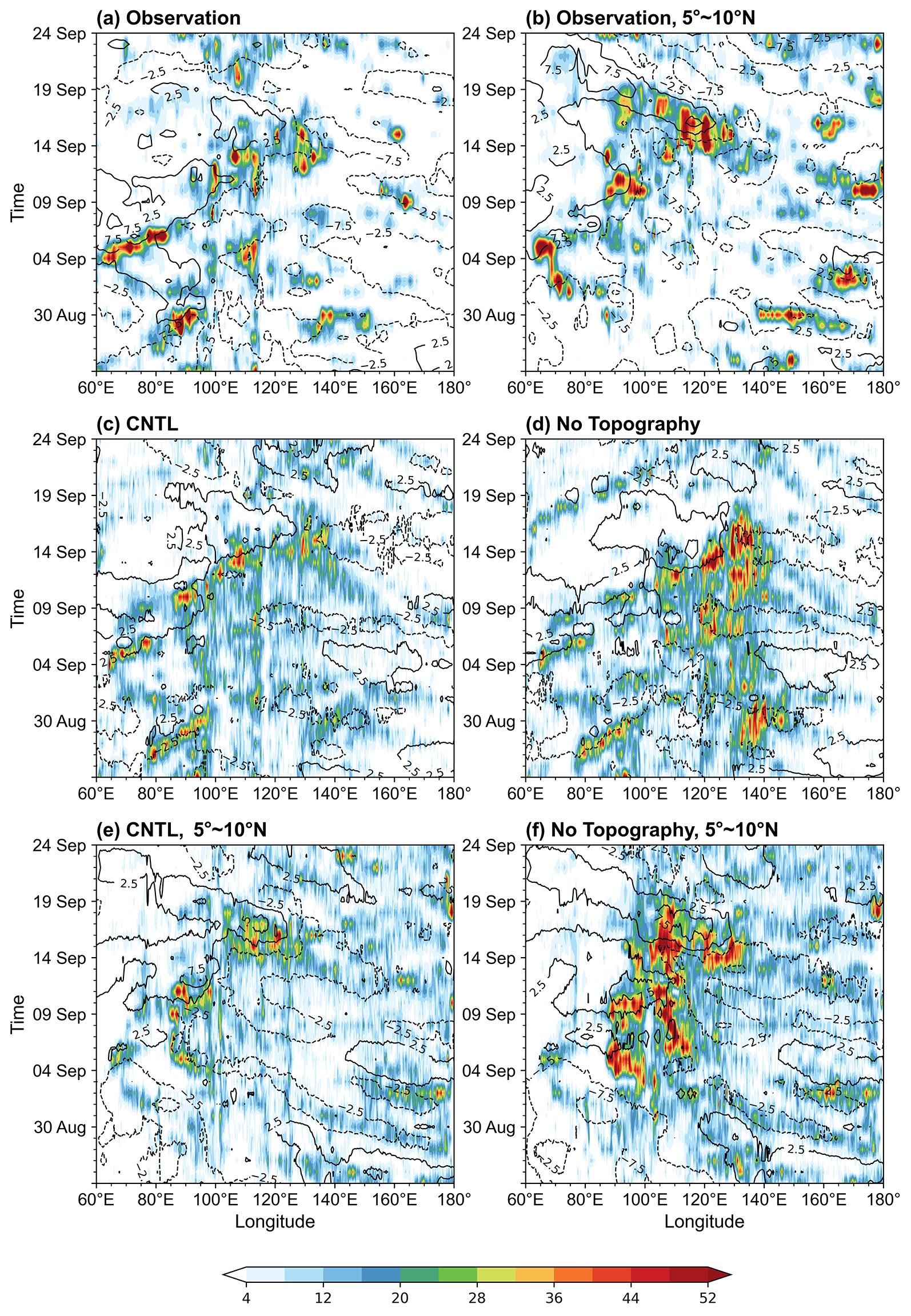
图4 观测/再分析的0°~5°N平均日降水量(填色图,单位:mm·d-1)和850 hPa纬向风异常(等值线图,单位:m·s-1)时间?经度平均图.(a, c, d)分别为观测、CNTL和No Topography试验, (b, e, f)分别为5°~10°N的观测、CNTL和No Topography试验
(e) CNTL, and (f) No Topography are the time?longitude diagrams of 5°~10°N
|
Fig.4 The time?longitude diagrams of 0°~5°N averaged daily precipitation (shading, unit: mm·d-1) and 850 hPa zonal wind anomaly (contours, unit: m·s-1) from (a) observation, (c) CNTL, and (d) No topography; (b) observation,
|
|
|
|
|
