海洋性大陆地形对夏季季节内振荡的影响:基于2020年9月个例的数值模拟分析
The influence of topography of Maritime Continent on the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation: Numerical simulation analysis based on a case in September 2020
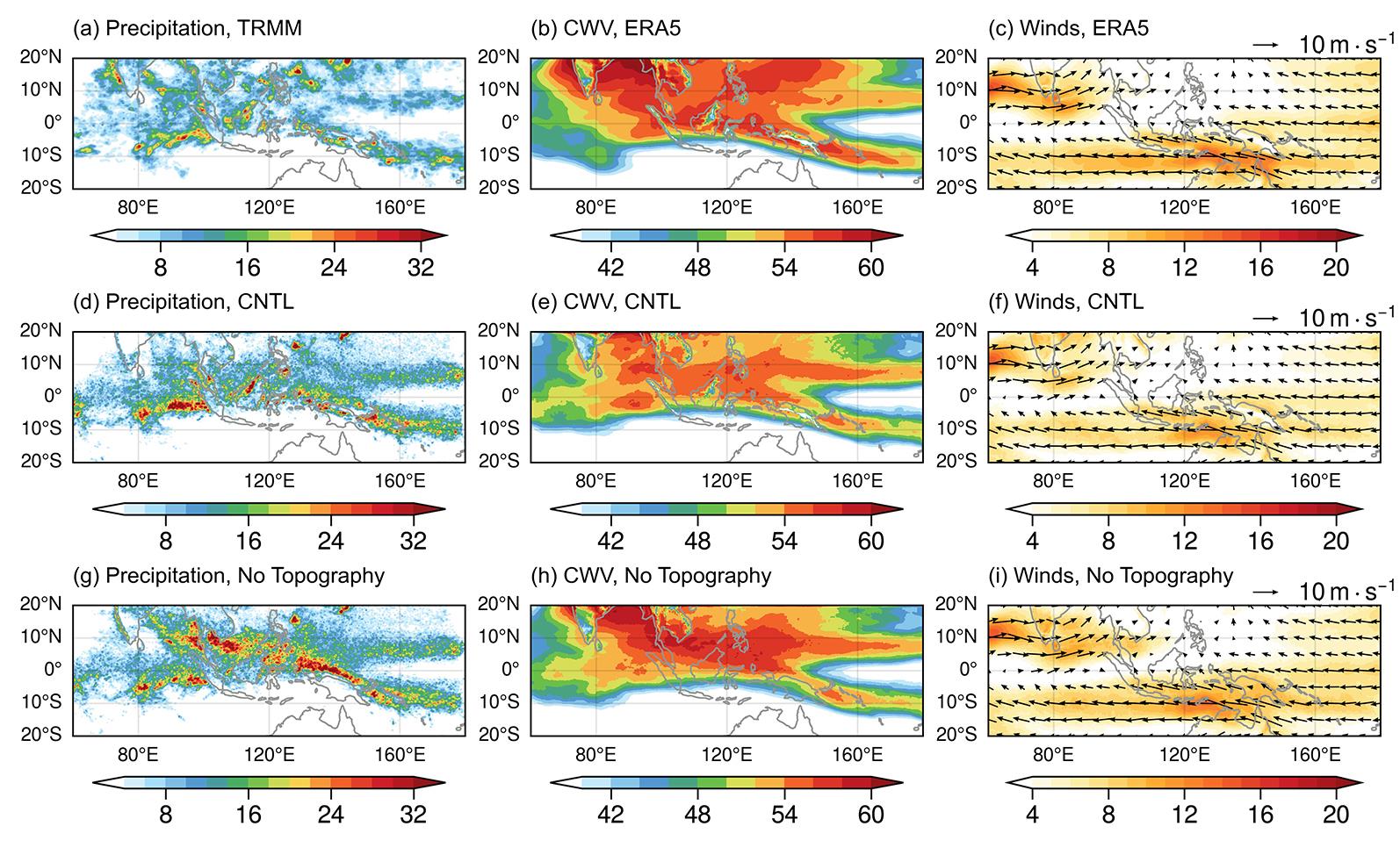
(d) CNTL, (g) No topography; (b, e, h) are the same as in (a, d) and (g), but for averaged CWV (unit: kg·m-2),
and (c, f, i) are the same as in (a, d) and (g), but for averaged wind at 850 hPa (unit: m·s-1), respectively