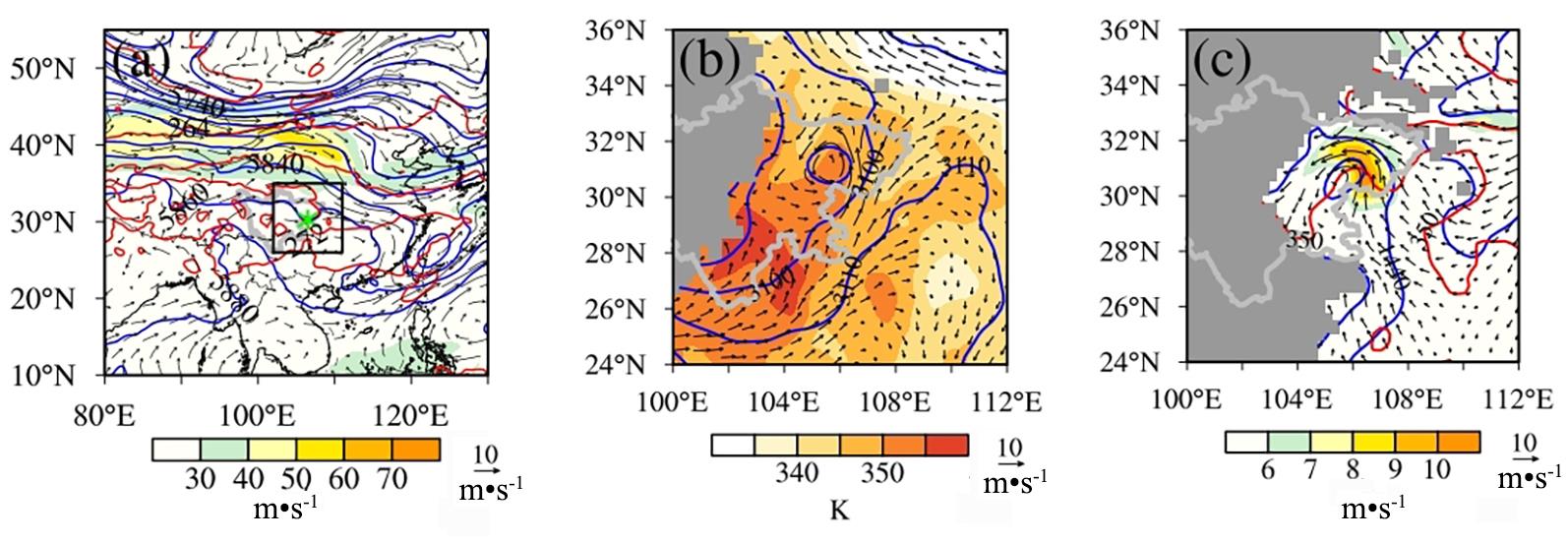
青藏高原东部地形对四川盆地东北部一次暴雨过程的影响
Effect of topography of eastern Qinghai⁃Xizang Plateau on a rainstorm occurred in northeastern Sichuan Basin
(a) 500 hPa geopotential height (blue contour line,unit: gpm),temperature (red contour line,unit: K),horizontal wind field (vector,unit: m·s-1),
and 200 hPa wind speed (colored,unit: m·s-1),in which the black box in the figure is the rainstorm area,and the mapping area in Fig.3b and Fig.3c,(b) 700 hPa geopotential height (blue contour line, unit: gpm), equivalent potential temperature (red contour line,unit: K),horizontal wind field (vector,unit: m·s-1),and (c) 850 hPa geopotential height (blue contour line,unit: gpm),temperature (red contour line,unit: K),
horizontal wind field (vector,unit: m·s-1),and wind speed (colored,unit: m·s-1).