非水饱和相矿物表面催化转化有机污染物的研究进展
|
|
黄姝晗, 范振辉, 谷成, 金鑫
|
Advances in mineral surface induced catalytic transformation of organic pollutants under the non⁃aqueous conditions
|
|
Shuhan Huang, Zhenhui Fan, Cheng Gu, Xin Jin
|
|
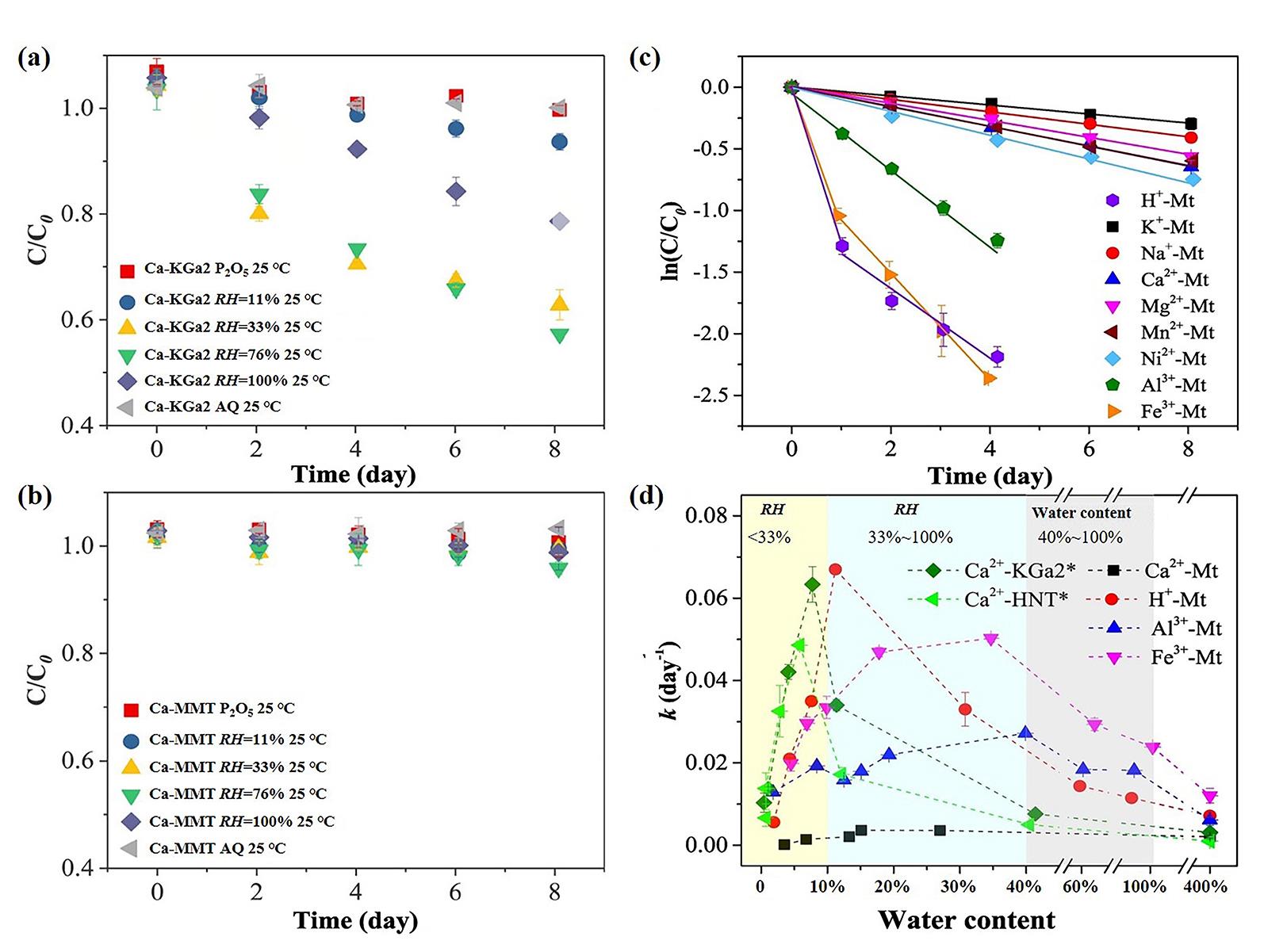
图4 不同相对湿度下CAP在(a)钙饱和高岭土(Ca?KGa2)和(b)钙饱和蒙脱石(Ca?MMT)上的降解动力学(25 ℃)[58];(c)在RH为76%时,CAP在不同阳离子交换蒙脱石上(M n+?Mt)的水解动力学(55 ℃)[97];
(d)不同阳离子交换蒙脱石上(M n+?Mt)CAP的水解速率常数(25 ℃)与黏土含水量的关系[97]
|
Fig.4 Degradation kinetics of CAP on (a) Ca?KGa2 and (b) Ca?SWy2 under different RHs at 25 °C (after ref. [58]), (c) the hydrolysis kinetics of CAP on different cation?exchanged montmorillonites (M n+?Mt) at RH=76% and reaction temperature of 55 ℃ (after ref.[97]), (d) The hydrolysis rate constants of CAP (at 25 ℃) as a function of clay water contents for different cation?exchanged montmorillonites (M n+?Mt) (after ref.[97])
“P2O5” indicates an RH<5 wt% controlled by P2O5; “AQ” stands for the aqueous solution with a water/clay mass ratio of 4∶1
|
|
|
|
|
