南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (2): 328–335.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.02.016
• • 上一篇
基于无线传播信道特征的非视距识别技术
- 长安大学信息工程学院,西安,710064
Identification of NLoS based on wireless propagation channel features
Xinyi Liu, Jingli Xie, Wei Wang( ), Zhilin Xu
), Zhilin Xu
- School of Information Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an,710064,China
摘要:
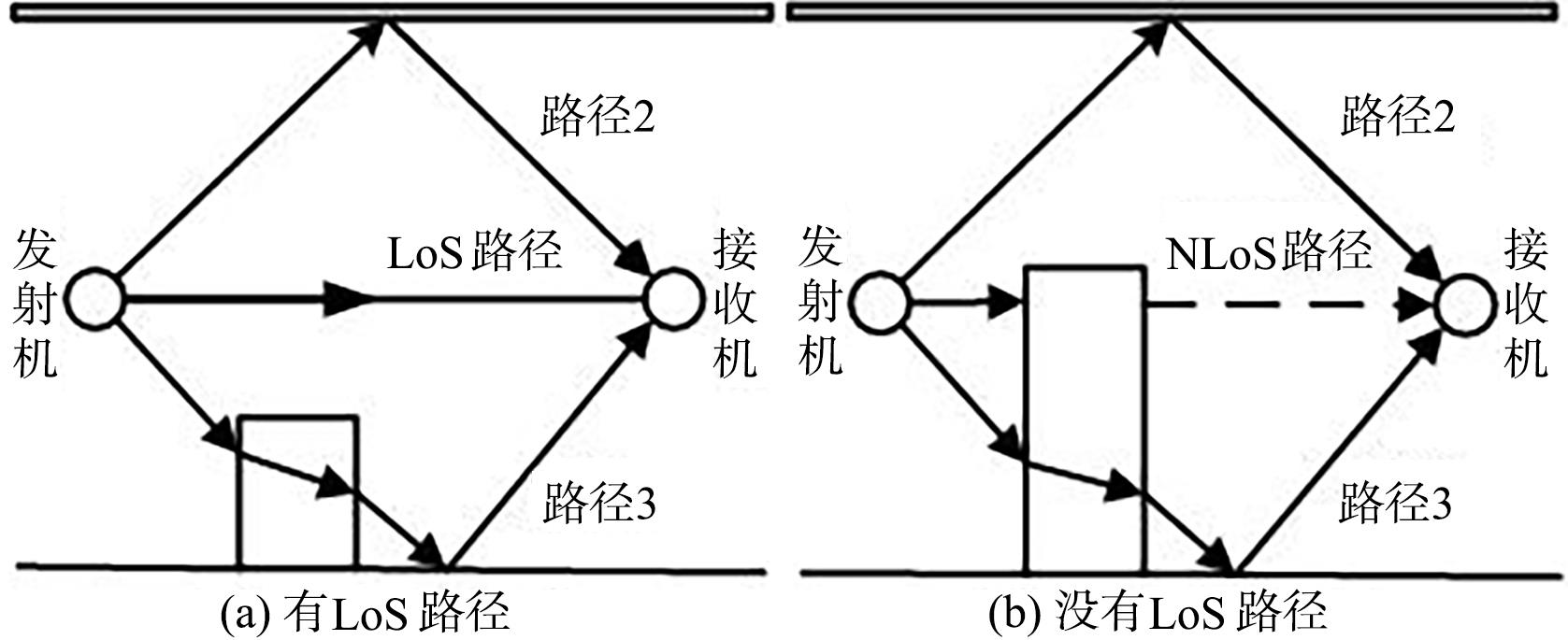
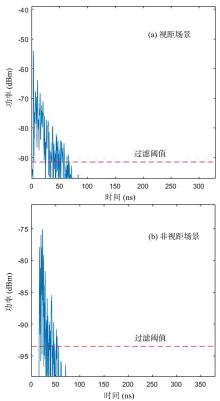
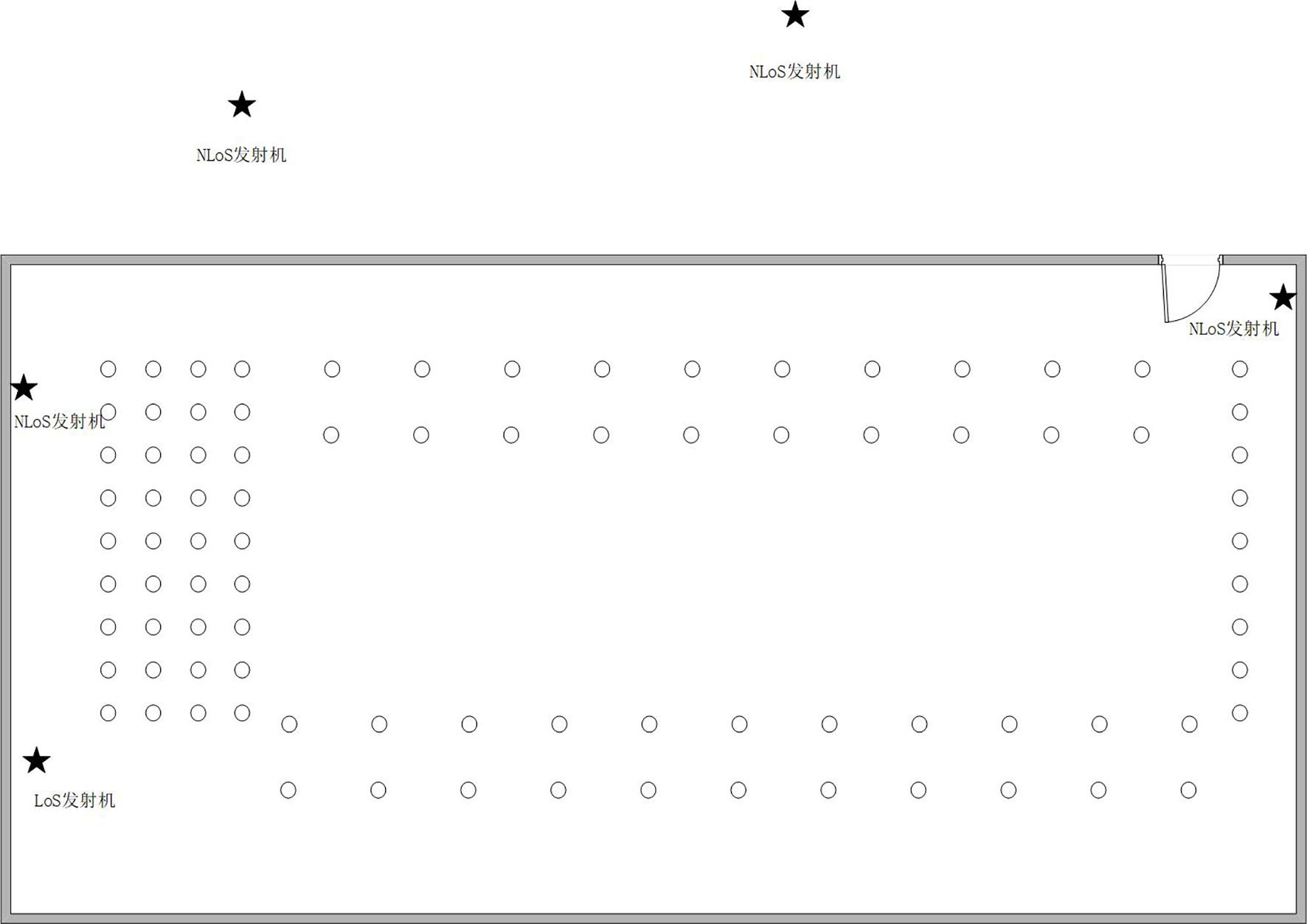
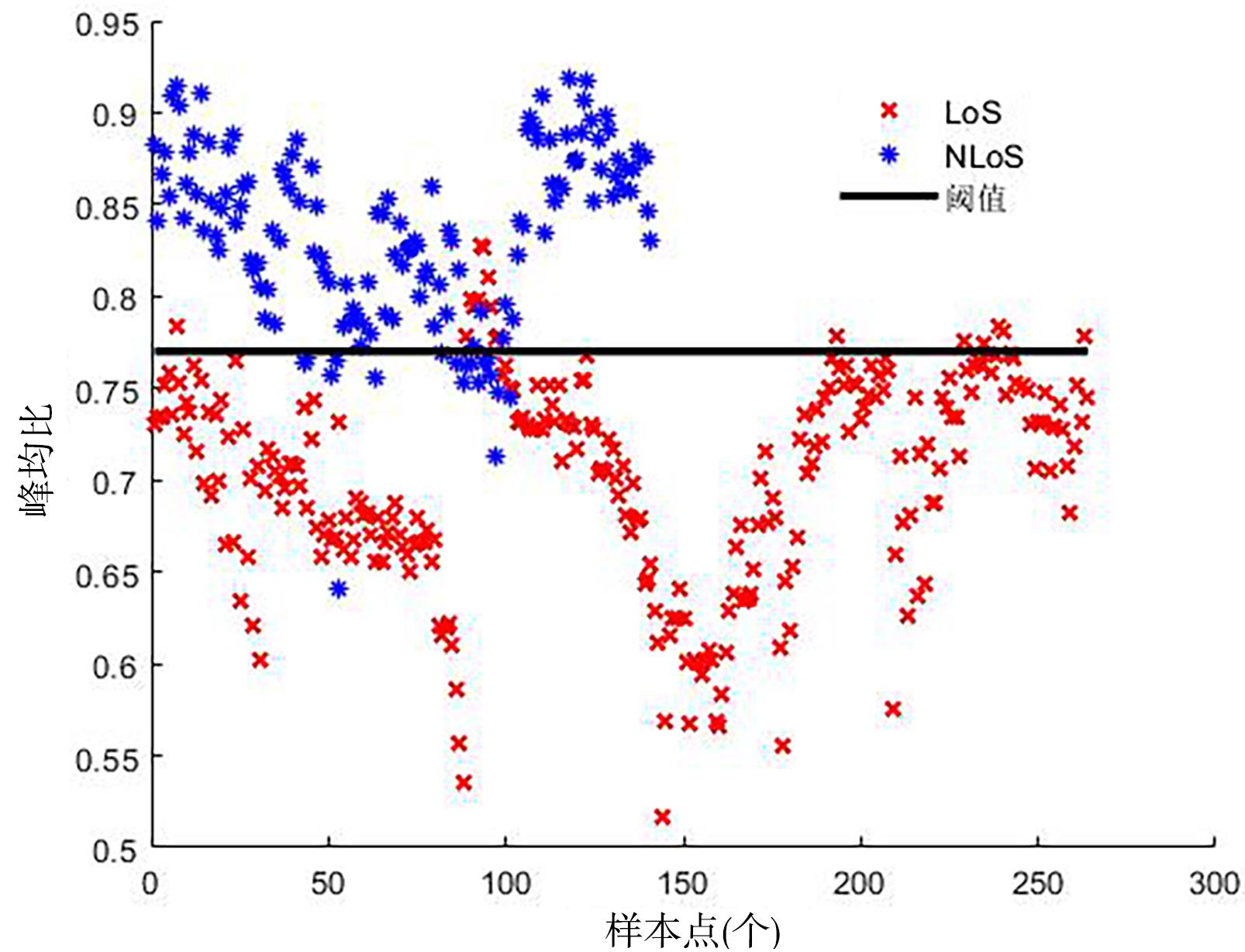
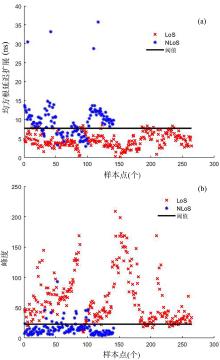
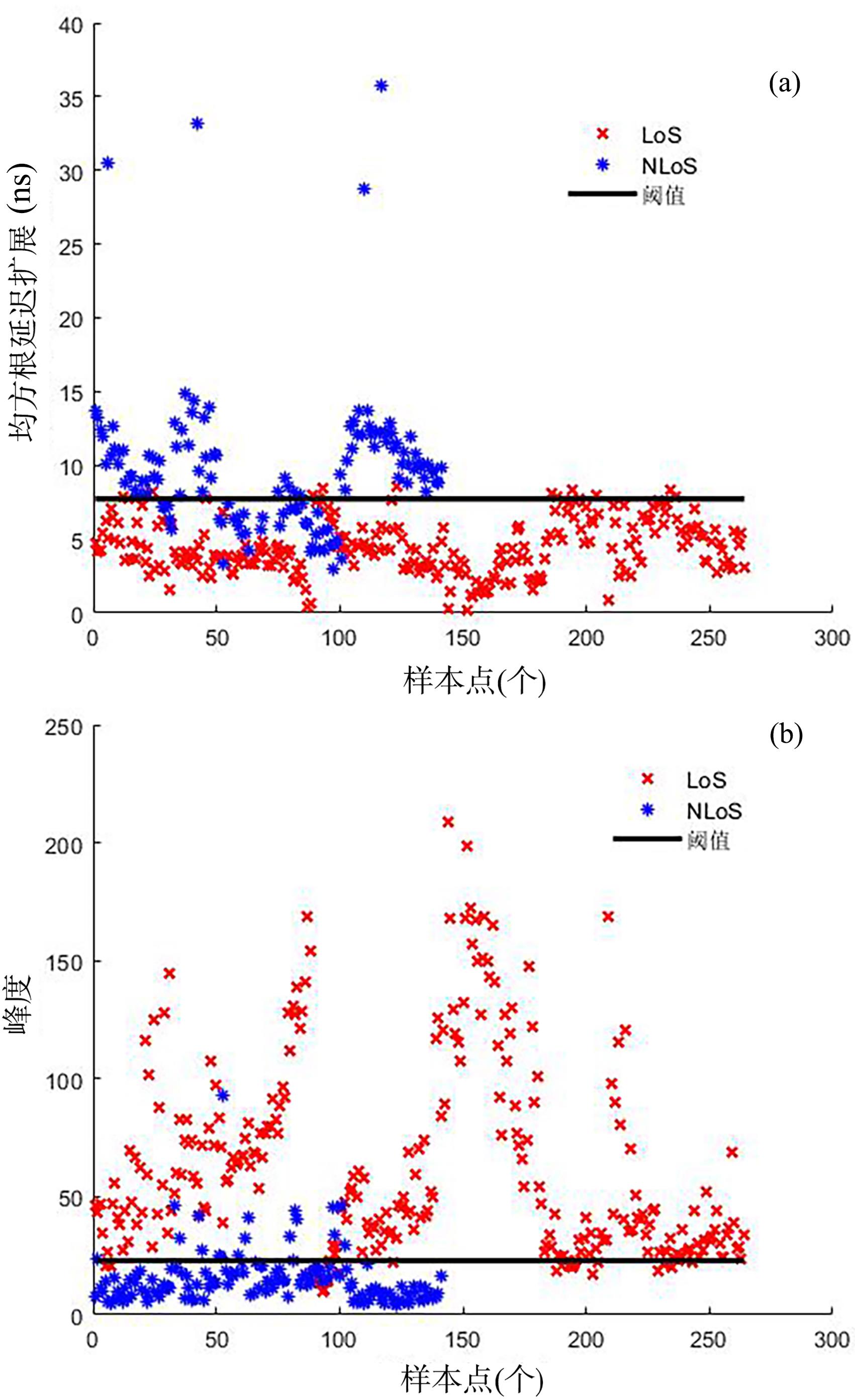
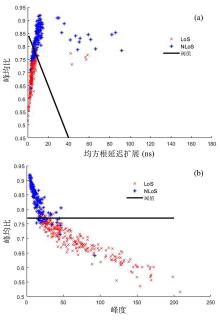
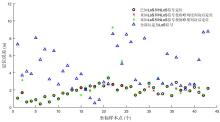
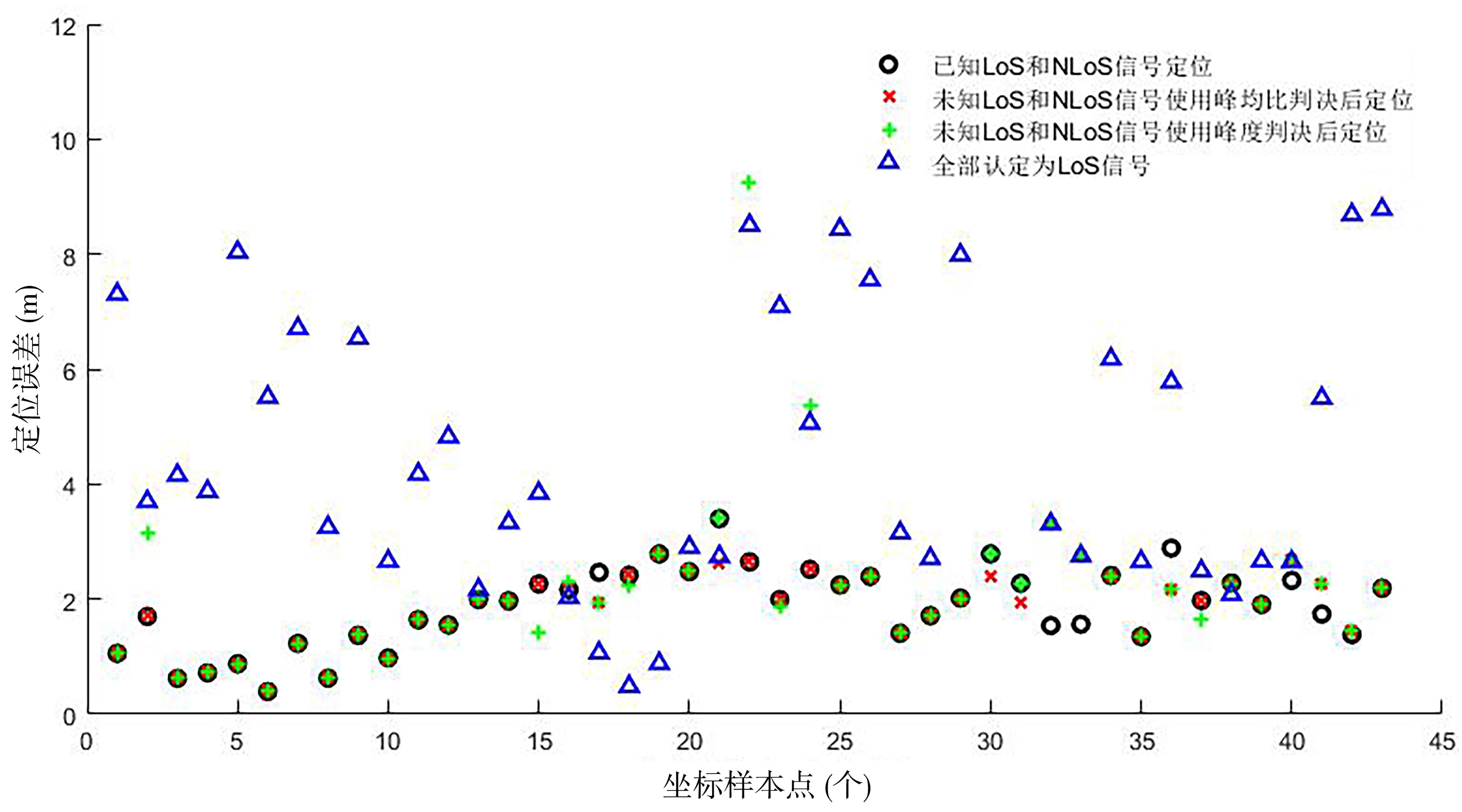
复杂的室内环境中存在的各种无法躲避的障碍物会导致无线定位的测距精度较低,其中最主要的因素是存在非视距传播,因此识别信道状态是否为非视距对室内定位精度较为重要.提出一种基于信道信息的视距/非视距信道识别方法:首先对信号进行过滤,获取重要的信道抽头;然后提取过滤后信号的峰值,并计算其功率;最后通过计算得出该信道信号的峰均比,并联合假设检验对信道状态进行判决.仿真结果表明,峰均比特征在视距/非视距信道上有明显差异,可以作为识别视距/非视距信道的特征.该特征的视距识别正确率达到93.56%,非视距识别正确率达到87.23%,比使用峰度特征在视距场景下的识别正确率提高了2.65%,非视距正确率提高了0.71%.使用本算法在定位过程中进行验证,能够有效降低定位误差,提高定位精度,说明该算法的识别效果较好,具有一定的应用前景.
中图分类号:
- TN925
| 1 | Hu B Y, Tian H, Fan S S. Millimeter wave LoS/NLoS identification and localization via mean?shift clustering∥2019 IEEE 30th Annual International Symposium on Personal,Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. Istanbul,Turkey:IEEE,2019:1-7. |
| 2 | Yu K G, Wen K, Li Y B,et al. A novel NLoS mitigation algorithm for UWB localization in harsh indoor environments. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,2019,68(1):686-699. |
| 3 | Fan J C, Awan A S. Non?line?of?sight identification based on unsupervised machine learning in ultra wideband systems. IEEE Access,2019(7):32464-32471. |
| 4 | Zhang S G, Yang C W, Jiang D M,et al. Nothing blocks me:Precise and real?time LoS/NLoS path recognition in RFID systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal,2019,6(3):5814-5824. |
| 5 | Schroeder J, Galler S, Kyamakya K,et al. NLoS detection algorithms for Ultra?Wideband localization∥2007 4th Workshop on Positioning,Navigation and Communication. Hannover,Germany:IEEE,2007:159-166. |
| 6 | Zeng Z Q, Liu S, Wang L. NLoS identification for UWB based on channel impulse response∥2018 12th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems. Cairns,Australia:IEEE,2018:1-6. |
| 7 | Tuchler M, Huber A. An improved algorithm for UWB?bases positioning in a multi?path environment∥Proceedings of 2006 International Zurich Seminar on Communications. Zurich,Switzerland:IEEE,2006:206-209. |
| 8 | Xiao F, Guo Z X, Zhu H,et al. AmpN:Real?time LoS/NLoS identification with WiFi∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications. Paris,France:IEEE,2017:1-7. |
| 9 | Miao Z M, Zhao L W, Yuan W W,et al. Application of one?class classification in NLoS identification of UWB positioning∥International Conference on Information System and Artificial Intelligence. Hong Kong,China:IEEE,2016:318-322. |
| 10 | Wang F, Xu Z, Zhi R X,et al. LOS/NLOS channel identification technology based on CNN∥2019 6th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science. Hanoi,Vietnam:IEEE,2019:200-203. |
| 11 | 张浩,梁晓林,吕婷婷,等. 一种新颖的基于偏度的非视距区分算法. 电讯技术,2015,55(5):484-490. |
| Zhang H, Liang X L, Lyu T T,et al. A novel non?line?of?sight identification algorithm based on skewness. Telecommunication Engineering,2015,55(5):484-490. | |
| 12 | Zheng Q B, He R S, Ai B,et al. Channel non?line?of?sight identification based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters,2020,9(9):1500-1504. |
| 13 | Huang C, Molisch A F, He R S,et al. Machine learning?enabled LoS/NLoS identification for MIMo systems in dynamic environments. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,2020,19(6):3643-3657. |
| 14 | 张旭,姜苏英,杨汨,等. 两种隧道场景下车对车无线信道衰落特性的测量与分析. 电波科学学报,2021,36(3):443-452. |
| Zhang X, Jiang S Y, Yang M,et al. Measurement and analysis of fading characteristics of V2V propagation channel in two tunnels. Chinese Journal of Radio Science,2021,36(3):443-452. | |
| 15 | Choi J S, Lee W H, Lee J H,et al. Deep learning based NLoS identification with commodity WLAN devices. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,2017,67(4):3295-3303. |
| 16 | Xiong C, Li X, Yuan R,et al. Identification and mitigation of NLOS based on channel state information for indoor WiFi localization∥2015 International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing. Nanjing,China:IEEE,2015:1-5. |
| 17 | 贾鸣华,张兴敢. 高速无线通信高阶多普勒谱估计方法. 南京大学学报(自然科学),2016,52(6):1121-1126. |
| Jia M H, Zhang X G. Method of high order Doppler frequency shift estimation for high?speed wireless communication. Journal of Nanjing Univer?sity (Natural Science),2016,52(6):1121-1126. | |
| 18 | Jiang C H, Chen S, Chen Y W,et al. An UWB channel impulse response de?noising method for NLoS/LoS classification boosting. IEEE Communications Letters,2020,24(11):2513-2517. |
| 19 | Xie H, Andrieux G, Wang Y D,et al. Efficient time domain threshold for sparse channel estimation in OFDM system. AEU?International Journal of Electronics and Communications,2014,68(4):277-281. |
| 20 | Kang Y, Kim K, Park H. Efficient DFT?based channel estimation for OFDM systems on multipath channels. IET Communications,2007,1(2):197-202. |
| 21 | Mantoro T, Ayu M A, Nugroho M R. NLoS and LoS of the 28 GHz bands millimeter?wave in 5G cellular networks∥2017 International Conference on Computing,Engineering,and Design. Kuala Lumpur,Malaysia:IEEE,2017:1-5. |
| 22 | Zhou Z M, Yang Z, Wu C S,et al. WiFi?based indoor line?of?sight identification. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,2015,14(11):6125-6136. |
| [1] | 贾鸣华1,2,张兴敢1,2*. 高速无线通信高阶多普勒谱估计方法 [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(6): 1121-. |
| [2] | 辛冠琳,刘惊雷*. 基于G方检验的CP-nets学习[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(4): 781-795. |
|
||