南京大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 393–404.doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2020.03.008
川南盆地长宁页岩气田五峰组⁃龙马溪组成藏动力学过程及其意义
刘文平1( ),周政2,吴娟2,罗超1,吴伟1,姜磊2,3,焦堃2,叶玥豪2,邓宾2(
),周政2,吴娟2,罗超1,吴伟1,姜磊2,3,焦堃2,叶玥豪2,邓宾2( )
)
- 1.中国石油西南油气田分公司页岩气研究院,成都,610002
2.油气藏地质及开发工程”国家重点实验室,成都理工大学,成都,610059
3.广东石油化工学院理学院,茂名,525000
Hydrocarbon generation and shale gas accumulation in the Wufeng⁃Longmaxi formations, Changning shale⁃gas field, Southern Sichuan Basin
Wenping Liu1( ),Zheng Zhou2,Juan Wu2,Chao Luo1,Wei Wu1,Lei Jiang2,3,Kun Jiao2,Yuehao Ye2,Bin Deng2(
),Zheng Zhou2,Juan Wu2,Chao Luo1,Wei Wu1,Lei Jiang2,3,Kun Jiao2,Yuehao Ye2,Bin Deng2( )
)
- 1.PetroChina,Southwest Oil and Gas Fields,Shale?gas Research Institute,Chengdu, 610002,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation,Chengdu University of Technology,Chengdu,610059,China
3.Faculty of Science,Guangdong Petrochemical College,Maoming,525000,China
摘要:
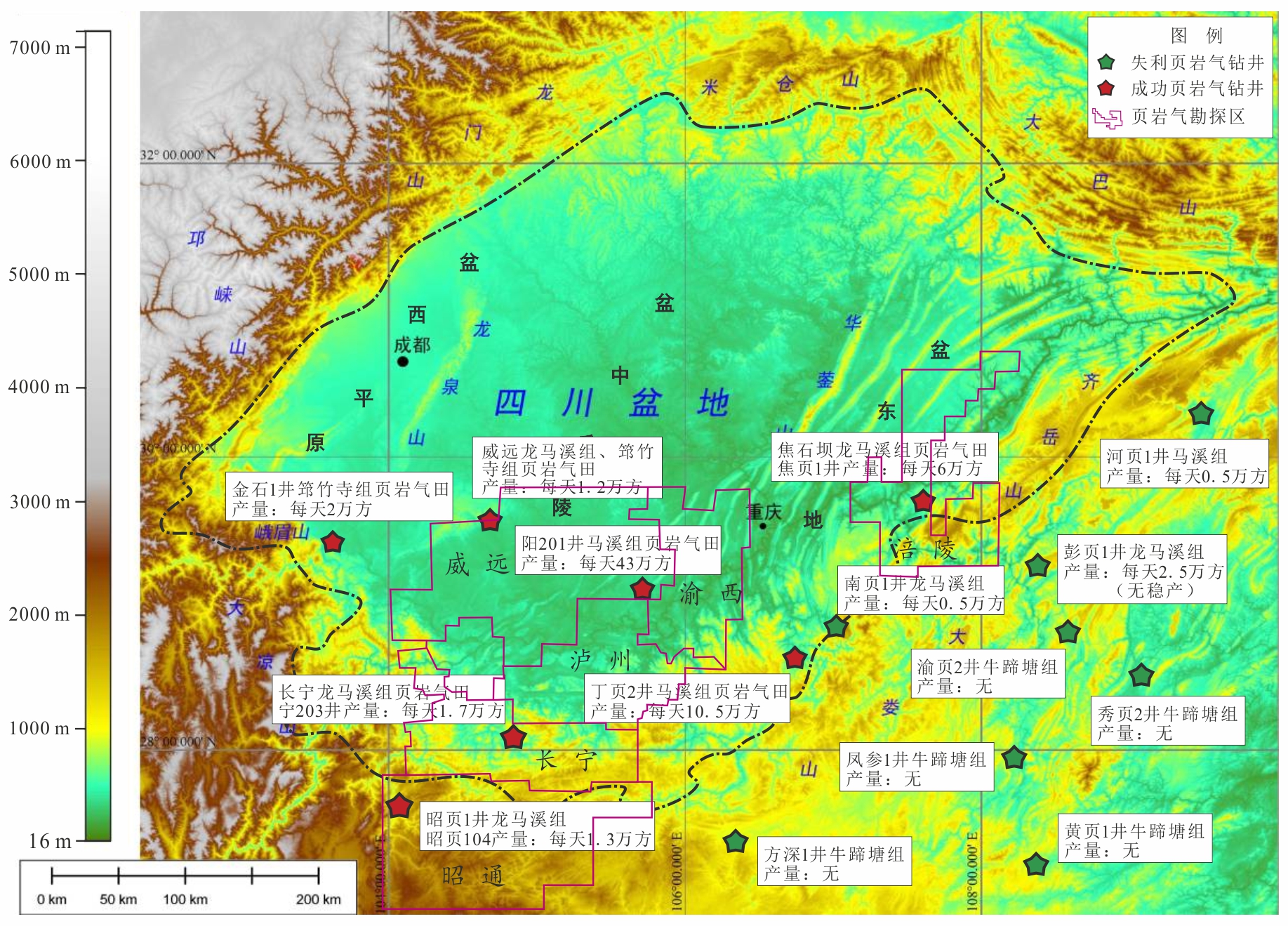
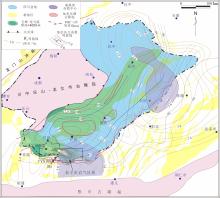
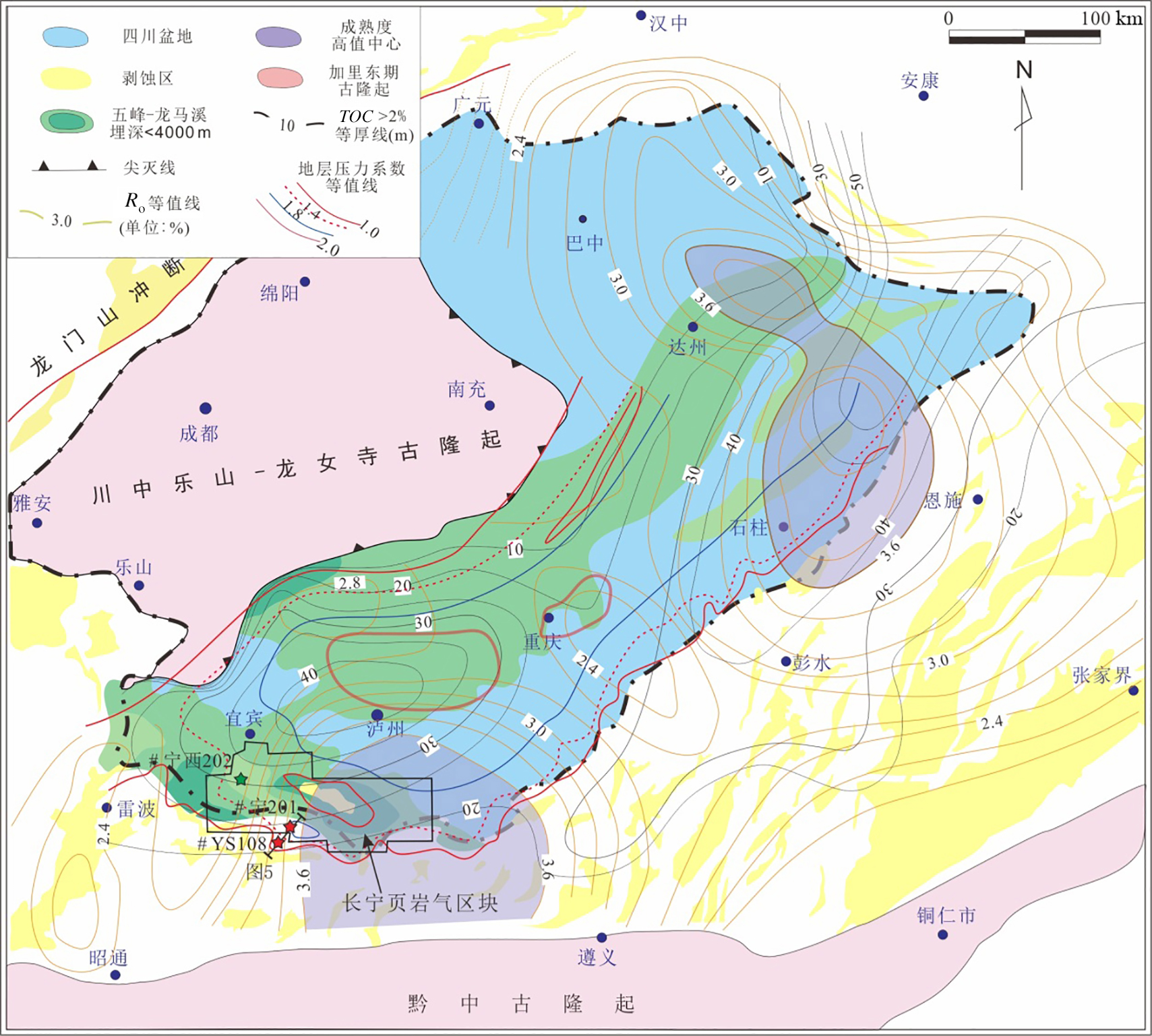
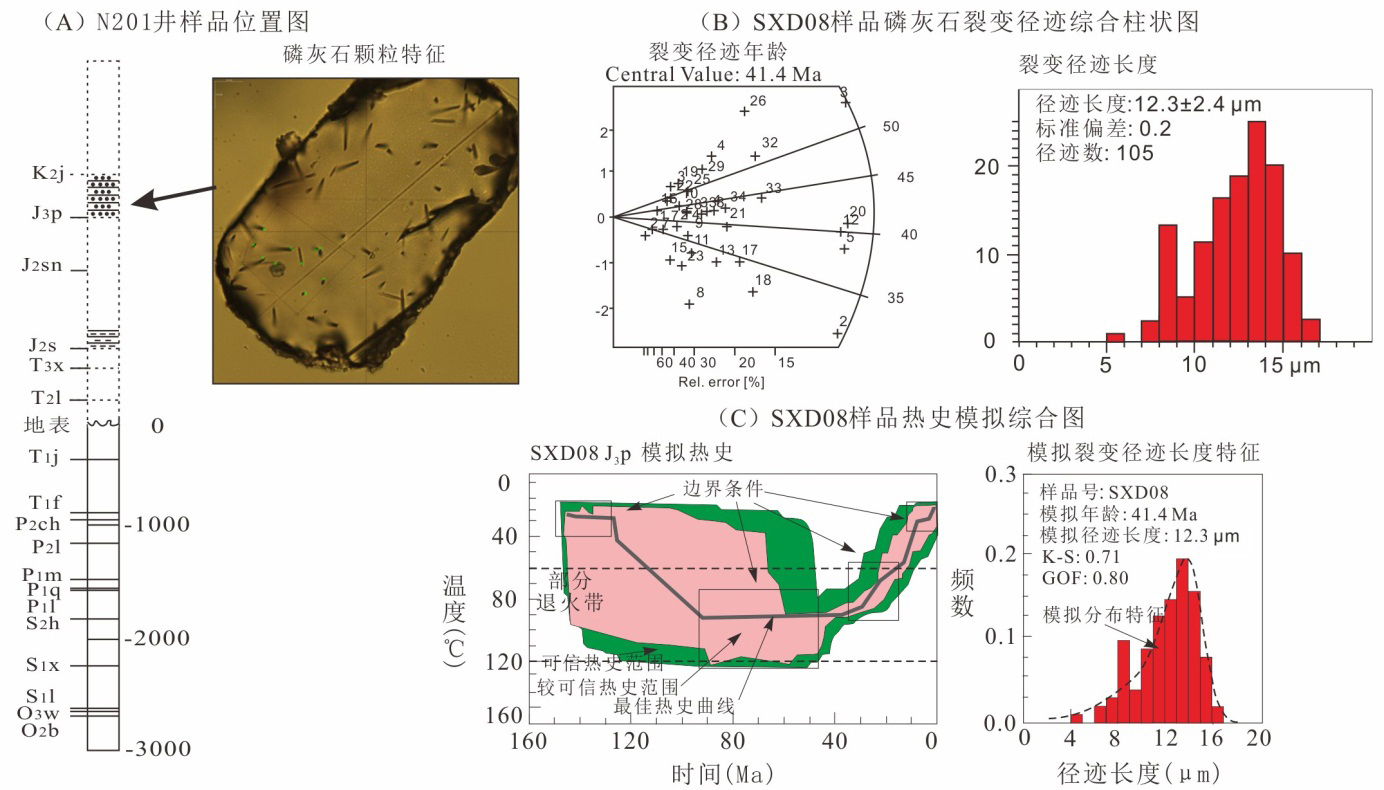
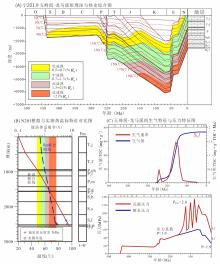
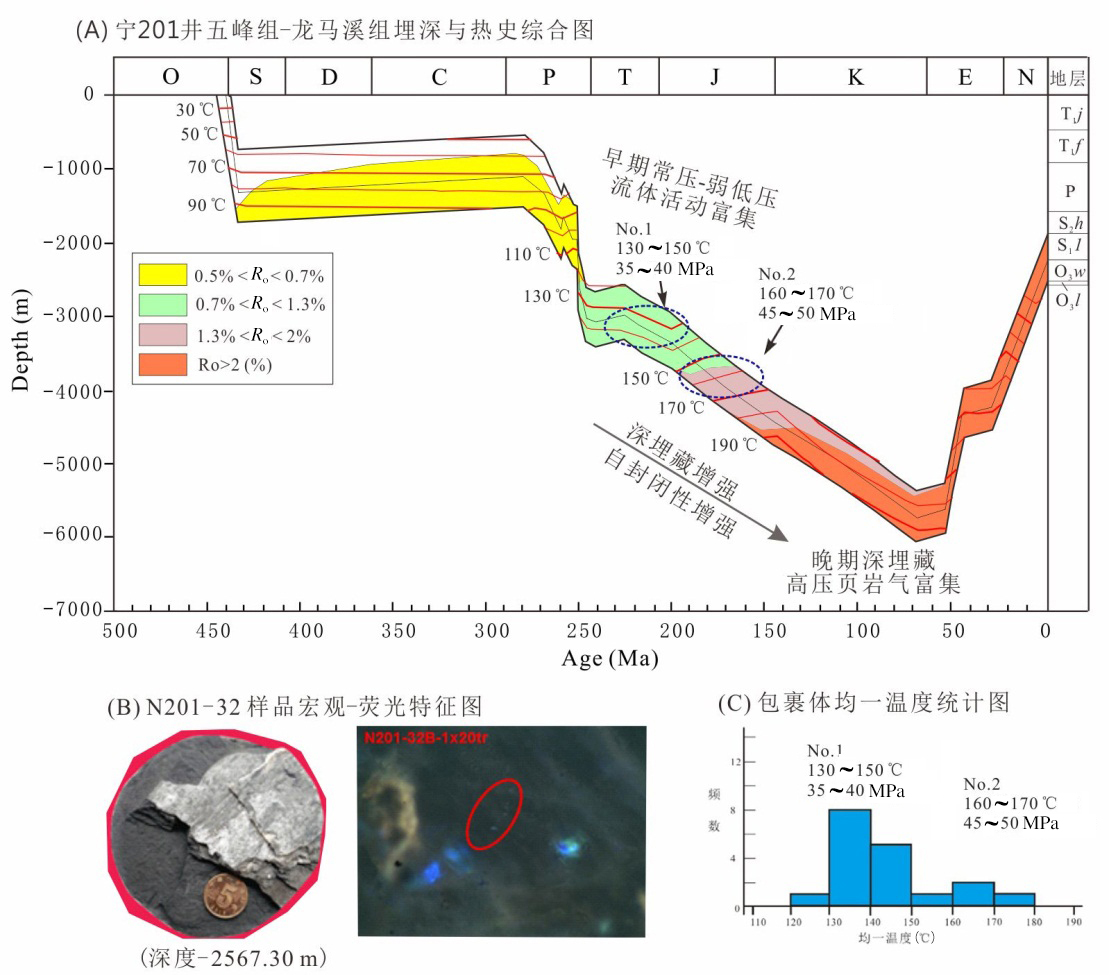
川南地区上奥陶统五峰组?下志留统龙马溪组黑色页岩层系是我国南方海相页岩气勘探开发最具代表性和示范性的地区,但其油气成藏过程及特征研究相对薄弱.基于含油气系统成藏动力学过程的基本原理,结合量化构造地质学、低温热年代学和盆地数值模拟等研究,以多期构造变形过程中五峰组?龙马溪组生烃动力学及其压力体系变化特征为载体,实现对其成藏过程的模拟表征和再现.以川南长宁页岩气田五峰组?龙马溪组页岩层系为研究对象,流体包裹体测试揭示其均一温度呈双峰分布特征,分别为120~140 ℃和160~180 ℃,捕获压力压力系数为1.0~1.1和1.1~1.3;低温热年代学定年和热史模拟揭示该区新生代地表抬升剥蚀量达2.0~2.5 km,五峰组?龙马溪组页岩热史模拟表明,中志留纪?中二叠世、晚二叠世?晚三叠世、早侏罗世?早白垩世和早白垩世以来烃源岩分别进入低成熟、中等成熟、高成熟和过成熟阶段.压力模拟结果显示,长宁地区五峰组?龙马溪组页岩层系早期长时间属于常压系统,至晚侏罗世地层持续埋深增温导致五峰组?龙马溪组生气速率达到高峰,地层压力剧增,逐步形成超压,早?中白垩世埋深达到最大,地层压力系数达2.0左右,新生代地表虽然遭受抬升剥蚀作用,但五峰组?龙马溪组超压被保存下来,现今压力系数仍有1.9.因此,川南地区长宁五峰组?龙马溪组页岩气田具有早期有限聚集、中晚期富集?保存超压型成藏特征.
中图分类号:
- P618.13
| 1 | 马新华,谢军. 川南地区页岩气勘探开发进展及发展前景. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(1):161-169. |
| Ma X H,Xie J. The progress and prospects of shale gas exploration and exploitationin southern Sichuan Basin,NW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(1):161-169. | |
| 2 | 赵文智,李建忠,杨涛等. 中国南方海相页岩气成藏差异性比较与意义. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(4):499-510. |
| Zhao W Z,Li J Z,Yang T,et al. Geological difference and its significance of marine shale gases in South China. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2016,43(4):499-510. | |
| 3 | 刘树根,邓宾,钟勇等. 四川盆地及周缘下古生界页岩气深埋藏-强改造独特地质作用. 地学前缘,2016,23(1):11-28. |
| Liu S G,Deng B,Zhong Y,et al. Unique geological features of burial and superimposition of the Lower Paleozoic shale gas across the Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Earth Science Frontiers,2016,23(1):11-28. | |
| 4 | 马永生,蔡勋育,赵培荣. 中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(4):561-574. |
| Ma Y S,Cai X Y,Zhao P R. China's shale gas exploration and development:understanding and practice. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(4):561-574. | |
| 5 | 郭旭升,胡东风,文治东等. 四川盆地及周缘下古生界海相页岩气富集高产主控因素——以焦石坝地区五峰组?龙马溪组为例. 中国地质,2014,41(3):893-901. |
| Guo X S,Hu D F,Wen Z D,et al. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity in marine shale gas in the Lower Paleozoic of Sichuan Basin and its periphery:a case study of the Wufeng?Longmaxi Formation of Jiaoshiba area. Geology in China,2014,41(3):893-901. | |
| 6 | 胡东风,张汉荣,倪楷等. 四川盆地东南缘海相页岩气保存条件及其主控因素. 天然气工业,2014,34(6):17-23. |
| Hu D F,Zhang H R,Ni K,et al. Main controlling factors for gas preservation conditions of marine shales in southeastern margins of the Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry,2014,34(6):17-23. | |
| 7 | Curtis J B. Fractured shale?gas systems. AAPG Bulletin,2002,86(11):1921-1938. |
| 8 | 边瑞康,张金川. 页岩气成藏动力特点及其平衡方程. 地学前缘,2013,20(3):254-259. |
| Bian R K,Zhang J C. Accumulation dynamic characteristics and the dynamic equations of shale gas. Earth Science Frontiers,2013,20(3):254-259. | |
| 9 | 罗超,王兰生,石学文等. 长宁页岩气田宁211井五峰组?龙马溪组生物地层. 地层学杂志,2017,41(2):142-152. |
| Luo C,Wang L S,Shi X W,et al. Biostratigraphy of the Wufeng to Longmaxi formation at well Ning 211 of Changning shale gas field. Journal of Stratigraphy,2017,41(2):142-152. | |
| 10 | 郭彤楼. 涪陵页岩气田发现的启示与思考. 地学前缘,2016,23(1):29-43. |
| Guo T L. Discovery and characteristics of the Fuling shale gas field and its enlightenment and thinking. Earth Science Frontiers,2016,23(1):29-43. | |
| 11 | 焦堃,谢国梁,裴文明等. 四川盆地下古生界黑色页岩纳米孔隙形态的影响因素及其地质意义. 高校地质学报,2019,25(6):847-859. |
| Jiao K,Xie G L,Pei W M,et al.The control factors and geological implications of the nanopore morphology of the lower paleozoic black shales in the Sichuan Basin,China.Geological Journal of China Universities,2019,25(6):847-859. | |
| 12 | Montgomery S L,Jarvie D M,Bowker K A,et al. Mississippian Barnett Shale,Fort Worth basin,north?central Texas:gas?shale play with multi?trillion cubic foot potential. AAPG Bulletin,2005,89(2):155-175. |
| 13 | Reiners P W,Ehlers T A,Zeitler P K. Past,present,and future of thermochronology. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,2005,58(1):1-18. |
| 14 | Ketcham R A,Donelick R A,Carlson W D. Variability of apatite fission?track annealing kinetics,III. Extrapolation to geological time scales. American Mineralogist,1999,84(9):1235-1255. |
| 15 | 邓宾,刘树根,王国芝等.四川盆地南部地区新生代隆升剥露研究——低温热年代学证据.地球物理学报,2013,56(6):1958-1973. |
| Deng B,Liu S G,Wang G Z,et al.Cenozoic uplift and exhumation in southern Sichuan Basin:evidence from low?temperature thermochronology. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2013,56(6):1958-1973. | |
| 16 | Green P F,Duddy I R. Thermal history reconstruction in sedimentary basins using apatite fission?track analysis and related techniques∥Analyzing the Thermal History of Sedimentary Basins:Methods and Case Studies. Oklahoma:SEPM Special Publication,2012,103:65-104. |
| 17 | 朱传庆,徐明,单竞男等. 利用古温标恢复四川盆地主要构造运动时期的剥蚀量. 中国地质,2009,36(6):1268-1277. |
| Zhu C Q,Xu M,Shan J N,et al. Quantifying the denudations of major tectonic events in Sichuan Basin:constrained by the paleothermal records. Geology in China,2009,36(6):1268-1277. | |
| 18 | 袁玉松,孙冬胜,李双建等. 四川盆地加里东期剥蚀量恢复. 地质科学,2013,48(3):581-591. |
| Yuan Y S,Sun D S,Li S J,et al. Caledonian erosion thickness reconstruction in the Sichuan Basin. Chinese Journal of Geology,2013,48(3):581-591. | |
| 19 | 黄涵宇,何登发,李英强等. 四川盆地东南部泸州古隆起的厘定及其成因机制. 地学前缘,2019,26(1):102-120. |
| Huang H Y,He D F,Li Y Q,et al. Determination and formation mechanism of the Luzhou paleo?uplift in the southeastern Sichuan Basin. Earth Science Frontiers,2019,26(1):102-120. | |
| 20 | 朱传庆,徐明,袁玉松等. 峨眉山玄武岩喷发在四川盆地的地热学响应. 科学通报,55(6):474-482. (Zhu C Q,Xu M,Yuan Y S,et al. Palaeogeothermal response and record of the effusing of Emeishan basalts in the Sichuan Basin. Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(10):949-956.) |
| 21 | 乐光禹,杜思清,黄继钧. 构造复合联合原理?川黔构造组合叠加分析. 成都:成都科技大学出版社,1996:1-285. |
| 22 | Deng B,Li Z W,Liu S G,et al. Structural geometry and kinematic processes at the intracontinental Daloushan mountain chain:Implications for tectonic transfer in the Yangtze Block interior. Comptes Rendus Geoscience,2016,348(2):159-168. |
| 23 | 冯子齐,刘丹,黄士鹏等. 四川盆地长宁地区志留系页岩气碳同位素组成. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(5):705-713. |
| Feng Z Q,Liu D,Huang S P,et al. Carbon isotopic composition of shale gas in the Silurian Longmaxi Formation of the Changning area,Sichuan Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2016,43(5):705-713. | |
| 24 | 姜磊,邓宾,刘树根等. 上扬子盆地新生代差异抬升剥蚀与分异过程. 地球科学,2018,43(6):1872-1886. |
| Jiang L,Deng B,Liu S G,et al. Differential uplift and fragmentation of upper Yangtze basin in Cenozoic. Earth Science,2018,43(6):1872-1886. | |
| 25 | 姜磊. 强改造作用下川南下古生界页岩气保存条件研究. 博士学位论文. 成都:成都理工大学,2019. |
| Jiang L. Research on the preservation conditions of lower Paleozoic shale gas in southern Sichuan under strong transformation. Ph.D. Dissertation. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2019. | |
| 26 | 孙博,邓宾,刘树根等. 多期叠加构造变形与页岩气保存条件的相关性——以川东南焦石坝地区为例. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2018,45(1):109-120. |
| Sun B,Deng B,Liu S G,et al. Discussion on correlation between multistage superimposed tectonic deformation and shale gas preservation conditions in the Jiaoshiba shale?gas field,Sichuan,China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2018,45(1):109-120. |
| [1] | 戴海亮,沈斌,李开开,张小涛,徐学敏,许智超,周晶晶. 地质条件约束下川北二叠系大隆组富有机质页岩热模拟生烃过程及特征研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 382-392. |
|